Now Reading: Study: Early Fire Use Linked to Meat Storage and Predator Defense Over Cooking
-
01
Study: Early Fire Use Linked to Meat Storage and Predator Defense Over Cooking
Study: Early Fire Use Linked to Meat Storage and Predator Defense Over Cooking

Swift Summary
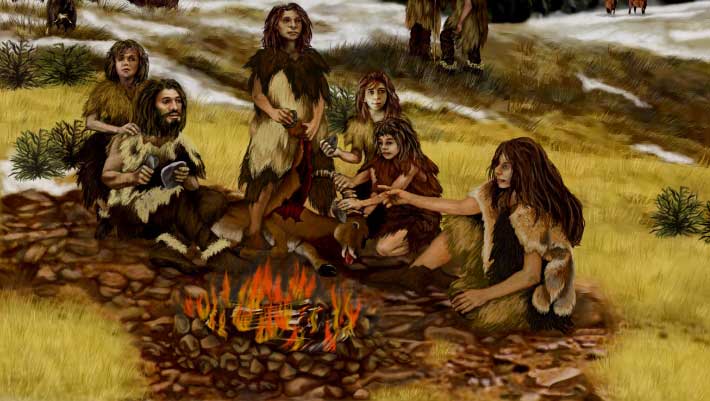
- Researchers at Tel Aviv University propose that early human fire use, particularly by Homo erectus during the Lower Paleolithic (1.9 to 0.78 million years ago), was primarily for meat preservation and predator protection, not cooking as traditionally believed.
- Fire usage before 400,000 years ago was sporadic and required significant effort, indicating it was utilized for specific purposes rather than general domestic needs.
- Studies of nine prehistoric sites with evidence of fire revealed commonalities such as large quantities of bones from large prey like elephants and hippopotamuses, animals critical to early human diets.
- Large prey provided millions of calories but required safeguarding from predators and bacteria over extended periods; researchers suggest fire allowed smoking or drying meat to prevent spoilage while also deterring scavengers.
- While occasional cooking may have occurred alongside these primary uses for minimal extra energy cost, this finding challenges previous assumptions about cooking’s central role in dietary evolution during this era.
- The study aligns with broader theories about prehistoric adaptations to hunting large animals amid their gradual disappearance over time.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study sheds light on the evolutionary ingenuity of early humans in utilizing limited resources efficiently-a principle relevant even today concerning conservation efforts across sectors like food security in India. Understanding prehistoric dietary practices through findings such as these can deepen insights into foundational elements like sustainable consumption or reducing waste-priority areas for India given its population density and nutritional needs.
Moreover, innovative interpretations challenging long-held assumptions reflect the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in solving ancient mysteries-a model India might apply in academic research collaborations conceiving localized solutions to modern issues rooted in historical contexts.
By bridging evolutionary anthropology with practical lessons learned from ancient survival strategies like resource preservation or energy efficiency, India could further enrich its intellectual discourse around development challenges informed by ecological balance principles observed centuries ago.Read more