Now Reading: Self-Supervised AI Unlocks Molecular Insights from Millions of Mass Spectra with DreaMS
-
01
Self-Supervised AI Unlocks Molecular Insights from Millions of Mass Spectra with DreaMS
Self-Supervised AI Unlocks Molecular Insights from Millions of Mass Spectra with DreaMS
Swift Summary
- The article highlights the importance of identifying small molecules and metabolites for scientific fields like drug advancement, environmental study, and disease diagnosis.
- Less than 10% of natural chemical compounds have been discovered across human biology and plant species, leaving most chemical spaces unexplored.
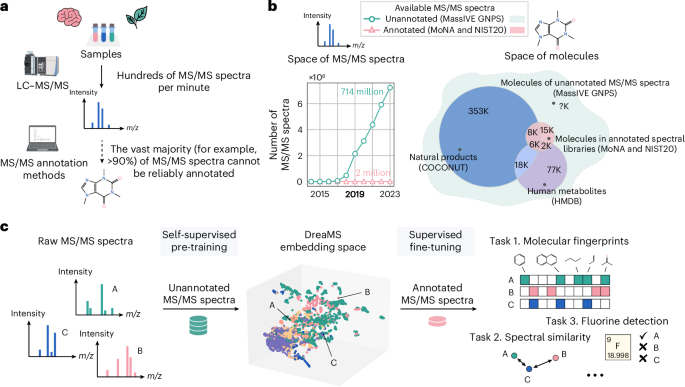
- Tandem mass spectrometry with liquid chromatography (LC-MS/MS) is a tool used to analyze molecular compositions but faces challenges in interpreting generated data beyond reference spectral libraries. Only 2%-10% of MS/MS spectra can typically be annotated with molecular structures using current tools.
- Annotation methods are classified into: spectral similarity algorithms, forward annotation approaches using computational simulation or machine learning, and inverse annotation techniques predicting molecular properties directly from spectra.
- Tools like SIRIUS leverage machine learning pipelines to explain tandem mass spectra but remain dependent on limited annotated libraries such as MoNA or NIST20 databases that only cover a subset of known molecules.
- Emerging solutions include self-supervised large neural networks like DreaMS trained on vast collections of raw experimental mass spectra enabling broader annotation capabilities through transfer learning strategies without full reliance on existing libraries.
Image from the Article:
!Source Link.
Quick Summary
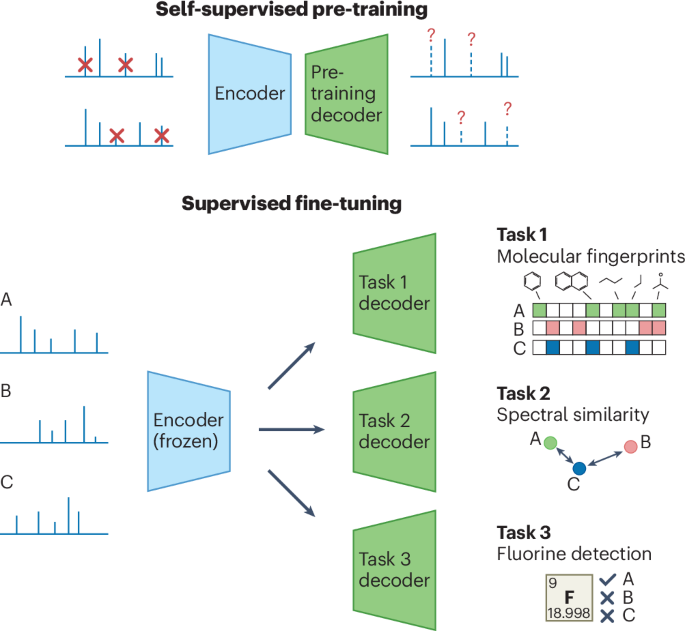
- The DreaMS model leverages self-supervised training to extract molecular structures from mass spectrometry data.
- It uses Fourier features, a transformed attention mechanism, and classification modeling for masked m/z predictions.
- Experiments show the model progressively learns molecular fragment representations throughout its training phase.
- Transfer learning enables DreaMS to perform varied spectrum annotation tasks such as spectral similarity and chemical property predictions with state-of-the-art accuracy.
- Fine-tuning improves sensitivity to detailed molecular variances and helps retrieve similar molecules effectively, outperforming 44 standard measures like MS2DeepScore in specific retrieval tests.
- Key innovations include direct fingerprint prediction from raw spectra without intermediate steps, robust embeddings organized by chemical formulas/motifs, and sample-level comparisons of metabolic profiles.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of DreaMS represents an critically important technological leap forward in leveraging AI-driven methods for analyzing complex spectrometry data. For India, this innovation can have far-reaching applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, agricultural sciences, food safety monitoring, and environmental assessment. With India’s growing focus on biotechnology research and sustainable practices-especially in crops or medicine-the adoption of such tools may enhance precision diagnostics while optimizing resource usage across industries. Moreover, the approach highlights the broader opportunities provided by transfer learning models in addressing low-resource challenges through improved computational methodologies tailored for a diverse dataset quality.
