Now Reading: Study Warns HIV Funding Cuts Could Cause 3 Million Deaths by 2030
1
-
01
Study Warns HIV Funding Cuts Could Cause 3 Million Deaths by 2030
Study Warns HIV Funding Cuts Could Cause 3 Million Deaths by 2030

Speedy Summary
- A study in Teh Lancet HIV warns that international funding cuts for HIV programs could lead to 10.8 million more infections and 2.9 million additional deaths by 2030 in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- International donors, including the U.S., U.K., france, Germany, and the Netherlands, which account for over 90% of such funding, have announced substantial reductions in aid.
- PEPFAR (U.S.-based funding program) has been specifically impacted by pauses ordered under an executive directive,with disruptions leading to clinic closures and limited services despite temporary waivers.
- LMICs rely on international sources for 40% of their HIV budget; vulnerable populations like sex workers and transgender individuals are particularly affected by these cuts.
- Researchers modelled several scenarios; the worst-case outcome predicts a near-total reversal of progress made since 2000 in combating the epidemic without alternative funding mechanisms.
- Even partial recovery through other resources could mitigate but not fully prevent long-term effects; ripple impacts may last decades nonetheless.
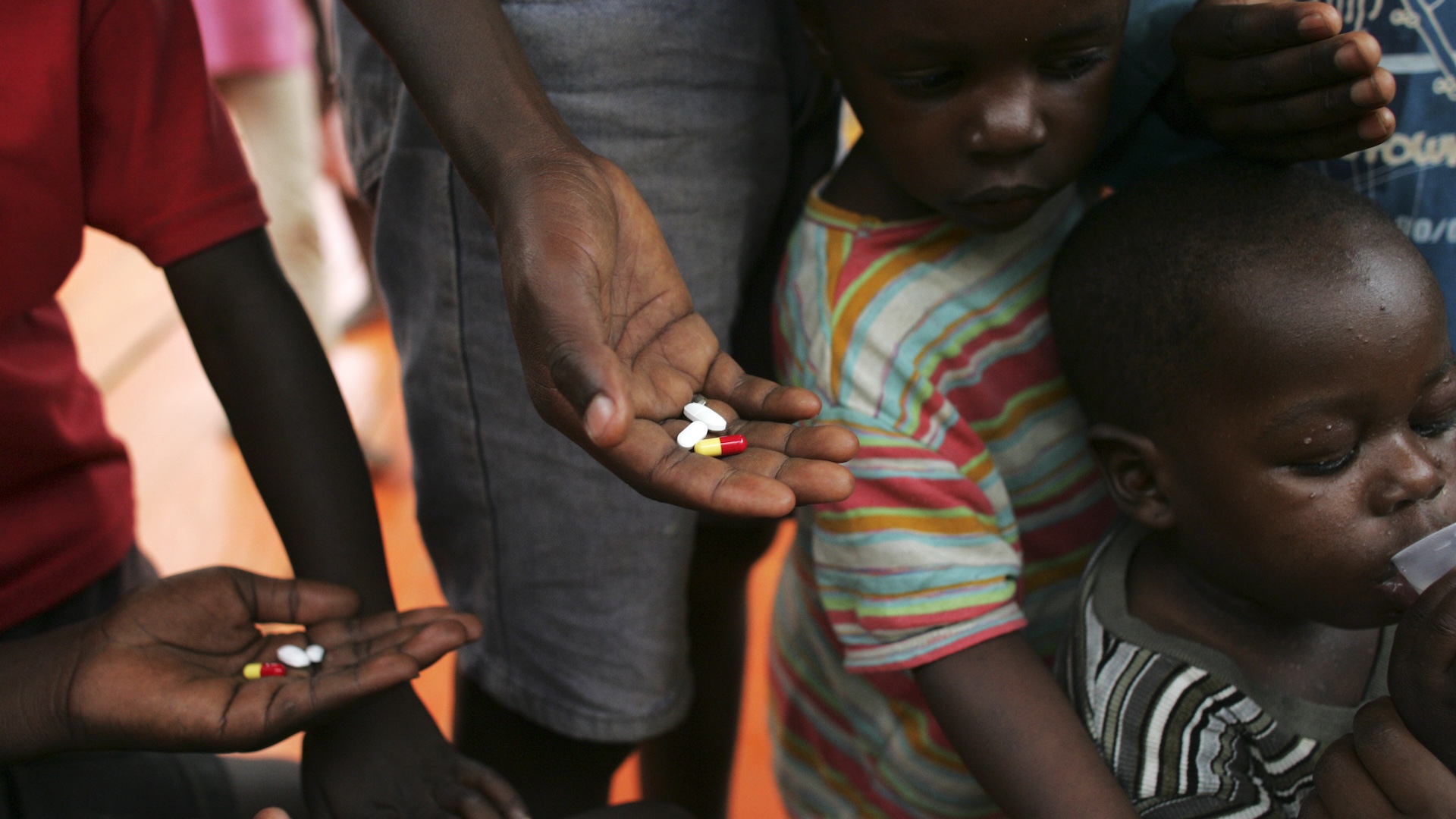
Image: Groups dependent on antiretroviral therapy risk disruption from these severe reductions in global aid.
Stay Informed With the Latest & Most Important News
Previous Post
Next Post
Loading Next Post...