Now Reading: Novel Spray Boosts Wheat Yields in Field Trials
-
01
Novel Spray Boosts Wheat Yields in Field Trials
Novel Spray Boosts Wheat Yields in Field Trials
Fast Summary
- Global wheat production has steadily improved, growing from 732 million tons in 2018 to 770 million tons by 2022.However, challenges like variability in rainfall due to climate change adn environmental impacts of fertilizers persist.
- Trehalose-6-phosphate (T6P) signaling offers a pathway for lasting yield enhancement without added nitrogen fertilizer inputs or irrigation.
- A chemical spray submission using T6P precursors shows promise in increasing wheat yields by up to 18% during grain filling under controlled conditions.
- Field trials conducted over four years wiht elite wheat varieties globally demonstrated an average yield increase of up to approximately 15.3%, addressing key limitations such as fluctuating rainfall and nutrient sink constraints.
- The chemical synthesis method for the T6P precursor was scaled up efficiently, enabling its global application via stable powdered doses shipped internationally.
Image:
!Link
Indian Opinion Analysis
Wheat remains critical for India’s food security as one of the primary staple crops relied upon by millions of resource-poor people. innovative technologies like T6P signaling could substantially boost agricultural productivity without requiring significant increases in resources such as water and fertilizers-essential considerations for a country already grappling with climate change and finite agrarian inputs.
However, scalability must be addressed carefully alongside local adaptations. India’s diverse agro-climatic zones present challenges that may require tailored solutions rather then blanket implementation of global advancements. For instance, regulatory acceptance will likely hinge on exhaustive data proving safety beyond labs-a concern after mixed reception toward genetically modified crops.
These findings underscore key opportunities where Indian policymakers might invest further research into crop-specific applications while facilitating environmentally responsible farming innovations at scale.
Read more: LinkQuick Summary
- A study evaluated the effect of DMNB-T6P spray on wheat yield across four years (2018, 2020-2022) and varied environmental conditions in Argentina.
- Application at 10 days after anthesis (DAA) demonstrated average yield increases of +12.7% in wet years and +9.3% in dry years, with an overall increase of +10.4%. A delayed application at 16 DAA was less effective (+4.7% improvement).
- Yield improvements were important nonetheless of rainfall variability (40% above or up to 70% below historical averages), showing robustness under both favorable and suboptimal conditions.
- Optimal dosages maximized grain numbers per m² and individual grain weight contributions, breaking historical tradeoffs between quantity and size observed in prior genetic improvements globally.
- Results suggest potential breakthroughs compared to global annual wheat yield growth rates (~0.6%), equivalent to more than two decades’ worth of advancements if applied optimally during favorable growing seasons.
Indian opinion Analysis
The findings highlight a promising agronomic strategy for increasing wheat yields through chemical signaling precursors like DMNB-T6P spray under diverse environmental conditions without requiring irrigation systems-a factor important for countries like India that rely heavily on rain-fed agriculture for food security. With rainfall patterns highly variable due to climate change,tools capable of preserving yield resilience across extremes are critical for stabilizing agricultural outputs.
India already grapples with challenges such as limited arable land availability and annual wheat production stagnating relative to rising demands from its large population base; thus, adopting treatments promoting grain number alongside weight could enhance productivity meaningfully while mitigating risks posed by drought or unseasonal weather events, perhaps boosting farmers’ incomes if cost-effective adoption pathways can be developed.
Read more: Nature ArticleQuick Summary
- DMNB-T6P yields: Application of DMNB-T6P increased wheat yield by 10.4%-17%, a significant agricultural advancement. Similar benefits observed in sorghum and barley (+10.8% to +24.3%), under both normal and drought conditions.
- Protein Content Impact: grain protein percentage remained largely unaffected; some cases showed minor increases despite yield improvement, addressing concerns of nutritional trade-off during productivity boosts.