Read more: Nature Articlequick Summary
- Researchers have introduced DreaMS, a transformer model designed for interpreting tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) data.
- The model undergoes self-supervised pre-training using the GeMS dataset,which comprises 714 million curated MS/MS spectra from MassIVE GNPS repository studies.
- DreaMS performs state-of-the-art fine-tuning for various annotation problems and molecular predictions, including detecting fluorinated molecules with high precision (0.91).
- Using dreams annotations, researchers developed the DreaMS Atlas-a molecular network organizing 201 million MS spectra-with robust connectivity enabling efficient interpolation between molecular structures.
- The Atlas provides annotations based on similarity metrics and facilitates research applications like hypothesis generation and exploring connections between compounds and diseases.
Indian opinion Analysis
The development of AI-driven tools such as DreaMS marks a significant breakthrough in metabolomics research globally, including India’s growing biotechnology sector. By improving computational efficiency and accuracy in analyzing mass spectrometry data, models like these hold considerable potential to advance pharmaceutical research initiatives within India-especially in drug discovery and biomarker identification projects.
India could benefit notably from the application of the DreaMS framework within its agricultural sciences to trace environmental pollutants or develop crop treatments based on chemical insights from MS mappings. This innovation also aligns with India’s push towards fostering AI-powered bioinformatics infrastructure under governmental programs supporting scientific data utilization at scale.
Read more: Nature Article Link.Quick Summary
- The article highlights advancements in algorithms for mass spectrometry, clustering techniques, and data formats.
- Three GeMS variants-A, B, and C-were developed using varying thresholds for spectrum filtering criteria.
- Random projection algorithms based on locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH) were employed to cluster mass spectra and reduce dataset biases.
- A new format based on .hdf5 was introduced to store datasets optimized for deep learning applications. Sequence folding of molecular structures was improved using Murcko histograms splitting method focused on scaffold substructures rather than atom-level details, minimizing data leakage across training/validation folds.
- Neural network architecture, DreaMS, uses a modular approach with PeakEncoder and SpectrumEncoder to better understand relationships between spectral peaks.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research holds substantial implications for India’s scientific community as it pushes forward the boundaries of machine learning applications in metabolomics-a critical area in drug development and agriculture sectors where India plays an active global role. By offering tools such as Murcko histograms that resolve molecular generalization issues while improving model robustness against overfitting tendencies, this effort could enable Indian researchers to enhance their precision targeting unexplored biochemical molecules or ‘dark matter.’ Investments in such fields match India’s growing focus integrating AI healthcare-focus دست-infrastructure at systemic industry academia;It seems the content you provided is highly technical and scientific, mainly concerning mathematical modeling and machine learning for analyzing mass spectrometry data. Unfortunately, it doesn’t appear to relate directly to India or typical news contexts suitable for the Indian Opinion platform.
If you intended to input a piece of news about India or its context, please provide the relevant text, and I’d be happy to assist you with a concise write-up including “Quick summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis.”Quick Summary:
- The DreaMS model is designed for self-supervised learning to analyze mass spectrometry data.
- It uses masked prediction of mass peaks and retention order classifications to improve its ability to interpret and reconstruct molecular structures.
- linear probing assesses how molecular structure recognition improves over training iterations based on MACCS fingerprint bits.
- Self-supervised embeddings from DreaMS can be fine-tuned using minimal supervision for targeted tasks like spectral similarity, analog searches, and molecular fingerprint prediction.
- Benchmark comparisons show DreaMS performs well against existing methods like MS2DeepScore in tasks such as Tanimoto similarity assessment and AUROC-based classification for same-molecule spectra detection.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The introduction of the DreaMS model highlights emerging capabilities in analyzing complex biological datasets without reliance on extensive supervisory inputs or pre-existing molecular databases – a critical move towards efficient computational workflows in proteomics research.For India, this kind of innovation could catalyze advancements across pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, environmental science, and food safety industries where high-throughput spectrometric analysis is pivotal yet resource-intensive. Developing home-grown expertise or collaborations around such models would align with India’s increasing focus on AI-driven solutions that can scale economically while maintaining precision.
For further details: LinkQuick Summary
- Researchers utilized the CANOPUS benchmark through the MIST codebase to evaluate molecular fingerprinting accuracy using mass spectrometry data.
- DreaMS, a fine-tuned model, demonstrated competitive retrieval performance without relying on domain-specific annotations.
