Now Reading: NASA Grants Firefly Aerospace $177M for Historic Moon South Pole Rover Mission
-
01
NASA Grants Firefly Aerospace $177M for Historic Moon South Pole Rover Mission
NASA Grants Firefly Aerospace $177M for Historic Moon South Pole Rover Mission

speedy Summary
- NASA awarded Firefly aerospace a $176.7 million contract under it’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative.
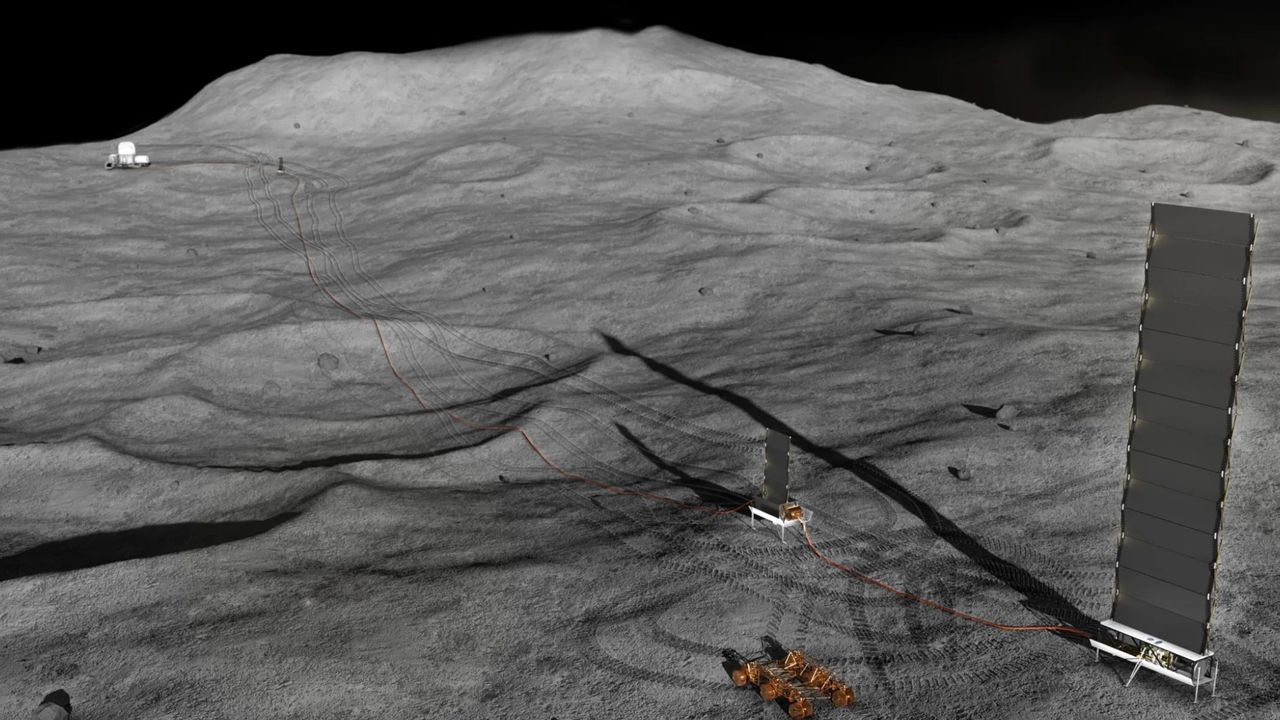
- Firefly will deliver two rovers and three scientific instruments to the moon’s south pole by 2029.
- This is the first CLPS mission that combines multiple rovers and instruments in a single flight to explore harsh lunar environments for usable resources like water ice.
- The mission aligns with NASA’s Artemis program, aiming to establish sustainable human presence on the moon and collect data for future crewed missions.
- Key contributors include Canada’s CSA and Switzerland’s University of Bern, with payloads including:
– MoonRanger – A microrover for mapping hydrogen-bearing volatiles in regolith (soil).
– Stereo Plume Cameras – To study effects of rocket descent exhaust on lunar surfaces.
– CSA rover – exploring shadowed craters and searching for water ice using imaging systems.
– Laser Retroreflector array & Laser Ionization Mass Spectrometer – Tools for precision measurements and regolith chemistry studies using robotic excavation systems.
- Earlier Firefly missions successfully delivered NASA payloads; future missions are planned from 2026 through 2028 focusing on various lunar regions, including far-side landings.
!Firefly Aerospace mission control room
Image credit: Houston Chronicle/Hearst Newspapers / Getty Images.
Indian Opinion Analysis
NASA’s selection of Firefly Aerospace underscores the growing role of commercial entities in space exploration under programs like Artemis and CLPS,which align cost-effectiveness with cutting-edge innovation through partnerships worldwide. For india, this development demonstrates an opportunity to draw lessons from such collaborative models as it strengthens its own lunar exploration efforts via ISRO initiatives like Chandrayaan or potential public-private collaborations domestically.
The focus on utilizing the moon’s natural resources-like water ice-is equally vital as ISRO similarly plans exploration targeting sustainability objectives both scientifically and strategically over time intervals comparable to Artemis timelines (2030 long-term phase overlap). As a rapidly emerging space power engaged diplomatically within multilateral frameworks such as LIGO/AERT domains facilitating resource-sharing programs actively parallel technological intersections quiet responsibly tier– partner refinement humanity globally