Now Reading: Revolutionizing Road Safety: New Optical Tech Powers Smarter Cars
-
01
Revolutionizing Road Safety: New Optical Tech Powers Smarter Cars
Revolutionizing Road Safety: New Optical Tech Powers Smarter Cars

Quick Summary
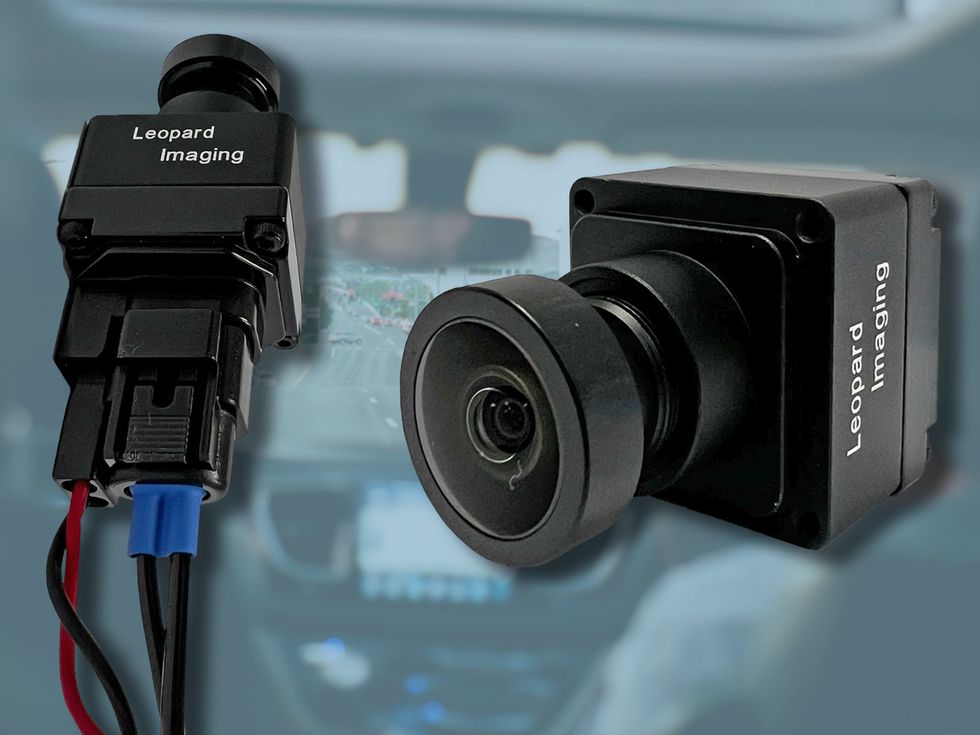
- Madrid-based KD and California’s Leopard Imaging introduced a revolutionary automotive camera system leveraging 10-gigabit-per-second Ethernet optical fiber technology.
- The system marks a critically important leap from legacy in-car networks like the CAN protocol, offering higher speed, centralized computing, and low latency ideal for autonomous driving and infotainment systems.
- KD’s optical transceivers comply with strict standards like IEEE 802.3cz for durability in harsh automotive environments,ensuring a 15-year lifetime.
- Optical fiber replaces traditional copper harnesses to reduce electromagnetic interference, cut vehicle weight, lower emissions, reduce costs, and improve safety performance.
- cameras paired with KD’s transceivers feature high-resolution imaging with reduced aerodynamic drag due to thier compact design (under 20mm size).
- Automaker interest is high globally; pilot projects are underway for premium vehicles expected within two to three model years.
Indian Opinion Analysis
KD’s innovation aligns closely with emerging transportation goals such as reducing emissions while advancing autonomous driving technologies. Replacing existing networks within vehicles offers both environmental benefits-thanks to reduced material weight-and improved data processing capabilities essential for self-driving cars. This technology could significantly enhance safety measures by enabling faster sensor response times and more reliable data transfers even in complex traffic environments.
Adoption of this optical network backbone will likely act as a catalyst for India’s automotive sector’s pursuit of sustainability through EV development while reinforcing its move toward greater digitization.Though, cost implications remain a consideration if similar upgrades extend into budget car segments-a critical focus given India’s price-sensitive auto market. Pursuing pilot projects could guide manufacturers on scalability challenges encountered during early-phase rollouts here.