Now Reading: New Dirt Ant Species Discovered in Dominican Amber
-
01
New Dirt Ant Species Discovered in Dominican Amber
New Dirt Ant Species Discovered in Dominican Amber
Rapid Summary
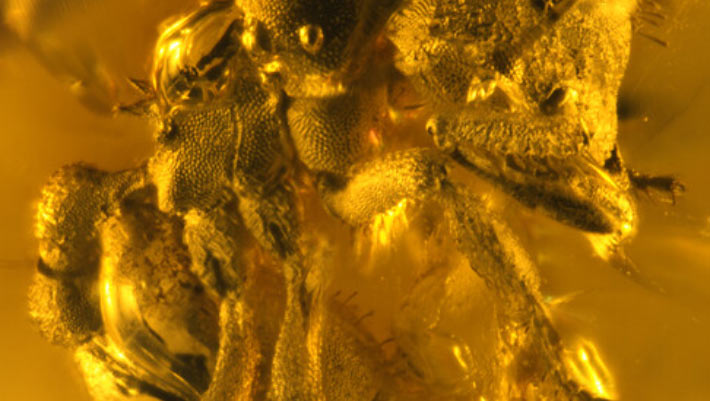
- Paleontologists discovered the first fossil of the dirt ant genus Basiceros, named Basiceros enana, in Miocene-aged dominican amber.
- Measuring 5.13 mm, Basiceros enana is significantly smaller than its modern relatives, which can reach nearly 9 mm.
- The fossil offers evidence that these ants once inhabited the Caribbean but went extinct during the Miocene epoch (23 to 5.3 million years ago).
- Advanced imaging techniques like Micro-CT scanning allowed researchers to study its unique adaptations and evolutionary lineage in detail.
- The fossil indicates that crypsis-related traits such as soil-adhering hairs existed at least 16 million years ago and contributed to their survival strategies.
- Adaptations include specialized hairs for soil adherence, a trapezoidal head structure, an upturned spine on its body segment, and predatory mandibles with triangular teeth.
- Researchers suggest ancient land bridges enabled their migration from mainland South America to the Caribbean islands.
- Extinction of predator ants in regions like modern-day Dominican Republic highlights ecological changes over millions of years; over a third of ant genera have gone extinct in this region since amber formation.
Indian Opinion analysis
The discovery of Basiceros enana provides crucial insights into how species adapt and evolve under environmental pressures while also highlighting extinction patterns within fragile ecosystems like those seen during Earth’s past epochs. For India, where biodiversity conservation is a pressing issue, lessons can be drawn on safeguarding against human-driven extinctions by studying factors contributing to historic ones-such as loss of niches or competition between species-as explained by this research team. Advancements in technologies like Micro-CT scanning demonstrate how interdisciplinary approaches coudl enrich studies in paleoecology worldwide, including within India’s own biodiverse landscapes such as the Western Ghats or Himalayan ecosystems.
By contextualizing extinction events across geological eras alongside evolving traits that enhanced survival strategies (like hidden behaviors and specialized adaptations), a holistic understanding emerges about balancing conservation efforts with sustainable advancement goals-a framework highly relevant for protecting dwindling biodiversity hotspots globally and locally.