Now Reading: NASA’s Cutting-Edge Radar to Monitor Quakes, Landslides, and Ice Loss from Space
-
01
NASA’s Cutting-Edge Radar to Monitor Quakes, Landslides, and Ice Loss from Space
NASA’s Cutting-Edge Radar to Monitor Quakes, Landslides, and Ice Loss from Space

Rapid Summary
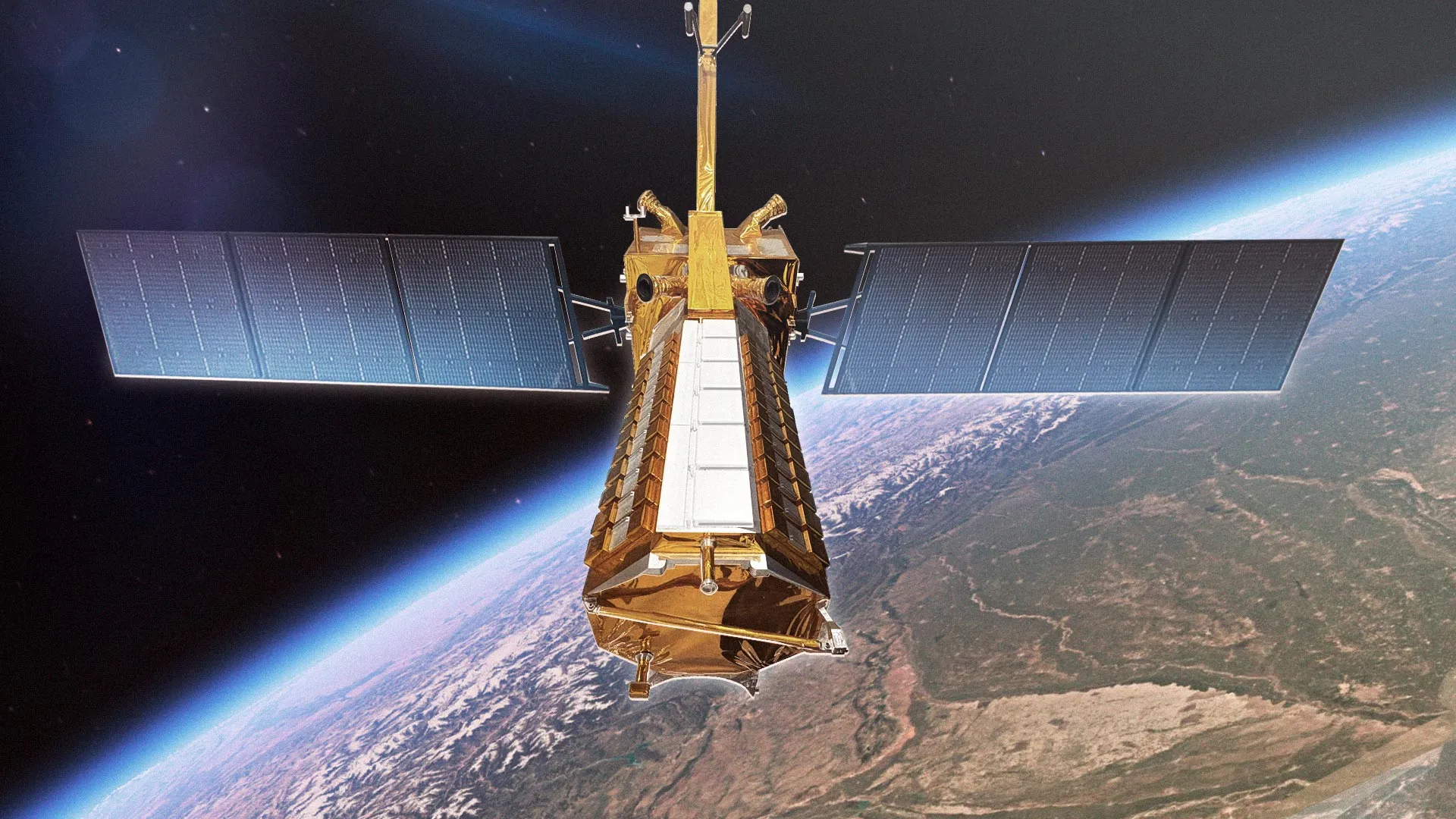
- NISAR satellite, a joint mission by NASA and ISRO, launched on July 30.
- It will orbit Earth for at least three years, scanning nearly all land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days.
- Mission focuses on studying natural hazards like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, and weather disasters such as hurricanes and flooding.
- Data will aid monitoring of infrastructure (e.g.,dams,bridges) and provide insights into Earth’s carbon cycle impacts from deforestation,fires,permafrost loss.
- First-ever hardware collaboration between NASA and ISRO on Earth observation; combines L-band radar (25 cm wavelength) with S-band radar (10 cm wavelength).
- Dual radars will capture synchronized data too measure soil moisture levels or detect surface deformation/movement accurately.
- Satellite offers unprecedented coverage of the Antarctic ice sheet to study its motion, deformation, melting process affecting ocean water levels.
Read more: ScienceDaily Article
Indian Opinion Analysis
The NISAR mission signifies a landmark moment in global scientific collaboration between India and the United States while showcasing cutting-edge engineering innovation by both nations’ space agencies-NASA and ISRO. By addressing key areas such as disaster response capabilities, environmental monitoring through synchronized radar systems offering unmatched precision on surface measurements globally-including India’s own diverse terrain-it could significantly enhance policymaking related to climate resilience strategies at home too skill alignment partnerships show mutual values but data importance matching outcomes broader sphere regional internationally necessities