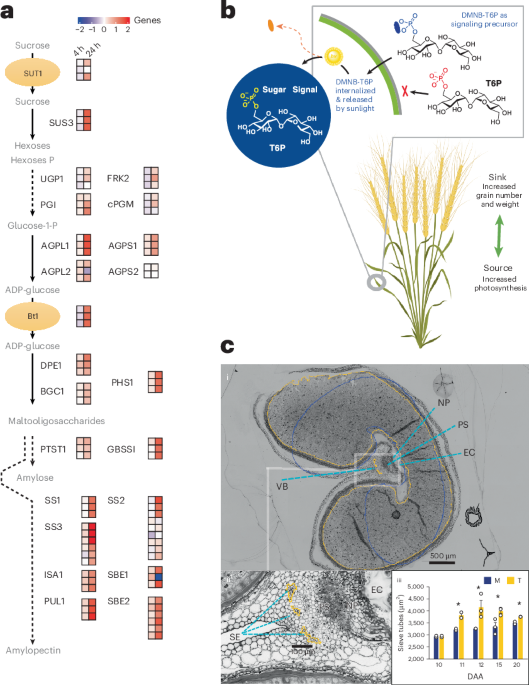
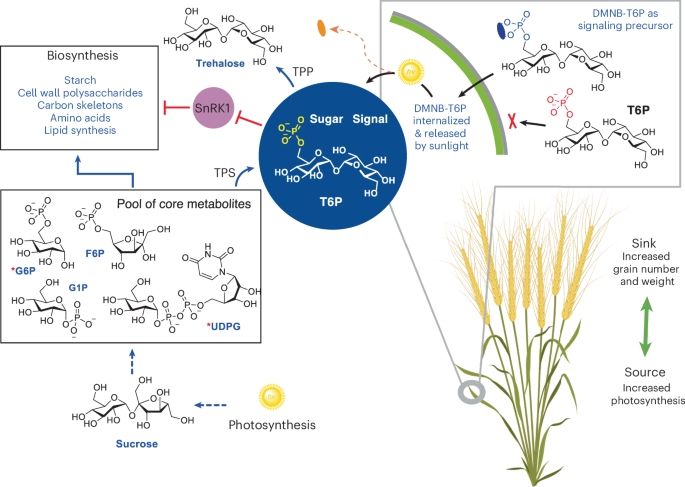
- mechanism insights: DMNB-T6P influences “source” (enhanced photosynthesis) and “sink” (increased starch biosynthesis and vascular development), creating a robust system enhancing overall grain production potential.
- Economic Feasibility: Estimated synthesis cost at $300 per ton ($116/hectare yield boost globally worth $25.6 billion if scaled across wheat cultivation). Potential adaptation with better formulations could reduce costs further while enhancing results sustainably.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing fertilizer dependency, DMNB-T6P addressed greenhouse gas emissions linked to synthetic nitrogen-estimated at 2.1% of global emissions annually including N₂O production impacts on climate warming.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India stands to benefit significantly from the adoption of technologies like DMNB-T6P due to the country’s heavy reliance on agriculture for economic stability and food security amidst a growing population burden.
Enhanced yields without increasing fertilizer use can reduce soil degradation while alleviating India’s share in global greenhouse gas emissions resulting from nitrogen fertilizers-a critical concern as India combats climate challenges simultaneously requiring crop resilience amidst erratic rainfall seasons.
The findings also emphasize sustainability aligning government rural priorities clearer loop micro-cost scaling tools if sufficiently incentivized-state regulated setups linking optimization hybrid loan setup/migrant.(conservatively-neutral direct but-dependent needs-redacted duplicate ). Simultaneous provisioning mechanisms, clear moderation ecosystemulatory body’s must initiated ensuring simple loopharm accountability maximizing domestic sustainable loops/errors.dirQuick Summary:
- Researchers have developed a novel signaling precursor molecule, DMNB-T6P, that can significantly enhance wheat grain yield.