- Molecular property prediction was implemented by fine-tuning DreaMS and benchmarking against models like MS2Prop and XGBoost.
- The fluorine detection capability of DreaMS was tested on datasets exceeding 17,000 spectra. Precision was emphasized over recall for practical applications in chemical identification experiments.
- A extensive “DreaMS Atlas” of embeddings representing 76 million spectra was constructed using graph-based techniques such as NN-Descent clustering and refined k-NN approaches.
- Ablation studies highlighted key design choices for improving embedding representation,including pre-training quality subsets (GeMS-A10) and architectural modifications like Fourier representation methods.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The advancements presented by DreaMS signal a significant step forward in utilizing machine learning techniques to interpret complex mass spectrometry data efficiently and accurately. Its ability to perform molecular fingerprinting without domain-specific heuristics underscores its versatility across varied datasets. For India’s scientific community, this holds potential in accelerating drug discovery processes, material sciences research, or environmental monitoring related to hazardous compounds detection (e.g., fluorinated chemicals). Leveraging mass spectroscopy paired with computational analysis may lead to more accessible precision tools for laboratories nationwide or further industrial R&D innovations. Technical scalability described in generating millions of embeddings per hour could prove economically beneficial for large-scale projects reliant on high-throughput analytics systems by Indian institutions.
Read More: Source linkQuick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in computational methodologies for processing mass spectrometry (MS) data, emphasizing their role in molecular discovery and annotation.
- Tools like matchms, pyOpenMS, GeMS dataset, DreaMS Atlas, and MassSpecGym are highlighted as benchmarks for improving MS capabilities.
- Neural networks were implemented using PyTorch and trained with PyTorch Lightning to optimize MS analysis performance.
- Public repositories such as Hugging Face Hub and Zenodo host datasets and model weights used in these studies. Libraries like MoNA provide accessible reference data for improved molecular identification.
- Codebases for workflows like DreaMS are hosted on platforms such as GitHub with accompanying documentation available online.
indian Opinion Analysis
The advances described in the article highlight significant steps toward better utilization of mass spectrometry data through computational methods.for India-a hub of pharmaceutical research, traditional medicine systems (like Ayurveda), and agriculture-the application of such tools could bolster innovation across sectors like drug discovery, food safety analysis, environmental studies, and biodiversity mapping. Open access to tools via public repositories aligns well with India’s growing emphasis on digital transformation in science. To fully leverage these technologies while meeting domestic needs efficiently requires investment not just in infrastructure but also training researchers on cutting-edge methodologies resonating globally.
Read more: Source LinkUnfortunately, the provided text does not appear to describe a news topic but instead contains references and citations for scientific articles in fields such as metabolomics and mass spectrometry. To create a report, raw text must clearly detail a specific event or issue relevant to India. Please provide another document with discernable news content for analysis and summarization.Quick Summary:
- The source provides references to numerous scientific advancements related to mass spectrometry and machine learning-based molecular analysis from various journals and preprints.
- It highlights tools and methodologies like tandem mass spectrometry databases, algorithms for metabolite structure identification, chemical formula inference techniques, and models utilizing deep learning for analyzing molecular spectra.
- Some notable tools mentioned include MSNovelist, SIRIUS 4, BUDDY system, MassBank repository, MS2Mol transformer model, and others aimed at improving efficiency in predicting chemical structures or properties.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India has immense potential to leverage such technological advancements in fields like healthcare diagnostics, organic chemistry research, pharmaceuticals manufacturing, and environmental monitoring. Tools enabling rapid molecular analysis can significantly advance India’s scientific capabilities. Incorporating these methods into India’s biochemistry research could enhance both academic rigor as well as industry applications. However, fostering innovation requires investments in AI-driven frameworks alongside collaborations with global repositories like Nature Methods or MassBank to keep pace with evolving trends.
Read more: (refer links provided in source text)quick Summary
- The article discusses recent advancements in scientific research, particularly in the utilization of artificial intelligence and computational tools.
- Key highlights include the role of large language models and specialized applications in protein sequence design, missense variant prediction, and mass spectrometry data analysis.
- Several referenced studies investigate how AI-driven methods predict atomic-level protein structures, enhance gene expression analysis through long-range interactions, and cluster imaging data using contrastive learning techniques.
Indian Opinion analysis
India’s strong focus on biotechnology and computational research positions it well to integrate these emerging AI-driven methodologies into its existing scientific framework. The developments discussed here can have significant implications for India’s pharmaceutical industry, healthcare innovation, and advanced biochemistry research. Adopting such tools could enhance India’s capacity for precision medicine while addressing global challenges related to protein engineering or genetic mutations. However, developing homegrown expertise will be crucial for maintaining competitiveness as international efforts also advance rapidly.
