Now Reading: Severus Uses Long-Read Sequencing to Uncover Cancer Genome Variations
-
01
Severus Uses Long-Read Sequencing to Uncover Cancer Genome Variations
Severus Uses Long-Read Sequencing to Uncover Cancer Genome Variations
swift Summary
- The CASTLE panel’s sequencing data has been made openly available via NCBI SRA bioproject under code PRJNA1086849.
- Controlled access for clinical samples is facilitated through the dbGaP study (phs002529).
- Supplementary materials provide individual accession codes and dataset references, including key datasets like COLO829, HCC1395, HG002, CHM1, and CHM13.
- Visualization tools and script outputs are accessible via Zenodo at doi:10.5281/zenodo.10856827, with reference genomes provided by NCBI (e.g., hg38).
- Specific links to structural variants research in cancer genomics are included from publicly available sources such as 1000 Genomes Vienna SV panel.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The availability of the CASTLE panel sequencing data represents a important advancement in genomics infrastructure that can aid Indian researchers in contributing to global cancer studies. With clinical sample access regulated through controlled pathways such as dbGaP, ethical standards for using sensitive biological material appear upheld-a promising precedent for India’s growing genomic medicine sector. India’s budding bioinformatics domain could utilize shared datasets or create collaborations around tools hosted on platforms like Zenodo for meaningful participation in international genome analysis initiatives.
Read more: NCBI BioProject | dbGaPQuick Summary
- No coherent news or details on India are present in the given text.
- provided references appear to relate to scientific articles about genomic structural variations and methodologies, but the article does not include India’s linkage or context explicitly.
Indian opinion Analysis
The provided material primarily consists of scientific references related to genetic research and technology developments like long-read sequencing, structural variant detections, etc., with no discernible connection to India mentioned in the text. For future Indian implications, related research could theoretically bolster advancements in biotechnology and genetic engineering sectors within the nation. However, no specific mention ties this data directly to Indian interests presently.
read more: Given URLs appear scholarly; direct relation unknownThe provided input does not contain sufficient details for a news article about India. Please provide a clear and comprehensive raw text of the news article so that I can create an accurate and unbiased report in the requested format. Thank you!Quick Summary:
- The news article highlights advancements in cancer genome analysis techniques, focusing on structural variations and long-read sequencing technologies.
- A series of studies have explored methods to detect somatic structural variants and copy number aberrations through new computational tools and sequencing approaches.
- Researchers emphasize the importance of detailed mapping of genomic rearrangements, such as detecting exact breakpoints using software like DeBreak or reconstructing genome karyotypes with InfoGenomeR.
- Innovations in tools like Truvari, nanomonsv, SVision-pro, jasmine, Iris, and SVDSS aim at improving accuracy in genomic investigations-especially for cancer-derived samples.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India could benefit substantially from embracing these cutting-edge technologies to enhance its capacity for precision oncology.With a rapidly increasing burden of cancer cases nationwide, accessible tools that improve diagnostic accuracy could transform treatment outcomes. However, the affordability and scalability of such advanced methods remain key challenges within India’s healthcare system. Policymakers should evaluate partnerships and funding opportunities aimed at integrating these discoveries into public health practices while creating training pipelines for genetic researchers. Advancing expertise in genomics could not only elevate healthcare standards but also position India as a leader in global biomedical research.
Read moreQuick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in genomic sequencing technologies and their applications in understanding structural variations and genomic rearrangements.
- Key breakthroughs include the use of single-cell sequencing to analyze genomic heterogeneity in cancer, and also the development of long-read sequencing techniques for more accurate structural variant detection.
- Several studies cited emphasize the importance of complete reference genomes to improve cancer mutation diagnostics and somatic variation analysis.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The technological strides outlined have implications for India’s healthcare, particularly in areas such as oncology diagnostics. As India faces a high burden of genetic diseases and cancers, integrating cutting-edge genomics technologies into mainstream medical practice could revolutionize patient care by enabling more precise diagnosis and tailored treatments at scale. However, these advancements also highlight the need for significant investment in genetic research infrastructure within India to compete globally in this rapidly evolving field.
Read more: LinkThe provided input doesn’t contain a coherent news article. It includes references and citations for academic papers and research studies, but no clear narrative or reported event relevant to India appears in the text.
If you have a specific news report or topic related to India,please provide it for accurate summarization and analysis!
