Now Reading: Small Star Sparks Big Cosmic Questions
-
01
Small Star Sparks Big Cosmic Questions
Small Star Sparks Big Cosmic Questions

Quick Summary
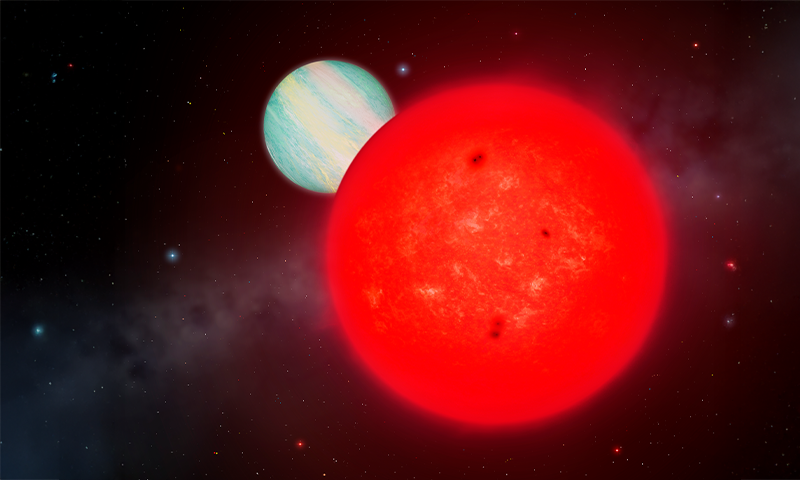
- Scientists have discovered an unusual red dwarf star, TOI-6894, orbited by a massive gas planet (TOI-6894b), challenging current theories of planet formation.
- Red dwarfs, being low-mass stars, are typically not thought to host large gas planets due to insufficient space dust and gas for core accretion-a prevailing formation theory.
- The discovery was made by analyzing over 90,000 observations from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite and reported in Nature Astronomy.
- Alternative theories like gravitational instability suggest planets might form from collapsing dust more rapidly than customary models allow but remain inconclusive based on simulations.
- Further analysis of TOI-6894b’s atmosphere may reveal its origins; metals in the atmosphere could support alternative formation theories like gravitational instability.
- The James Webb Space Telescope is expected to study TOI-6894b within a year. Scientists believe understanding such systems could deepen insights into the formation of our own solar system.
Lead image credit: University of Warwick/Mark garlick
Indian Opinion Analysis
The discovery surrounding TOI-6894 and its massive companion planet challenges established frameworks for planetary science. For India’s scientific community-which increasingly participates in global astronomical endeavors through ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) initiatives-this breakthrough emphasizes the importance of collaborative international research efforts. As India continues expanding its space exploration capabilities with missions like Gaganyaan and future telescope projects, insights into unconventional planetary systems enable researchers globally to refine their models.
Moreover, advancements like NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite set benchmarks that burgeoning Indian programs could seek while deepening contributions toward planetary science. If instruments such as the James Webb Telescope successfully analyze TOI‑6894b’s atmospheric composition soon, findings may influence modeling techniques applicable in studying extraterrestrial worlds or even habitability conditions.
India can leverage discoveries such as these to foster talent pipelines towards theoretical astrophysics while investing strategically within space infrastructure projects already underway-keeping pace with rapidly evolving knowledge domains critical for exploring uncharted cosmic phenomena effectively.