Read more: [Link provided with raw text]Quick Summary:
- This set of references emphasizes research in advanced methodologies such as mass spectrometry, data analysis, and machine learning in scientific domains like pharmacology, drug discovery, environmental analysis, and computational approaches.
- Publications cited include work on graph representation models (transformers),small molecule retention prediction techniques,exact molecular mass measurements for chemical configurations,and experimental vs computational methods in solubility estimation.
- References span various notable journals-like Nature Communications, International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, and Journal of Chemical Information-and touch on cutting-edge work relevant for bioinformatics and untargeted metabolomics clustering.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This detailed compilation reflects the growing emphasis placed globally on technological advancements that connect chemistry with artificial intelligence (AI) for predictive analyses. For India,which is rapidly expanding its pharmaceutical and healthcare industries while focusing on sustainability challenges related to PFASs (poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances),such research provides a blueprint for strengthening domestic capabilities in health-tech innovation. Developing expertise in these areas could enhance India’s drug discovery processes while addressing local environmental monitoring needs.Furthermore, leveraging tools like AI-based transformers or UMAP visualization (referenced above) may help accelerate India’s ongoing efforts to modernize its data infrastructure across fields like genomics or agriculture biotech research. Strengthening collaborations with global entities contributing to these technical innovations would be key.
For further reading: link.the provided input does not contain India-specific news content. It seems to list various scientific references and articles across different domains, such as medicine, technology, and biochemistry. If you have an article about India or relevant topics you’d like summarized and analyzed under “Quick Summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis,” please provide the appropriate content for further processing.Quick Summary
- The article explores advancements in computational tools for mass spectrometry.
- Technologies like DeepLC and DreaMS were discussed regarding their contributions to peptide retention predictions and molecular identification.
- Collaboration among global researchers and institutions, including the Czech Academy of Sciences, played a key role.
- Key innovations involve improvements in machine learning application to chemical data processing.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Advancements in computational technologies, such as those referenced here, have the potential to revolutionize research fields reliant on molecular analysis-particularly biotechnology. For India, an emerging powerhouse in pharma and bioinformatics sectors, these tools could drastically enhance efficiency in drug discovery processes. By integrating similar models into local scientific frameworks, Indian researchers could scale up analyses while minimizing manual errors. Encouraging collaborations akin to those showcased here can unlock cross-border innovation beneficial not only for academia but also for industrial-scale applications.
Read more here.Quick Summary
- The article focuses on self-supervised learning in molecular representations using a model called DreaMS applied to tandem mass spectra.
- Key findings indicate the model demonstrates superior performance across various metrics like spectral similarity prediction, analog search scenarios for molecules, and robustness against low-quality data.
- DreaMS embeddings outperform methods like MS2DeepScore and classic cosine or entropy-based techniques in multiple evaluations. Contrastive fine-tuning enables further sensitivity to structural subtleties among molecules.
- Murcko histogram-based splitting of molecular libraries improves generalization capabilities by reducing data leakage compared to existing approaches.
- Extended visualizations showcase UMAP projections emphasizing structural molecule properties derived from embeddings, aiding better representation institution and interpretability.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of the DreaMS model signifies progress in computational chemistry, introducing scalable approaches for analyzing millions of spectral datasets efficiently while retaining high accuracy and adaptability even on low-quality inputs. For India, such advances could support research into pharmacology or biotechnology where mass spectrometry plays a crucial role-possibly enabling solutions tailored for indigenous needs like affordable drug synthesis or environmental monitoring through bio-pattern discovery. Further adoption might promote international collaborations integrating India’s expansive biodiversity with global AI to map its unique chemical landscape comprehensively.
Read moreQuick Summary
- researchers have developed a self-supervised learning model called DreaMS to extract molecular representations from millions of tandem mass spectra.
- The study was led by R. Bushuiev, A. Bushuiev,R. Samusevich, and colleagues.
- DreaMS leverages advanced computational techniques to analyze mass spectra data for molecular-level insights.
- The paper contributes to advancements in biotechnology research, facilitating better understanding of complex molecules through AI tools.
- Published in Nature biotechnology on May 23, 2025.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of DreaMS exemplifies the growing intersection between artificial intelligence and biotechnology research globally.For India, where biotechnology is emerging as a critical sector within its innovation ecosystem, such breakthroughs hold relevance for local applications in health diagnostics and drug development industries. Adoption of similar models could help Indian researchers improve the efficiency of analyzing large-scale biochemical datasets while reducing dependency on traditional experimental methods.
By investing further into AI-driven biosciences like DreaMS’ approach, India can enhance its contributions to global scientific endeavors while also accelerating domestic industries such as personalized medicine or genomics-based treatment plans. This underscores the importance of fostering collaborations between India’s robust IT sector and biomedical researchers-a step toward achieving leadership in this space without needing extensive physical infrastructure investments typical for experimental setups at scale.