Now Reading: New Solar Telescope Reveals Intricate Magnetic Curtains on Sun’s Surface
-
01
New Solar Telescope Reveals Intricate Magnetic Curtains on Sun’s Surface
New Solar Telescope Reveals Intricate Magnetic Curtains on Sun’s Surface
speedy Summary
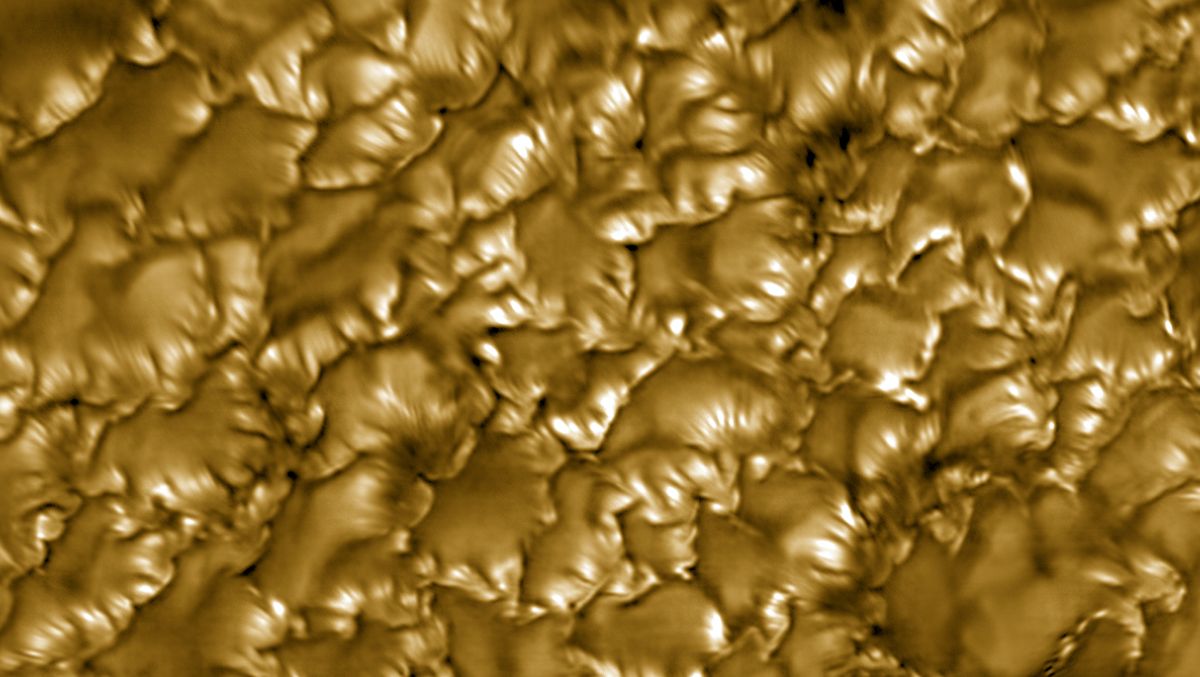
- The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope, located in Maui, Hawaii, has captured the sharpest-ever images of the sun’s surface.
- The images reveal ultra-fine stripes (striations) in the sun’s photosphere (the thin atmospheric layer), which are traces of variations in magnetic fields.
- These striations alternate between dark and shining patterns along solar granules – convection cells that transport heat from inside the sun to its surface.
- Changes in brightness occur as light passes through magnetic “curtains,” with darker regions indicating weaker magnetic fields and brighter regions stronger ones.
- The telescope uses a Visible Broadband Imager operating within a specific G-band of visible light to detect these subtle structures.
- Understanding these fine-scale magnetic field variations offers insights into larger solar phenomena like solar flares or coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which influence space weather and potentially impact Earth.
- Findings were published on May 20 in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
!Sharpest-ever image of sun showing striations
Ultra-fine stripes revealed by high-resolution imaging.
(Image credit: NSF/NSO/AURA)
Indian Opinion Analysis
This breakthrough holds importent scientific implications globally but carries indirect importance for India. As a growing spacefaring nation, awareness about solar dynamics plays an essential role in mitigating disruptions caused by space weather events such as geomagnetic storms. India’s satellite systems for interaction, navigation, and remote sensing could be impacted by CMEs or solar flares.
While this finding showcases advanced technological capabilities primarily spearheaded by US agencies, it underscores an possibility for collaboration between nations investing heavily in astrophysics research. India’s efforts via ISRO and its Aditya-L1 mission studying the heliosphere align well with such findings contributing collectively to better predictions about space weather phenomena affecting Earth’s technology-dependent systems.