Now Reading: Revolutionary Machine Converts Air into Gasoline
-
01
Revolutionary Machine Converts Air into Gasoline
Revolutionary Machine Converts Air into Gasoline

Quick Summary
- Transportation Emissions: In 2022, transportation accounted for 28% of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from gas-powered cars.
- Electric Vehicle Challenges: EVs make up only around 8% of vehicles in the U.S.; high costs and mineral extraction concerns are barriers to broader adoption.
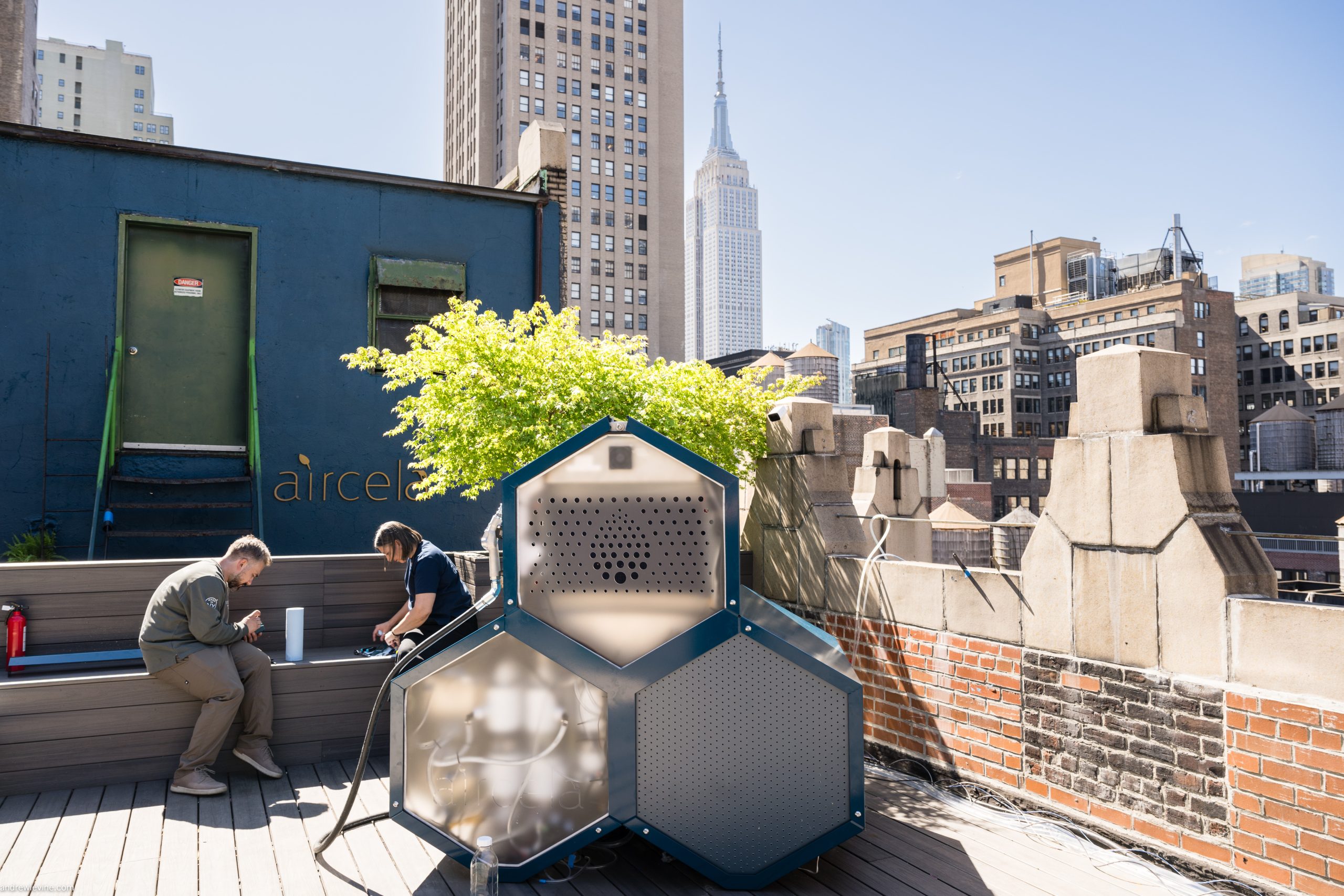
- Aircela’s Innovation: New York-based startup Aircela unveiled a machine that produces gasoline “from thin air” using direct air capture (DAC) technology combined with fuel synthesis powered by renewable energy.
- How It Works: The machine captures CO₂ from the atmosphere and converts it into gasoline free of sulfur, ethanol, or heavy metals. It can produce one gallon of fuel per day while storing up to 17 gallons at a time.
- Prototype Exhibition: The device was showcased in New York as functional rather than experimental; it resembles a commercial refrigerator with sections for air capture and synthesis.
- Scaling Vision: Designed for both residential and industrial users; potential deployment ranges from individual homes to larger customers like gas stations.
- Renewable Dependency: Success depends on access to renewable energy sources; reliance on fossil-fuel-powered grids limits its carbon neutrality impact.
Read More: https://www.popsci.com/environment/aircela-gasoline-machine/
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of Aircela’s DAC device is an intriguing advancement in the ongoing pursuit of reducing transport-related emissions globally. While India’s transportation sector significantly contributes to local pollution as well as carbon emissions, solutions requiring massive systemic change-like electric vehicles-face hurdles akin to those seen elsewhere, including affordability and infrastructure gaps.
Aircela’s concept offers an option route by enabling the continued use of existing gas-powered vehicles while possibly reducing their environmental footprint through low-carbon fuels synthesized directly from atmospheric CO₂. For India-a country heavily reliant on fossil fuels-such technology could represent an interim solution bridging current dependencies with longer-term goals like transitioning entirely to renewables or EVs.
However, scalability remains critical-both globally and domestically-to meaningfully impact emissions reduction efforts while aligning with India’s strong emphasis on cost-effective measures for wide-scale deployment. The innovation must also be evaluated within India’s unique context of renewable grid expansion as its sustainability ultimately hinges upon clean energy availability.
If priced optimally over time through mass production and paired efficiently with locally sourced renewables such as solar power growth seen across rural areas, Aircela-like technologies could supplement india’s diverse institutional approaches targeting pollution control amid economic constraints.