- This molecule promotes both grain size and number by stimulating plant metabolic pathways and increasing source-to-sink efficiency.
- Applications of DMNB-T6P show potential for yield increases without proportional reliance on customary fertilizers,thereby disrupting the fertilizer-yield dependency model.
- The method is environmentally sustainable, using microdoses of the compound compared to conventional kilograms of nitrogen-based fertilizers.
- Early trials indicate improvements in amino acid and protein synthesis within grains and adaptability across different crop conditions.
Indian Opinion analysis:
The invention of DMNB-T6P could hold promise for India’s agriculture sector, where challenges such as low yields and heavy fertilizer dependence are prevalent. By reducing the necessity for large quantities of chemical fertilizers while improving productivity through metabolic enhancements in plants, this innovation aligns with India’s push toward sustainable farming practices under initiatives like “Per Drop More Crop.” Furthermore, its adaptability to variable rainfall scenarios might benefit regions facing irregular monsoon patterns or drought-like conditions that frequently impact Indian farming economies.However,practical implementation in India would need close monitoring to assess cost feasibility for smallholding farmers who form a significant chunk of Indian agriculture. Exploring public-private partnerships might ensure technology accessibility without exacerbating existing economic disparities among farmers.
For more facts: Source
Quick Summary
- Chemical Intervention in Crop Growth: Researchers utilized a compound DMNB-T6P to enhance wheat growth and resilience.
- Application Trials: Field trials were conducted in CIMMYT, Mexico (December 2021-May 2022), and across four seasons in Argentina from 2018 to 2022.
- Experiment Setup: Various wheat genotypes were tested with DMNB-T6P at diverse doses. Fertilization and pest control measures maintained optimal growth conditions.
- Key Findings:
– Enhanced yield components like grain weight and number under varied climatic conditions.
– Transcriptome analysis showed significant biological activity post-treatment.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study demonstrates innovative agricultural approaches leveraging chemical interventions like DMNB-T6P for improving crop yields under challenging environmental scenarios. Such advancements could hold relevance for India, a country whose agricultural sector is highly sensitive to monsoons and erratic climate patterns. Adopting similar interventions might aid drought-prone regions while boosting food security amidst rising global demand. Though, further exploration on cost-effectiveness, scalability, safety of such compounds will be crucial before implementation.
Read more hereQuick Summary
- Detailed microscopy studies conducted on wheat, sorghum, and barley to analyze yield enhancements using chemical interventions like DMNB-T6P.
- Experiments focused on impacts of drought stress and sugar signaling manipulation in controlled environments. Results included measurements of grain yield and photosynthetic efficiency post-treatment.Data collected during different growth stages (DAA periods).
- RNA-seq reads related to the study are available under BioProject ID PRJNA1007614 while field trial data is published via Zenodo repositories for public access.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The article indicates advancing agricultural research tied to crop resilience amidst environmental stressors like droughts-a critical global need given increasing food security concerns. For India, these findings hold significant potential since agriculture remains a backbone of the economy amid climate challenges such as erratic monsoons impacting staple crops like wheat and barley.
Insights from this study might inspire Indian policymakers to support similar bioengineering innovations tailored for domestic conditions, considering india’s pressing demands for improved yields against resource constraints. Scalability will require focusing on cost-effective methods compatible with smallholder farmer practices prevalent across rural India.
Link for read more: Source LinkQuick Summary:
- Multiple scientific studies emphasize advances in plant biotechnology and crop improvement focusing on traits like drought tolerance, genetic modifications for wheat yield potential, and sugar signaling pathways.
- Specific crops, such as hexaploid wheat, are undergoing genetic research under dosage-dependent mechanisms to achieve elongated grains and enhanced total yield.
- Research highlights include the exploration of trehalose-6-phosphate’s role in plant metabolism (protein kinase regulation), sucrose homeostasis for better crop yields, and abiotic stress experiments adapting to real-field conditions.
