Now Reading: Rome’s Dolphins Clash: Unusual Behavior Sparks Concern
-
01
Rome’s Dolphins Clash: Unusual Behavior Sparks Concern
Rome’s Dolphins Clash: Unusual Behavior Sparks Concern

Swift Summary
- Location: Less than an hour from Rome, at the tiber River’s estuary in the Tyrrhenian Sea.
- Population: Around 500 bottlenose dolphins frequent the area; approximately 100 are permanent residents (mostly females and their offspring).
- Study Findings:
– Health Issues: Over 70% malnourished with visible ribs, caused allegedly by overfishing. Nearly all dolphins exhibit signs of skin disease due to pollution from tainted water and wastewater.
– Physical Injuries: Widespread marks from fishing gear entanglement, some showing amputations; teeth scratches indicating unusually high rates of aggressive interactions likely linked to food scarcity.
- Past Context: Dolphins in this area have existed for thousands of years, depicted in ancient Roman mosaics as stealing fish from nets.
- Concerned Experts:
– Daniela Silvia Pace highlights pressures like pollution and lack of conservation management for their decline.
– Bruno Díaz López notes that similar issues affect bottlenose dolphin populations worldwide due to human activity.
- conservation Call-to-action: Researchers recommend declaring this location a “Site of Community Importance” for habitat protection but acknowledge political challenges.
Images included:
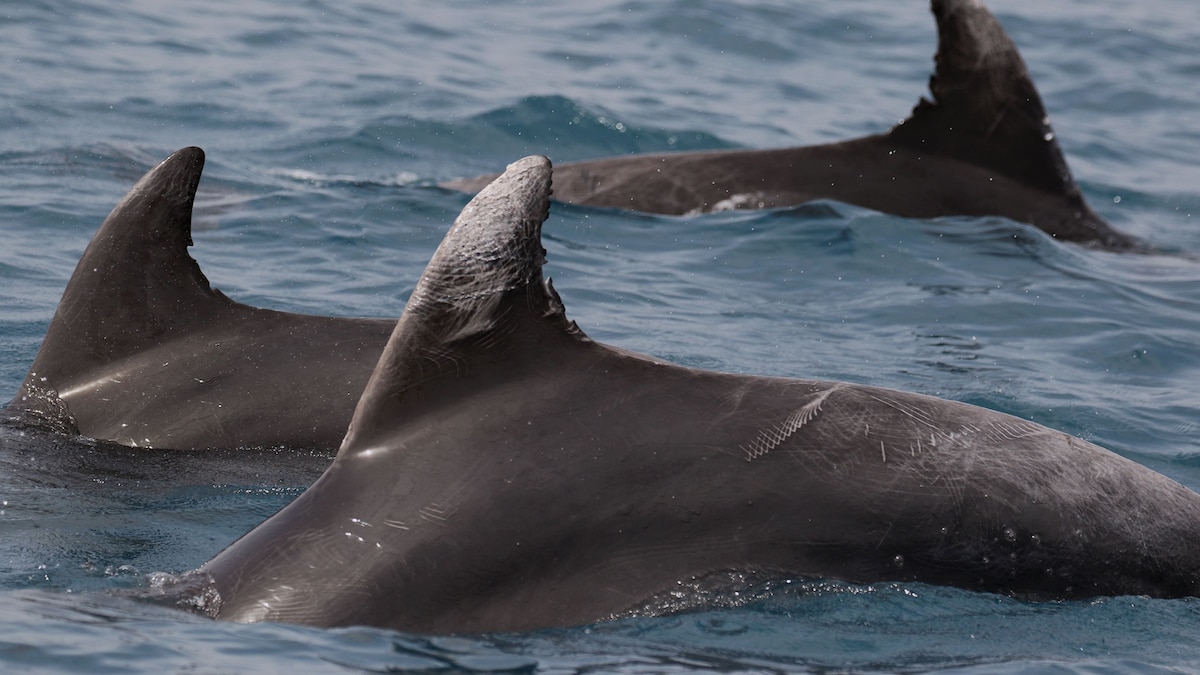
- Aggressive interaction between two male dolphins off Rome’s coast.
- Dolphin fin showing blood-providing evidence of fighting.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The plight of the Capitoline dolphins underscores broader environmental challenges that resonate even beyond Mediterranean waters-rapid resource depletion and pollution fueled by unregulated human activities place fragile ecosystems under intense stress worldwide. For India, home to marine dolphin species such as Irrawaddy and Gangetic river dolphins (some critically endangered), thes findings act as a cautionary tale emphasizing the urgent need for robust conservation efforts.
India’s extensive coastline faces similar threats-overfishing near breeding zones endangers aquatic life while pollutants from industries harm biodiversity balance across critical habitats like Sundarbans or Gujarat’s coasts. Establishing protected marine reserves akin to Italy’s proposed “Site of Community Importance” could offer tangible benefits for species preservation while aligning local community interests with lasting exploitation practices.
Furthermore, researchers’ advocacy suggesting public awareness campaigns presents valuable lessons on influencing policy outcomes through grassroots support-a strategy Indian conservationists may consider adapting within domestic contexts fostering biodiversity harmony amidst development demands.