Now Reading: NASA’s Webb Unveils Secrets of Mysterious Exoplanet Type
-
01
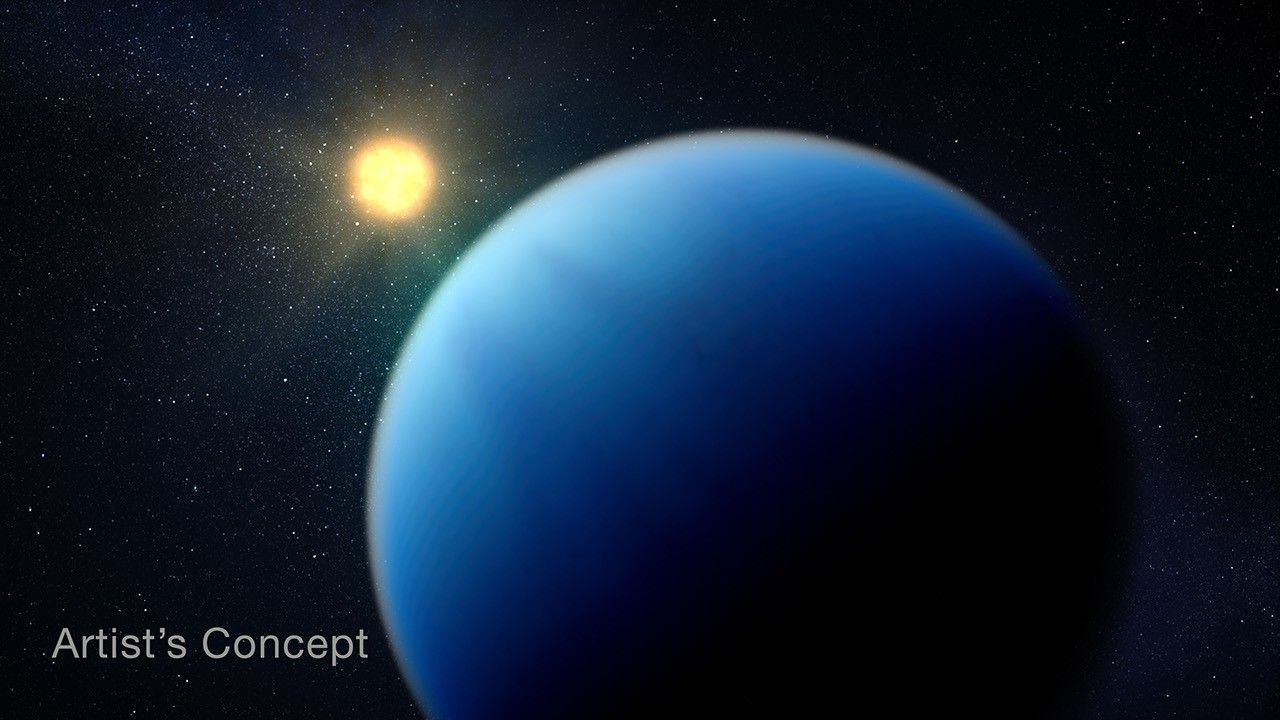
NASA’s Webb Unveils Secrets of Mysterious Exoplanet Type
NASA’s Webb Unveils Secrets of Mysterious Exoplanet Type

fast Summary
- Sub-Neptunes are a common type of exoplanet, larger than Earth but smaller than gas giants, characterized by hazy atmospheres and difficult observation.
- NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope observed TOI-421 b,an exoplanet wiht a clearer atmosphere due to its high temperature (~1,340°F),deviating from previously studied cooler sub-Neptunes.
- Key findings include the presence of water vapor and potential signatures of carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide in TOI-421 b’s hydrogen-dominated atmosphere. Methane and carbon dioxide were notably absent.
- Researchers hypothesize that TOI-421 b’s hydrogen-heavy atmosphere may reflect the composition of its host star-a Sun-like star unlike other sub-Neptunes that orbit red dwarfs.
- These findings suggest significant diversity in sub-Neptune formation and evolution, prompting further studies to explore broader trends among hot sub-Neptunes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The breakthrough led by NASA’s james Webb Space Telescope exemplifies advancements enabling deeper inquiry into planetary sciences. while focused on distant worlds outside our solar system, such research holds significance for India as it accelerates global understanding of planetary systems essential for future exploration ambitions.India’s own efforts in space missions like Chandrayaan or AstroSat can complement these findings by synergizing related scientific advancements.
Beyond curiosity about alien worlds lies practical inspiration-studying atmospheres like that of TOI-421 b propels innovative methodologies applicable even for atmospheric analysis within India’s region or climate research frameworks. It underscores how science remains an interconnected pursuit transcending borders through collaborative expertise.