Now Reading: Custom Care Plans for Children Orphaned by Wayanad Landslides
-
01
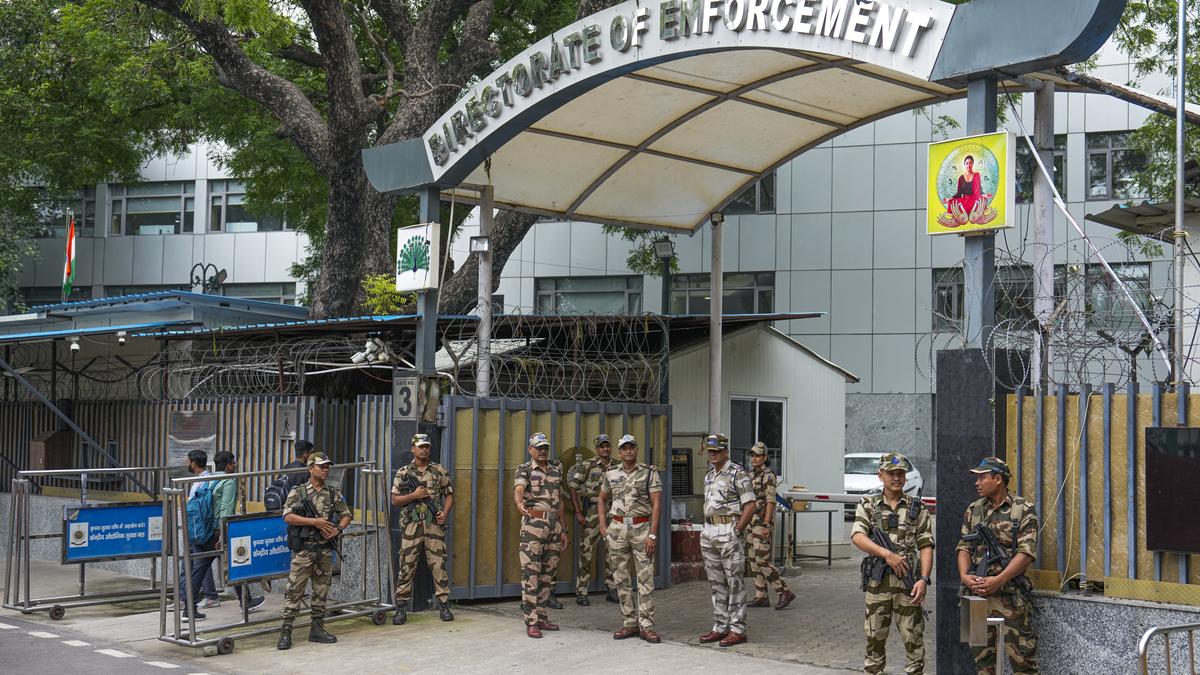
Custom Care Plans for Children Orphaned by Wayanad Landslides
Custom Care Plans for Children Orphaned by Wayanad Landslides
Fast Summary
- Devastating Landslide in Wayanad (2024): Landslides last year caused widespread destruction, loss of lives, and displacement of villagers. Several children lost one or both parents in the tragedy.
- Impact on Children: Six children lost both parents,10 lost one parent,and nine families were left incapacitated. Post-traumatic struggles are significant among affected children.
- rehabilitation project: The Women and Child Progress (WCD) department,UNICEF,and other stakeholders introduced a complete post-disaster child protection model aimed at supporting rehabilitation.
- Individual Costed Care Plans (ICCPs): personalised plans developed by Rajagiri College Social Work Department map each child’s needs up to age 21.
– iccps address four domains: family caregiving needs, physical/mental health issues, education gaps/aspirations, and economic rehabilitation requirements.
– Plans include specific interventions such as training for livelihood skills or educational tools tailored to individual cases.
- Empirical Methodology: ICCPs are based on field visits to affected areas, interviews with survivors/government agencies involved in support efforts, thematic analyses of issues faced by impacted children/families.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the aftermath of the Wayanad landslides highlights the long-term social ramifications disasters can have on vulnerable populations such as children. The individual care strategies under ICCPs exemplify a forward-thinking approach by incorporating a multidimensional perspective-marrying economic projections with psychosocial well-being for holistic recovery. Engaging external partners like UNICEF strengthens institutional capacity but also underscores gaps within existing government frameworks that previously lacked targeted solutions for complex post-disaster needs.Institutionalising such models could substantially improve India’s disaster response systems; however,scalability remains dependent on funding channels like CSR initiatives or inter-agency partnerships. The inclusion of progressive socioeconomic tools may set benchmarks for replicable best practices in disaster management. For affected individuals like orphaned adolescents or injured families recovering livelihood capabilities thru skill-based workshops could be transformative-not only helping emotional recovery but fostering independence.Read more:
Original Source