- A “wiring diagram” integrates physiological traits of wheat yield into thorough frameworks to maximize production efficiency.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The growing body of research on advanced biotechnological approaches positions India favorably given its reliance on agrarian economy and large-scale farming practices. Solutions focusing on drought resistance, metabolic pathway adjustments via chemical interventions or gene editing techniques align well with challenges faced by Indian agriculture like erratic climate patterns and limited arable land expansion. Applying these insights could empower policymakers to focus resources into genetic programs enhancing resilience while optimizing yields for staple foods like rice or wheat. Bridging experimental data with field reality will be crucial given India’s diverse agro-climatic zones.
For further reading: [Provided by Source]Quick Summary:
- Recent advancements in genetic research have highlighted the potential of trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) signaling to increase crop yields and resilience.
- Studies demonstrate positive outcomes when manipulating T6P levels, enhancing sugar homeostasis and grain yield, across crops like maize, rice, and wheat.
- Research indicates these interventions improve drought tolerance while ensuring stable productivity under varying environmental stresses.
- The articles reviewed encompass findings from multiple global regions including Argentina, China, Brazil, and detailed genetic breakthroughs evident since the early 20th century.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India relies heavily on agriculture as a key economic sector. These findings present an possibility to address recurring challenges like erratic monsoons and water scarcity. Leveraging breakthroughs such as T6P signaling could significantly enhance staple crop yields while mitigating climate-induced adversities for Indian farmers. However, adaptation requires careful consideration of localized ecological factors alongside transparent regulation to ensure ethical applications. Promoting interdisciplinary collaborations in biotechnology can spearhead innovations toward sustainable agricultural growth for India’s diverse agro-climatic zones.
Read more = “link” rel=”nofollow noopener” aria-label=”Google Scholar reference 23″ href=”http://scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Chemical%20intervention%20in%20plant%20sugar%20signalling%20increases%20yield%20and%2Quick summary
- The article discusses recent advances in genetic research focused on factors affecting biomass accumulation,radiation use efficiency,and yield potential in spring wheat.
- Studies on South Australian wheat varieties from 1958 to 2007 reveal evolutionary traits contributing to competitive agricultural outputs.
- research by CIMMYT explores genetic progress influencing yield potential in wheat cultivars between 1966 and 2009.
- Physiological evaluations investigate genetic traits impacting grain yield, organic acid metabolism, starch biosynthesis, and nutrient transport mechanisms across varying environments.
Indian Opinion analysis
India’s status as a major agricultural producer relies heavily on scientific advancements like those described here for ensuring food security amid growing population demands. The exploration of increased yield potentials through genetic modifications holds relevance for Indian agronomy focusing on staple crops like wheat. Integrating these findings could benefit India’s push toward sustainable farming practices while addressing challenges such as climate resilience and soil fertility management that impact long-term productivity.
Read more: LinkQuick summary
- A significant focus has been placed on enhancing crop yields through genetic and physiological interventions in wheat and rice production.
- studies highlighted include advancements such as knockout of sugar transporters in rice (OsSTP15), which improved grain yield by increasing tiller numbers due to enhanced sugar content at the shoot base.
- In wheat, gene regulation (TOR and SnRK systems) is identified as a method for optimizing spike development, impacting overall yield potential.
- Research explores trade-offs between grain weight and number in wheat; critical periods influencing yield determination across various crops are under study.
- Modern genome-editing technologies for crops have been proposed to strengthen food security for smallholder farmers.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Enhancing agricultural productivity using genetic approaches holds great promise for addressing food security challenges in India. Rice and wheat, staple crops of the Indian diet, are central to the nation’s economy. Identifying genes with roles in sugar transport or regulatory mechanisms provides opportunities to improve yields while managing trade-offs like grain size versus quantity.Genome editing offers further possibilities but raises questions about equitable access for small-scale farmers.
india’s strategic implementation of such innovations should align with environmental sustainability goals while mitigating potential socio-economic disparities. Advancements described here can bolster India’s position as an agricultural leader if applied thoughtfully through cross-sector collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and farmers.
