Now Reading: NASA’s Solar Probe Completes Second Closest Sun Flyby
-
01
NASA’s Solar Probe Completes Second Closest Sun Flyby
NASA’s Solar Probe Completes Second Closest Sun Flyby

Quick summary:
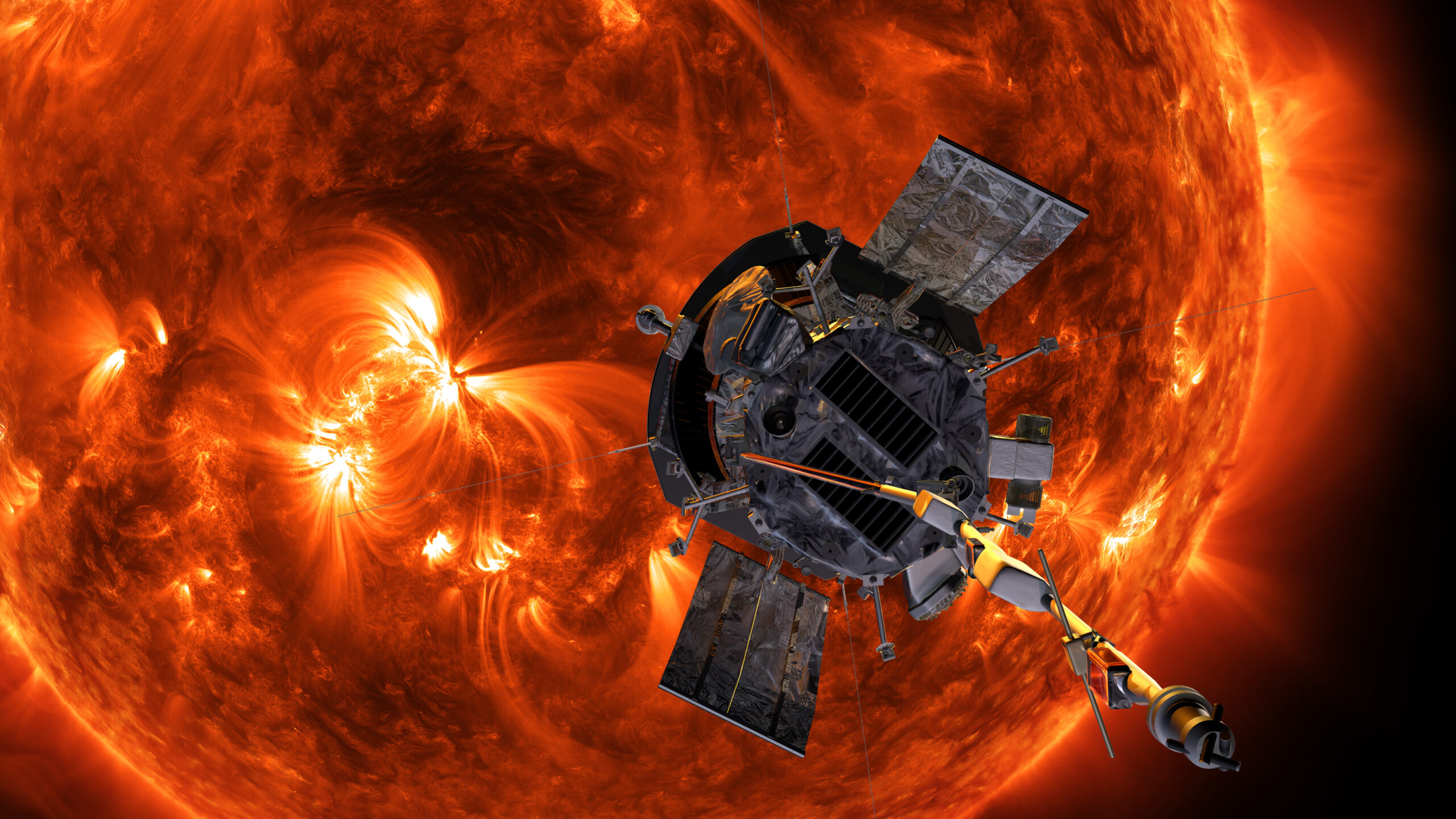
- NASA’s Parker Solar Probe completed its second close flyby of the sun on March 22, operating autonomously and collecting data from the solar corona.
- The spacecraft reached a record-setting distance of 8 million miles (6.1 million kilometers) from the sun’s surface at speeds of 430,000 miles per hour (692,000 kilometers per hour), matching its December performance.
- The probe transmitted a beacon tone to confirm that it remains in good health and all systems are functioning normally.
- Scientists aim to use data collected to understand solar wind behavior and why the sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) is far hotter than its surface.
- The Parker Solar Probe relies on an advanced heat shield that allows its instruments to function at room temperature despite extreme conditions near the sun.
- NASA Acting Administrator Janet petro emphasized how groundbreaking this mission is for solar science research, describing it as rewriting scientific knowledge about our star.
- Recognizing these advancements, the project team received the prestigious Robert J. Collier Trophy for contributing significantly to spaceflight technologies and aeronautics innovation.
- A final flyby for this year is scheduled for June 19.
(image Credit: Steve gribben/NASA/Johns Hopkins APL)
!Parker Solar probe illustration
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The achievements of NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mark significant progress in understanding celestial phenomena critical not only for space exploration but also terrestrial implications like predicting space whether that affects communications systems globally, including India’s burgeoning digital infrastructure reliant on satellites. For India-a nation advancing rapidly in aerospace through ISRO-the technology breakthroughs demonstrated by this mission could propel collaborative or autonomous projects focusing on similar high-challenge explorations such as closer studies of solar activity influencing monsoons or sustainable satellite operations under harsh conditions.
Additionally, fostering connections with such trailblazing missions aligns well with India’s ambition toward self-reliance in global energy forecasting linked to renewable sources like solar energy-a sector deeply impacted by understanding long-term patterns derived from space-based observation platforms.
India’s aspirations in aerospace demand careful evaluation of reusable technologies like thermal protection systems pioneered by NASA; lessons learned may inspire cutting-edge progress applicable domestically across broader scientific disciplines while maintaining sustainable resource allocation strategies focused within core challenge zones critical between Earth-scaling adaptive innovations possible downstream collisions yielding limitations unless cooperatively resolved.”