Now Reading: Analyzing Silhouette Limitations in Single-Cell Integration Benchmarks
-
01
Analyzing Silhouette Limitations in Single-Cell Integration Benchmarks
Analyzing Silhouette Limitations in Single-Cell Integration Benchmarks
Fast Summary
- Study Focus: The research addresses limitations in using silhouette-based metrics to evaluate single-cell data integration, particularly for batch affect removal and biological signal conservation.
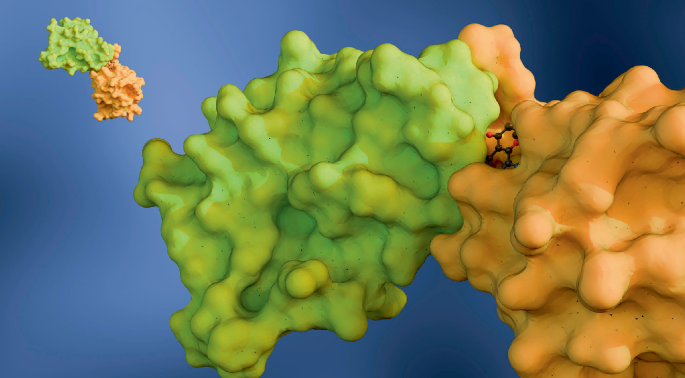
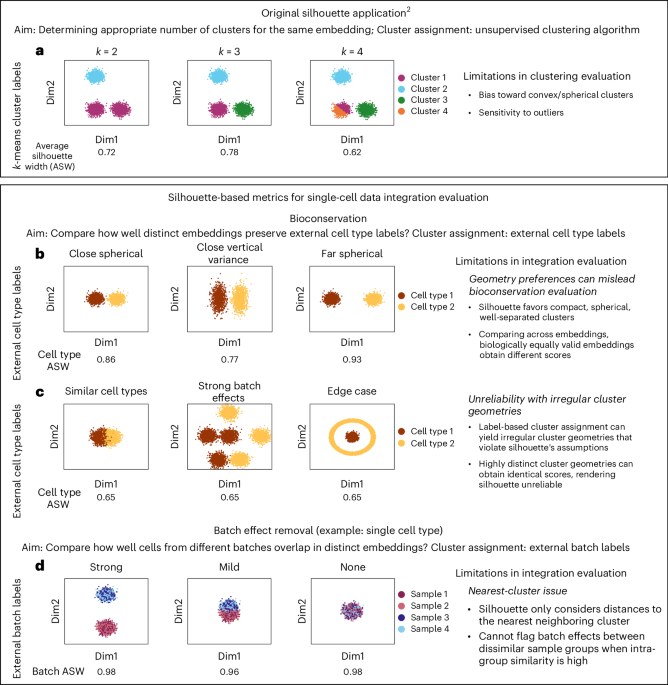
- Silhouette Metric Issues: Silhouette assumes compact, spherical clusters which often misrepresent the irregular shapes inherent in horizontal data integration tasks.
- Key Findings: Metrics like Batch ASW (global) and Cell Type ASW cannot reliably measure data integration quality, as they reward poor integration or fail to distinguish between suboptimal and effective results.
- Research Methodology: Simulations and real-world datasets illustrate how silhouette scores provide misleading evaluations under certain conditions, impacting bio-conservation assessment and batch effect removal accuracy.
Images Included:
Read full article here.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study highlights critical flaws in widely adopted metrics for single-cell genomic analysis, potentially prompting a re-evaluation of established practices across research institutions worldwide. For India, where biotech innovation is gaining momentum alongside initiatives such as G20-led global health frameworks, this raises questions about the robustness of evaluation methods in emerging fields like precision medicine or genomics.
Promoting awareness about advanced alternatives could directly benefit India’s scientific community by avoiding reliance on outdated methodologies. Furthermore, fostering partnerships with global entities might expedite progress of reliable tools tailored for local challenges-such as variability from diverse genetic pools within India’s population-without compromising scientific accuracy or efficiency.Quick Summary:
- Researchers investigated the limitations of silhouette-based metrics in evaluating single-cell data integration, particularly regarding biological assumptions and computational biases.
- Two datasets-Human Lung Cell Atlas (HLCA) and Human Breast Cell Atlas (HBCA)-were studied to showcase the metric’s inadequacies in bio-conservation and batch effect removal.