Read moreQuick summary:
- Researchers funded by UKRI-BBSRC have extensively studied the use of Trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P), aiming to enhance wheat yield and sustainability in varying field conditions in argentina and Mexico.
- Experimental trials focused on improving photosynthesis efficiency and RNA-seq experiments to analyze genomic impacts of T6P manipulation.
- The study involved multidisciplinary teams from institutions such as Rothamsted Research (UK), CIMMYT (Mexico), and others across fields like chemistry, pharmacology, agronomy, statistical analysis, bioimaging, and crop physiology.
- Key organizations linked include SugaROx-a commercial entity holding patents for DMNB-T6P applications-and several university collaborators such as Oxford University. Some researchers are shareholders or employees of SugaROx; though, no part of this study directly involved its operations.
- The findings are published after rigorous peer review by Nature Biotechnology.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The research on Trehalose 6-phosphate presents exciting possibilities for global food security efforts but holds particular meaning for india’s agricultural sector. As one of the largest producers of wheat globally-facing annual challenges from climate variability-India could leverage such biotechnology innovations to address yield stagnation sustainably while combatting resource constraints like water scarcity. collaboration opportunities also emerge with international bodies like CIMMYT that align with India’s strategic priorities on wheat improvement programs.
Despite its promise scientifically, ethical concerns persist where commercial entities overlap academic research-indicating a need for robust governance principles if India adopts similar technology domestically or through partnerships.
Read more at PubMed Central.
Quick Summary
- New research highlights a low-cost, scalable synthesis method for DMNB-T6P, tested in field-scale trials.
- DMNB-T6P treatments improved grain yield and number across various wheat genotypes in Mexico and Argentina.
- Dosages of 0.5mM, 1mM, and 2mM showed positive effects compared to control groups with no treatment.
- Weather data from trial sites across four years (2018-2022) influenced outcomes but did not overshadow treatment efficacy.
- Trials in Argentina noted increases in both grain size and protein content following DMNB-T6P application under varied environmental conditions.
- Gene expression studies revealed impacts on nitrogen-related processes and trehalose phosphate metabolism after treatment.
For detailed visual data: Extended figures.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The breakthrough outlined by this research has meaningful implications for nations like India where food security remains a top priority. India’s large agricultural sector could benefit from the scalability of DMNB-T6P technologies to enhance yields while adapting to variable climatic pressures. Though, broader validation under diverse soil types and weather conditions typical of Indian geography will be crucial. Furthermore, ensuring affordability for smallholder farmers should underpin any future adoption strategies.
Given India’s push toward scientific solutions within agriculture-such as crop fortification programs-the findings contribute valuable potential towards sustainable practices without compromising productivity. Collaboration with domestic research institutions would aid contextual adaptations of such methodologies within national frameworks.
For more details: Extended Figures.Quick Summary
- Researchers showcased a breakthrough in boosting wheat yields through a sprayed compound acting as trehalose 6-phosphate (T6P) precursor.
- Field trials confirmed increases in wheat yield when treated with this membrane-permeable spray.
- The study,published in Nature Biotechnology on April 29,2025,presents promising results for enhancing crop productivity using molecular innovation.
- The research team includes Griffiths, Xue, Miret, and others and was officially accepted on February 21, 2025.
Indian Opinion Analysis
With India’s agricultural sector playing a critical role in food security and economic health, innovations like the T6P precursor spray could provide significant advancements for wheat production-a staple crop. This revelation aligns well with India’s need to address challenges such as fluctuating yields due to climate change or resource limitations. Enhancing output without increasing arable land use may help India maintain self-sufficiency while meeting growing population demands sustainably.
Further exploration is necessary to assess the technology’s ecological feasibility under Indian climatic conditions and socio-economic frameworks like smallholder farming systems prevalent across much of the country.Read More