Now Reading: Star’s ‘Guts’ Spilled in Violent Pre-Supernova Burst
-
01
Star’s ‘Guts’ Spilled in Violent Pre-Supernova Burst
Star’s ‘Guts’ Spilled in Violent Pre-Supernova Burst
Quick Summary:
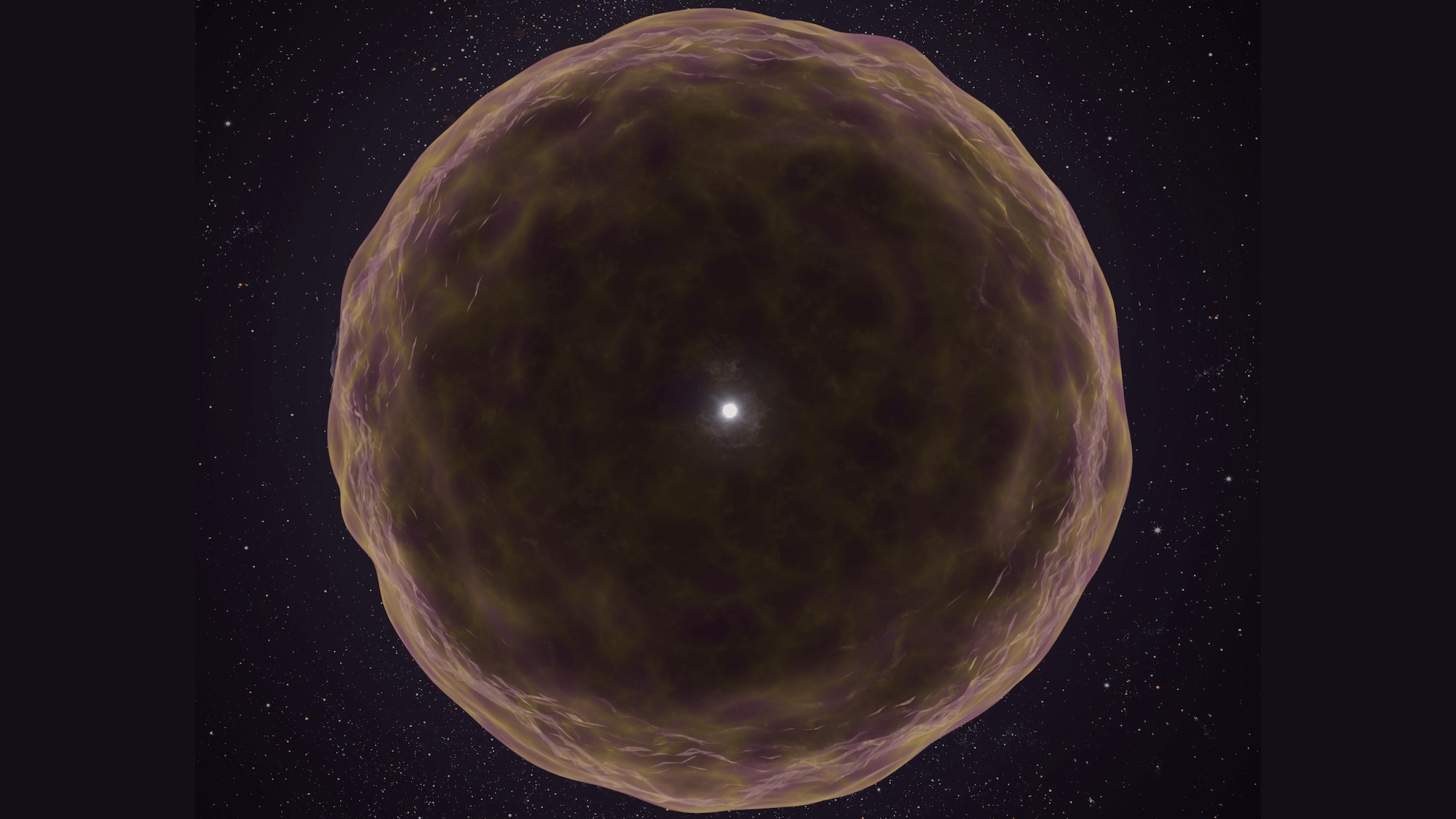
- Researchers have documented SN2021yfj,a supernova located 2.2 billion light-years away, using the Zwicky Transient Facility in California and the W.M. Keck Observatory in Hawai’i.
- This finding provides unprecedented insights into the internal structure of massive stars before their destruction.
- SN2021yfj revealed unexpected elemental composition, including silicon, sulfur, and argon instead of helium, carbon, nitrogen, or oxygen-suggesting extremely rare stellar processes.
- The star is believed to have undergone violent events stripping it of most outer layers due to repeated pair-instability episodes or possibly other causes like strong winds or a collision with another star.
- Researchers theorize that these processes reignited powerful nuclear fusion near its end-of-life phase.
- The study hints at “exotic pathways” for a star’s demise beyond conventional theories in astrophysics.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The discovery of SN2021yfj challenges established understandings of massive stellar evolution and death, opening doors to new astrophysical research. Such advancements resonate beyond astronomy by showcasing humanity’s ability to probe cosmic phenomena at incomprehensible distances-showcasing technological marvels like wide-field cameras and spectrograph tools.
From India’s perspective as an emerging leader in space science (bolstered by missions like Chandrayaan), discoveries such as this highlight opportunities for Indian researchers to further collaborate on global astronomy initiatives. strategic investments into observatories and partnerships can deepen India’s contributions in unlocking mysteries about worldwide origins-a subject with deep cultural resonance across various Indian traditions.Read More
