- Alternatives like CiLISI and BRAS metrics were proposed as more accurate for assessing cell type mixing and ranking embeddings across datasets.
- Issues with nested batch effects were highlighted, showing how common evaluation tools fail to address nonconvex clusters found in real-world biological data.
- Adjustments such as cosine distance within silhouettes improved discriminative power but needed alignment with integration goals for optimal consistency.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The study underscores critical gaps in current tools used for benchmarking single-cell genomics data integration-a fast-growing area within precision medicine research. The findings have broader implications for India’s biotechnology sector, which increasingly relies on single-cell techniques for disease mapping, drug revelation, and personalized medicine development. Emphasizing reliable metric adjustments can lead to more accurate evaluations of cellular variability across India’s genetically diverse population-a valuable asset globally due to India’s unique lineage diversity profile. To ensure local capability aligns with global benchmarks, Indian researchers must adapt or develop robust methods like those suggested here while prioritizing reproducibility standards affecting downstream analyses.
Read More: LinkQuick Summary:
- The research focuses on benchmarking metrics for integrating single-cell genomic data, emphasizing accuracy in handling batch effects.
- Several implementations and adjustments of commonly used metrics were explored, including CiLISI, BRAS, and silhouette-based scores.
- Data from publicly available sources like NeurIPS datasets, HLCA and HBCA were processed using tools like PCA embeddings for analysis.
- Updates to clustering algorithms (like transitioning from Louvain to Leiden) aimed at optimizing resolution according to ARI and NMI metrics across datasets.
- The scripts and study-generated data are accessible via platforms such as Zenodo for reproducibility of results.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This study addresses a critical hurdle in genomics-efficient integration of diverse single-cell datasets while accounting for batch effects. Such advancements are valuable as they allow scientists globally, including researchers in india working on genomics projects like the Human Cell Atlas or disease-specific genomic studies (e.g., cancer or rare diseases), to access robust methodologies ensuring greater data reliability. By improving tools available in public packages, this analysis promotes transparency and accessibility within scientific communities-a principle crucial for developing nations equipped with growing aspirations but limited resources.For further details: Read MoreQuick Summary:
- researchers from the Max-Delbrück Center for molecular Medicine in Berlin developed advanced methodologies for integrating and analyzing single-cell data.
- Studies highlighted include batch correction, multi-omics integration, and transcriptomics data benchmarking, focusing on tools such as SCANPY and SPLATTER.
- Funding sources include grants from Chan Zuckerberg initiative DAF and Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft MDC. Open-access funding provided by MDC supports collaboration across research institutions in Germany.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The advancements in single-cell genomics have potential global significance, including applications in healthcare innovation within India. India’s growing biotechnology sector can benefit from adopting cutting-edge tools like SCANPY to accelerate data-driven disease modeling and precision medicine development. these findings emphasize the importance of international collaborations to elevate technical expertise,address regional health challenges,and contribute meaningfully to global scientific discoveries given India’s focus on leveraging digital health landscapes.
For further reading: PubMed.Quick Summary
- The article addresses the limitations of the silhouette method used in benchmarking single-cell integration.
- Authors emphasize shortcomings in its request for assessing data quality and clustering consistency.
- Peer reviewers include experts such as Dmitry Kobak, Wolfgang Huber, and Malte Lücken.
- Published by Springer Nature under an open-access Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The evaluation of data clustering methods like silhouette has implications for scientific research, including biotechnology developments that India increasingly engages with. As India invests in genomic studies and healthcare innovation, robust benchmarking tools will be crucial to ensure consistent results. Staying updated with global advances allows Indian researchers and institutions to refine their computational strategies. Neutral frameworks like those provided here ensure international collaboration without jurisdictional bias.
Read more: Nature Biotechnology ArticleQuick Summary
- The article highlights research accepted and published in nature Biotechnology.
- Key dates: Research was received on January 21, 2025, accepted on june 19, 2025, and published on July 30, 2025.
- The study is accessible via DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02743-4.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The publication of new research in a prestigious journal like Nature Biotechnology underscores the global significance of scientific advancements that may impact sectors such as healthcare or technology. India’s evolving role in contributing to or utilizing such research remains critical given its expanding biotech industry and focus on innovation-driven growth. Ensuring active engagement with cutting-edge studies can pave the way for local application and development while enriching global collaborations in science.