Now Reading: SpaceX Revamps Starship Fuel Transfer System
-
01
SpaceX Revamps Starship Fuel Transfer System
SpaceX Revamps Starship Fuel Transfer System

Quick Summary
- SpaceX’s operations at Starbase faced challenges due to persistent rain and an explosion during Ship 36’s static fire test.
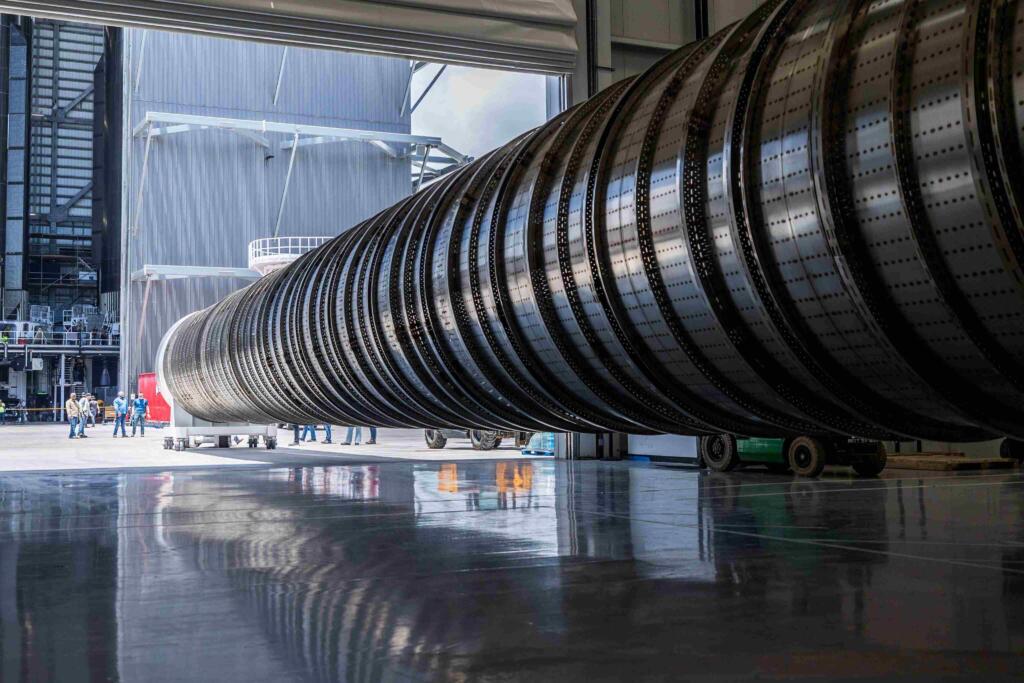
- A redesigned fuel transfer tube for the Superheavy booster was installed, bringing key upgrades: simultaneous ignition of all 33 engines, enhanced thrust performance (up to 9,800 tons), improved reusability, and better landing reliability. The design supports the new Raptor 3 engines with increased thrust capabilities (280 tons each).
- The nitrogen side of the tank farm is operational again, supporting testing preparations for Booster 18.1 and Ship 38 with cleanup efforts ongoing at Massie test site post-damage caused by Ship 36.
- Modifications are underway at Pad A to conduct static fire tests on Starships using repurposed equipment originally designed for boosters while also repairing worn-out launch infrastructure like the orbital launch mount.
- Cameron County Commissioners approved a new air separation unit at Starbase to reduce reliance on gas delivery trucks by producing nitrogen and oxygen onsite; this requires environmental compliance monitoring.
- Construction continues on Block 3 ships (Ship 39/40) with targeted launches in late months of the year pending timely completion despite complexities in design changes.
- Gigabay Construction foundation is being built entirely onsite unlike previous approaches while engine testing activity remains robust with McGregor facility conducting over 21 Raptor tests recently.
Indian Opinion Analysis
SpaceX’s developments showcase its push toward engineering innovations aimed at boosting efficiency, reliability, and sustainability in rocket launches-a critical element as it scales up space exploration objectives globally.
From India’s outlook as a growing player in space technology through ISRO initiatives or private collaborators like Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos stepping into commercial areas-SpaceX’s strategies concerning reusable components or site-specific production reflect benchmarks Indian entities could observe to enhance operational economics domestically despite differing scale thereby creating incentives expand science frontier long run pathways comparative metrics policy response indirect positive ripple interaction Note dismissal safety-slips crucial horizontal-errors mar stakeholder-trust-system aerospace delegation overseeing readaptive-launch-readiness-specific-improved Read More