Quick Summary
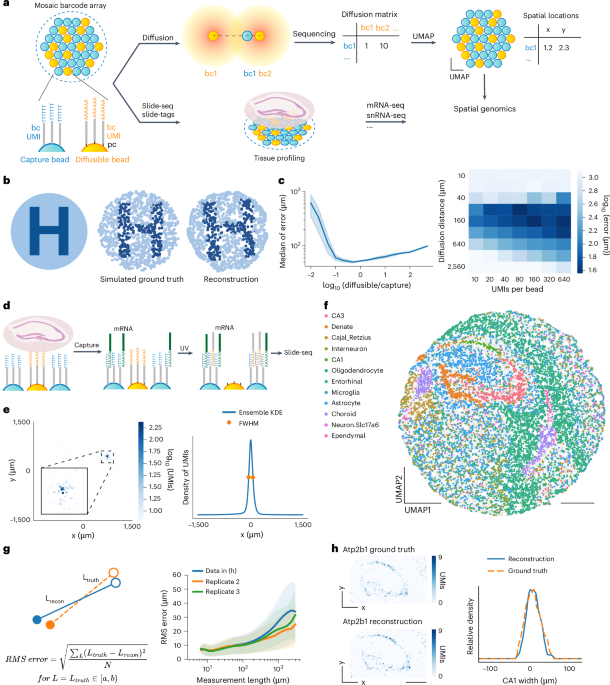
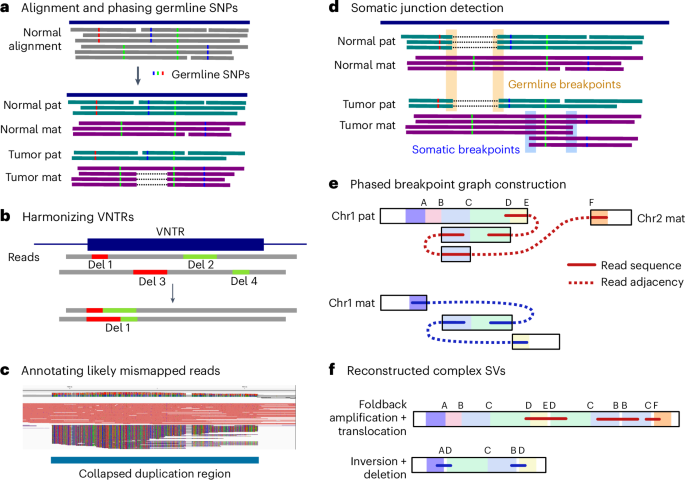
- The article discusses advancements in genome sequencing technologies,particularly long-read sequencing tools,for detecting structural variations in tumor genomes.
- A new computational tool called Severus has been developed for accurate detection of somatic structural variants using long-read data.
- another complementary tool, Minda, was introduced to enhance the alignment accuracy of sequencing results.
- research involved collaboration across institutes such as NIH, University of Maryland, Children’s Mercy Hospital, and Oxford Nanopore Technologies.
- The study utilized resources like NIH’s High-Performance Computing cluster and engaged multiple teams focusing on cancer research technologies and bioinformatics analysis.
for further details: Google Scholar Reference 71
Indian Opinion Analysis
This development in genomic technology could hold significant implications for cancer research globally and within India. With increasingly precise tools like Severus and Minda that leverage long-read sequencing data, researchers can better identify somatic mutations that underpin various cancers. For India-a country grappling with a growing burden of noncommunicable diseases including cancer-such innovations offer promising avenues to improve diagnostic accuracy.
The benefits stretch beyond diagnostics; more precise identification of genetic variants may empower both targeted therapies and preventive medicine initiatives. However, the financial cost associated with cutting-edge genomic tech remains an obstacle to broader implementation across diverse healthcare setups in India. Collaborative international approaches similar to those seen here could play a pivotal role in bridging access gaps while advancing regional research capabilities.
For further exploration: PubMed Reference 73
Quick summary
- Research Development: A study published in Nature Biotechnology highlights the use of Severus, a novel technology employing long-read sequencing to detect somatic structural variations and complex rearrangements in cancer genomes.
- Collaboration: The research involved contributions from scientists A.G. Keskus, A. Bryant, T. Ahmad, and others.
- Technology Focus: Severus uses advanced genomic techniques to better understand cancer mutations by analyzing structural changes that are typically difficult to detect with short-read sequencing methods.
- Publication Timeline:
– Received on August 21, 2024.- Accepted on February 26, 2025.
– Published on April 4, 2025.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of technologies like Severus marks significant progress in global healthcare research and diagnostics for diseases such as cancer. For India-where cancer rates are rising steadily-this innovation offers potential long-term benefits if adopted into research or clinical settings locally. India’s strong biotechnological sector could leverage tools like this for expanded precision medicine initiatives or integrate them within its National Cancer Grid framework for broader applicability across diverse populations.Additionally, Indian institutions might explore collaborations with international teams to further refine such technologies while focusing on cost-effective deployment strategies suited for resource-constrained environments.