Now Reading: Sol 4553: Resuming Explorations of Boxwork Formations
-
01
Sol 4553: Resuming Explorations of Boxwork Formations
Sol 4553: Resuming Explorations of Boxwork Formations

Quick Summary
- The Mars science Laboratory Mission team resumed operations after the Memorial Day weekend.
- Curiosity rover drove approximately 42 meters during the long weekend,making its total travel distance around 35 kilometers since landing nearly 13 years ago.
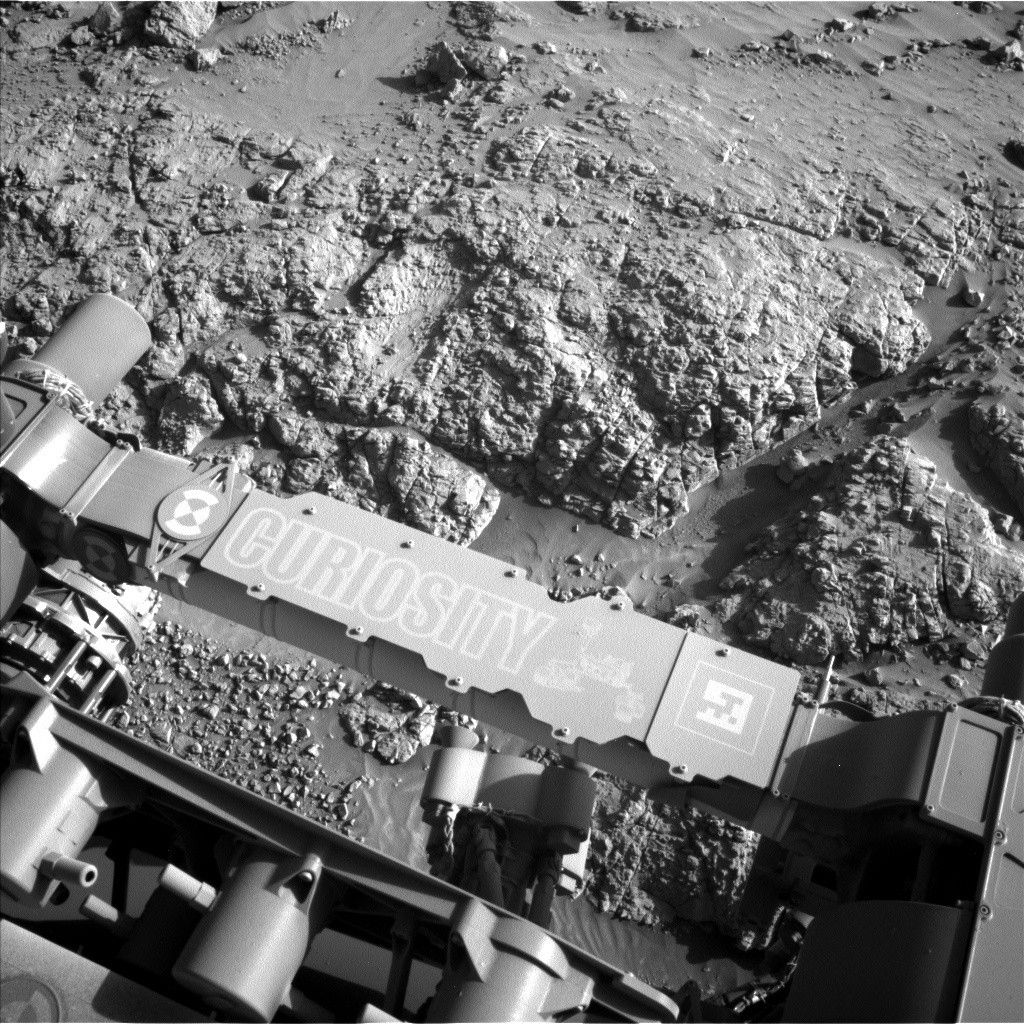
- The rover has climbed over 850 meters in elevation and recently reached new terrain characterized by unique boxwork structures.
- These boxwork formations include resistant ridges studied for signs of enhanced fluid flow and cementation. ChemCam and APXS instruments where used to analyze formation composition, accompanied by Mastcam imaging for broader documentation.
- A remote ChemCam imaging mosaic was planned to capture views up to a record distance of 91 kilometers, comparing ground-level images with HiRISE orbital pictures for a potential 3D reconstruction.
- Additional activities included Navcam dust-devil surveys, MARDI terrain imagery post-drive (24-meter drive planned), as well as REMS (weather monitoring), DAN (neutron spectrometry), and RAD (radiation assessment).
Indian Opinion analysis
The continued success of NASA’s Curiosity rover highlights humanity’s sustained advancements in planetary exploration more than a decade into its mission.These findings-such as studying Mars’ boxwork formations-offer critical insights into understanding fluid processes potentially relevant to early Martian geological history and even extraterrestrial life possibilities.
For India’s scientific community, such missions reiterate opportunities in planetary geology research beneficial not only to space-faring nations but also emerging players like ISRO planning Mars-focused efforts like MAVEN counterparts or follow-ups beyond Mangalyaan’s legacy.
While India efficiently tackles challenges on Earth amid domestic priorities versus budget allocation constraints-a mission teaser of adapted deeper coordinated partnerships remains pragmatically strategic so worth tracking ahead possible HA-bio inclusions future avenues detailed-experimentations..