Now Reading: Risk of Resurgence: Falling U.S. Vaccination Rates Could Revive Eliminated Diseases
-
01
Risk of Resurgence: Falling U.S. Vaccination Rates Could Revive Eliminated Diseases
Risk of Resurgence: Falling U.S. Vaccination Rates Could Revive Eliminated Diseases
Quick Summary
- diseases like measles, rubella, polio, and diphtheria have been nearly eliminated in the U.S. due to high vaccination rates over several decades.
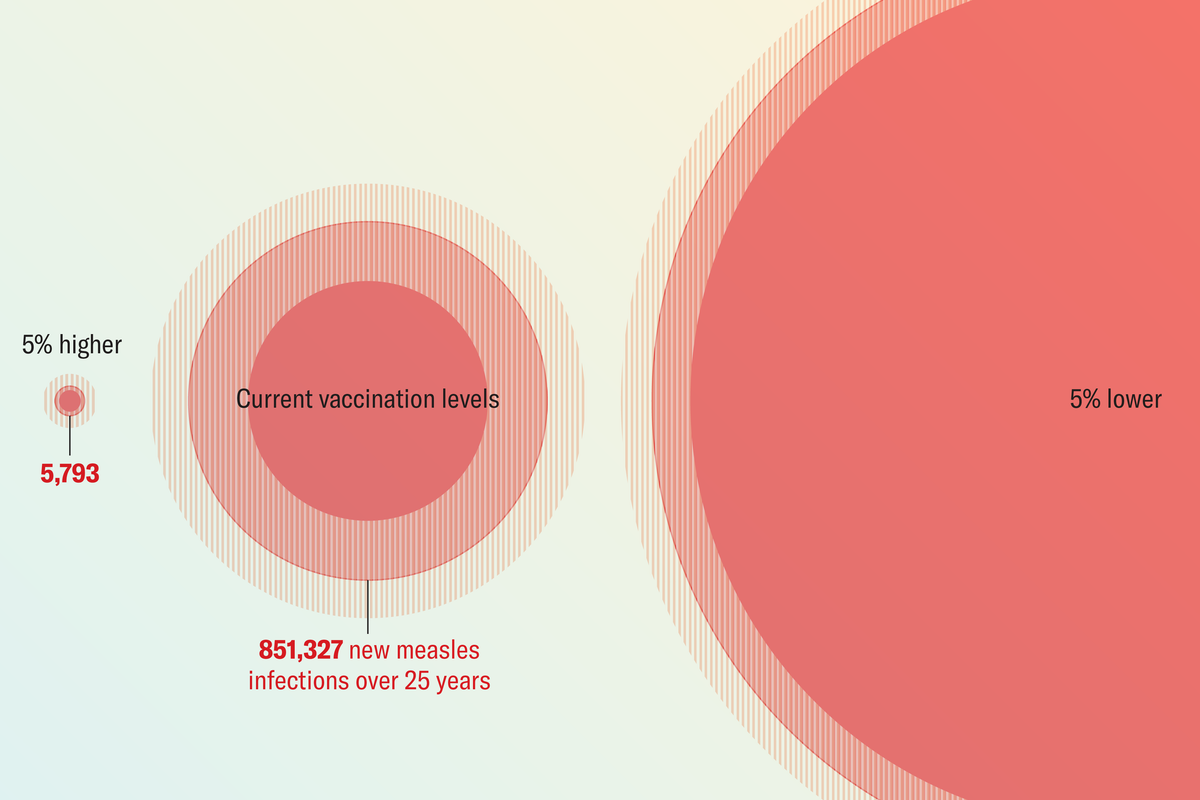
- A study published in JAMA reveals that slight declines in childhood vaccination rates could lead to a resurgence of these diseases over the next 25 years:
– A 5% drop in measles vaccine coverage could result in an estimated 5.7 million cases, whereas a 5% increase would limit cases to just 5,800.
– Polio and rubella are less sensitive but still susceptible with sharper downturns (30-40%) needed for notable reemergence.
- Routine childhood immunization rates have declined recently due to missed COVID-era appointments and growing public resistance influenced by political factors.
- Reduced U.S. vaccination rates could worsen global eradication efforts as unvaccinated travelers may spread diseases internationally.
- The study also warns against overly pessimistic assumptions about massive vaccine rate decreases but highlights political polarization as a possible destabilizing factor.
Indian Opinion Analysis
India’s public health policies face parallels with issues discussed here: declining trust in vaccines and challenges of maintaining high immunization rates post-pandemic. Despite high success via routine immunizations like its polio elimination campaign,vaccine hesitancy has emerged globally,including India-with misinformation on platforms or politicized narratives amplifying distrust.
for India specifically:
- Global Implications: With international disease eradication efforts receiving funding cuts (USAID/gavi), the ripple effects may hamper India’s own health initiatives reliant on external collaborative frameworks for vaccine development and distribution.
- Local Submission: Insights from this study underline the catastrophic risks of even small vaccination gaps-applicable especially given India’s ongoing battles with measles outbreaks due to regional disparities in coverage levels.
Countering hesitancy through grassroots education campaigns that leverage India’s cultural diversity while prioritizing scientific clarity can help ensure its progress does not falter amidst global shifts toward reduced immunity thresholds.