Now Reading: NASA’s Webb Telescope Discovers Frozen Water in Young Star System
-
01
NASA’s Webb Telescope Discovers Frozen Water in Young Star System
NASA’s Webb Telescope Discovers Frozen Water in Young Star System

Rapid Summary
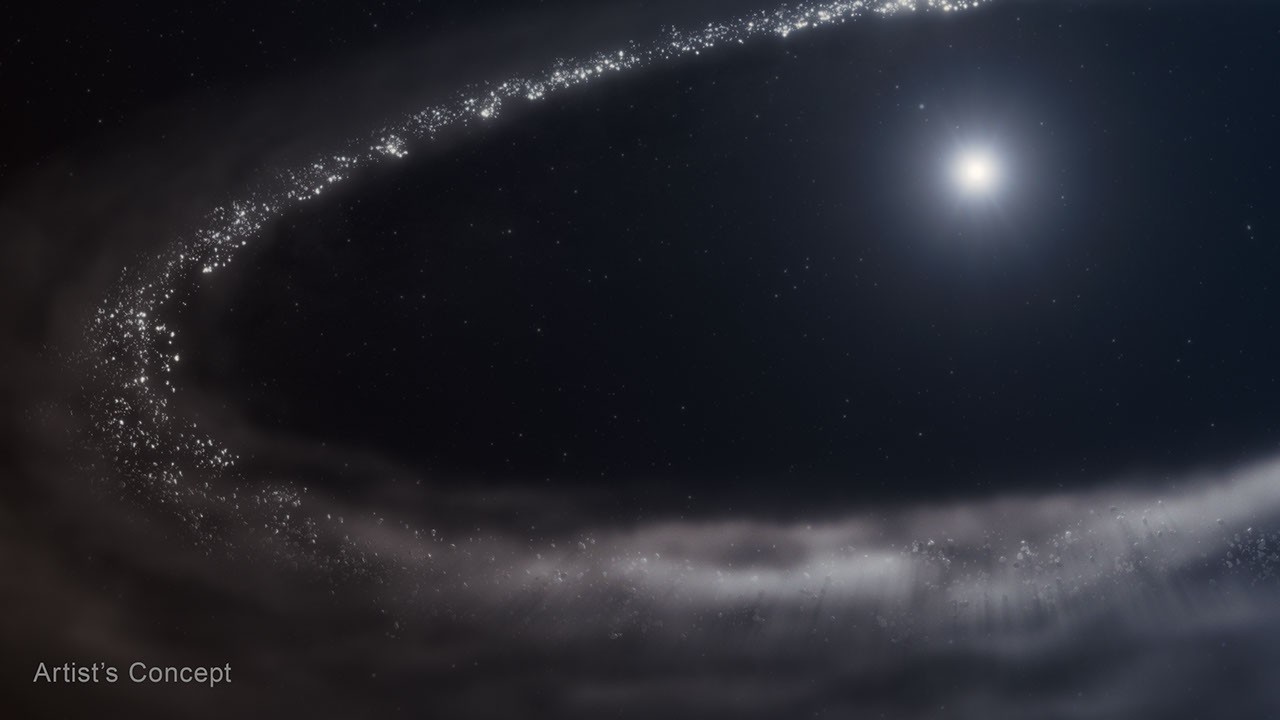
- Astronomers have confirmed the presence of crystalline water ice in a debris disk around the Sun-like star HD 181327, located 155 light-years away.
- Observations were conducted using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and published in the journal Nature.
- The debris disk contains fine dust particles paired with frozen water, akin to “dirty snowballs.”
- Significant gaps exist between the star and its debris disk, which resembles our solar system’s Kuiper Belt – a region where icy bodies collide and release particles.
- Water ice distribution varies in the disk based on proximity to the star:
– outer areas contain over 20% water ice due to colder temperatures.
– middle regions show about 8% water ice with faster generation than destruction.
– Inner areas show minimal or no detectable frozen water due to vaporization by ultraviolet light or sequestration within planetesimals that cannot be observed by Webb.
- HD 181327 is younger (23 million years old) and larger than our Sun (4.6 billion years old), resulting in active collisions within its system, producing observable icy particles.
- Detecting water ice opens avenues for understanding giant planet formation and how icy materials are delivered to rocky planets via comets or asteroids.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope provide ground-breaking insights into planetary systems beyond our own. Crystalline water ice detection in a young solar system like HD 181327 reinforces theories surrounding planet formation processes: how essential elements like frozen water play critical roles not only during early development but also potentially influence habitability later. For scientists worldwide, including Indian astronomers working toward space exploration goals-with growing national interest through missions like Chandrayaan-the study provides actionable knowledge applicable across future research strategies.
Studying phenomena akin to Earth’s Kuiper Belt expands India’s global scientific collaborations connecting astronomy efforts tied towards outer-system comparisons could directly aid. While encouraging learnings might serve bridge perspectives amplify connections deeper milky-way observations broaden inclusion planetary observational milestones shaping next-gen universality science community United India curious tech-prospects rocket-enhancements underway developmental forefront thinkers engaging scales distance-driven pursuits unraveling periphery depths complexed universe dimensions-space literals transformed-century onwards.
Read More