Now Reading: Quantum Computer Error Correction and Signs of Quantum Supramacy in 2025
-
01
Quantum Computer Error Correction and Signs of Quantum Supramacy in 2025
Quantum Computer Error Correction and Signs of Quantum Supramacy in 2025
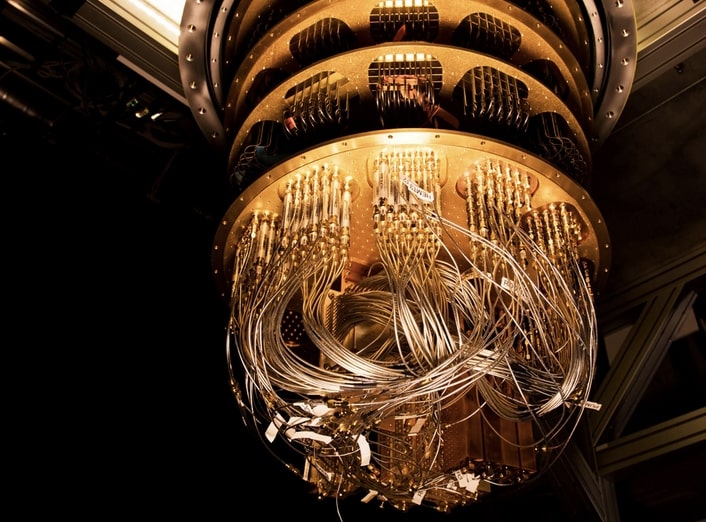

Quantum computing breakthroughs from IonQ, D-Wave, QuEra, Alice & Bob, and others in the last six months, with dates, achievements, and their impact on error-corrected, scalable quantum systems.

IonQ
May 7, 2025, IonQ Demonstrated a 12% speed improvement over classical computing in a real-world simulation (heart pump modeling with Ansys). This shows practical quantum advantage for specific tasks, suggesting IonQ’s trapped-ion systems are maturing toward commercially relevant performance
August 14, 2024, IonQ, introduced CliNR (Clifford Noise Reduction), a novel, efficient quantum error correction (QEC) method. CliNR reduces logical error rates by a factor of two with much lower overhead than traditional QEC (qubit overhead ~3:1, gate overhead 2:1). This approach bridges the gap between error mitigation and full error correction, making scalable, error-corrected systems more feasible in the near term.
May 2025, IonQ znnounced acquisition of Lightsynq, a quantum memory company. Lightsynq’s technology is expected to accelerate IonQ’s roadmap toward tens of thousands (and eventually millions) of qubits, a key step for error-corrected, large-scale quantum computers and future quantum networking.
D-Wave Systems
On June 4, 2025, DWave Systems (Quantum Annealing) demonstrated “real-world quantum supremacy” on the Advantage2 system, solving a complex magnetic simulation in minutes (estimated to take a million years on classical supercomputers). This is the first practical, large-scale demonstration of quantum supremacy, showing D-Wave’s annealing technology can outperform classical systems in real enterprise settings. The Advantage2 system (4,400+ qubits) is already in use for manufacturing, telecom, and drug discovery.
QuEra
In March 21, 2025 QuEra and NVIDIA, developed a transformer-based AI decoder for quantum error correction. The AI decoder significantly accelerates and scales QEC decoding, outperforming traditional methods in both speed and fidelity. This enables real-time error correction as systems scale, a critical step for practical, error-corrected quantum computing at scale
In November 19, 2024, QuERa launched a full-stack quantum algorithm co-design program. By integrating hardware, software, and application development, QuEra aims to maximize the efficiency of current quantum resources and accelerate progress toward scalable, error-corrected systems.
Alice & Bob
December 4, 2024, Alice & Bob released a five-step roadmap to a universal, fault-tolerant quantum computer by 2030, leveraging cat qubit technology. Cat qubits actively stabilize against errors, reducing error correction from a two-dimensional to a one-dimensional problem. This allows for “6-nines” (99.9999%) logical qubit fidelity with far fewer physical qubits, making error-corrected quantum computing more resource-efficient and scalable
March 6, 2025, Alice & Bob completed the first roadmap milestone by mastering cat qubits (Boson series). They are progressing toward error-corrected logical qubits with the Helium chip series. These advances directly address the biggest bottleneck in quantum computing—efficient, scalable error correction—paving the way for practical, large-scale quantum systems

Brian Wang is a Futurist Thought Leader and a popular Science blogger with 1 million readers per month. His blog Nextbigfuture.com is ranked #1 Science News Blog. It covers many disruptive technology and trends including Space, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence, Medicine, Anti-aging Biotechnology, and Nanotechnology.
Known for identifying cutting edge technologies, he is currently a Co-Founder of a startup and fundraiser for high potential early-stage companies. He is the Head of Research for Allocations for deep technology investments and an Angel Investor at Space Angels.
A frequent speaker at corporations, he has been a TEDx speaker, a Singularity University speaker and guest at numerous interviews for radio and podcasts. He is open to public speaking and advising engagements.