Now Reading: Simple Ways to Disable Apple’s Ads on iPhone, iPad, and Mac
-
01
Simple Ways to Disable Apple’s Ads on iPhone, iPad, and Mac
Simple Ways to Disable Apple’s Ads on iPhone, iPad, and Mac
Quick Summary
- Apple’s own ads on iPhone, iPad, and Mac cannot be fully blocked by ad blockers or DNS-based content blockers.
- Recommendations to minimize Apple’s ads and data collection:
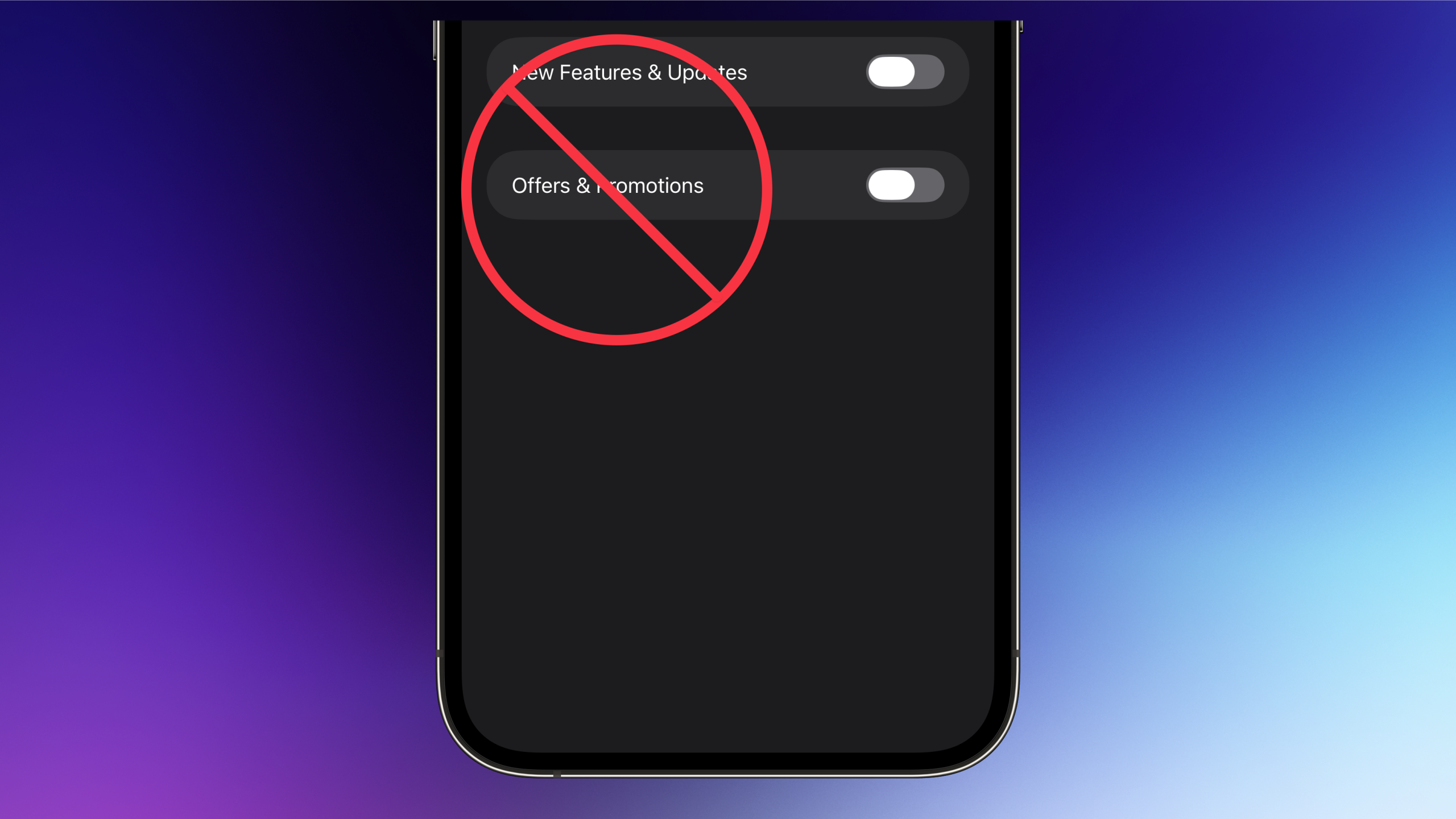
– Disable promotional notifications: Turn off offers and promotions in apps like Wallet, App Store, Music, etc., selectively or entirely.
– Turn off personalized ads: In Privacy & Security settings, disable personalized ad tracking on both iPhones and Mac.
– Limit location access for Apple apps: Restrict location services for apps not needing them (e.g. App Store) while retaining functionality for others like Find my.
– Reduce analytics and data collection: Disable options under Privacy & Security > Analytics & Improvements to limit non-essential data sharing.
– Use alternatives for discovery: Explore third-party applications or websites to find content rather than relying solely on Apple’s ecosystem.Images featured include examples of menu settings being turned off across various devices.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Apple’s increasing focus on advertisements within its ecosystem raises broader questions around user autonomy and digital privacy. While users can mitigate the impact through careful adjustments in app settings and permissions as outlined, complete independence from such ad integrations appears challenging without leaving the ecosystem itself. For India-a country experiencing rapid digitization where Apple products see a growing yet niche adoption-such practices could create awareness about maintaining consumer privacy against corporate-driven marketing strategies. It’s also vital that technology providers balance revenue from services with respect for user rights.
Reducing dependency on proprietary ecosystems could position Indian consumers more firmly in control of their digital interactions while paving ways to analyze ethical AI-driven decisions globally.