Now Reading: Targeted Cancer Therapy Advanced with Antibody-Bottlebrush Prodrug Conjugates
-
01
Targeted Cancer Therapy Advanced with Antibody-Bottlebrush Prodrug Conjugates
Targeted Cancer Therapy Advanced with Antibody-Bottlebrush Prodrug Conjugates
Quick Summary:
- The article discusses advancements in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), a promising class of targeted cancer therapies.
- ADCs use antibodies to precisely deliver cytotoxic drugs to cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
- Recent research highlights improvements in payload delivery, receptor-mediated endocytosis mechanisms, and enhanced safety protocols.
- Innovations have broadened ADC applications across solid tumors and specific tumor histologies like glioblastoma.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The evolution of Antibody-Drug Conjugates reflects a significant milestone in oncology treatment by enhancing precision targeting for various cancers, including historically challenging types such as glioblastoma. India can benefit from this transformative technology as it directly aligns with the global shift toward personalized medicine-addressing both its extensive cancer burden and improving patient outcomes while ensuring safety standards. Public-private collaboration could be central to making these innovative therapeutics accessible domestically through partnerships with global pharmaceutical firms or fostering indigenous R&D capabilities.
Read more: Link.Quick Summary:
- The article discusses antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), which are a form of targeted cancer therapy described as “biological missiles.”
- ADCs uniquely connect chemotherapy drugs to antibodies that target tumor cells specifically, minimizing damage to healthy cells.
- FDA-approved ADCs and ongoing clinical trials are highlighted in the text for their applications in various cancers, including leukemia, lymphoid malignancies, solid tumors, and multiple myeloma.
- The advancements in ADC linker chemistry and mechanisms of resistance are also reviewed.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India has a growing presence in biotechnology research; developments like antibody-drug conjugates have significant implications for its healthcare sector. As the world shifts toward more targeted therapies like ADCs for cancer management, Indian biotech firms could explore opportunities to invest further into this innovative approach. Though, considerations such as cost-effectiveness-critical in India’s diverse healthcare ecosystem-and adaptation of such research findings into accessible treatment options will be key challenges moving forward. Encouraging partnerships with international entities might accelerate accessibility across Indian markets while advancing local expertise further.
For more information: PubMed CentralQuick Summary
- The article explores mechanisms of resistance to antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), recent advancements in ADC technology, and therapeutic strategies.
- ADCs are a promising class of targeted therapies for cancer, combining monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic drugs to deliver precise treatment while minimizing systemic toxicity.
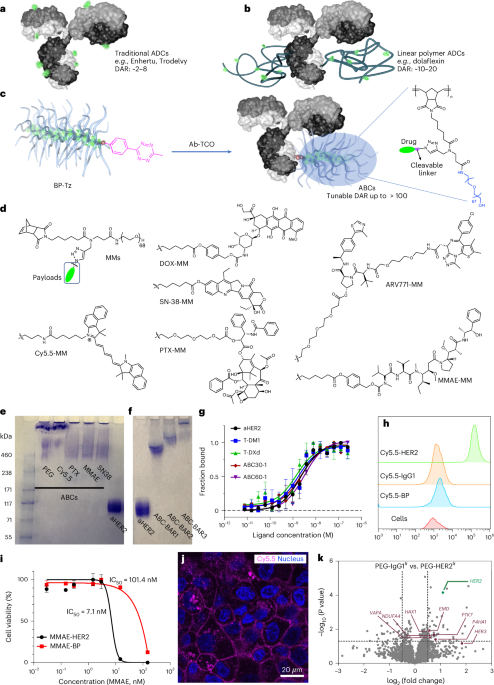
- Key areas discussed include strategies for enhancing tolerability, reducing hydrophobicity for better pharmacokinetics, advancements in drug loading platforms like Dolaflexin, and innovations in nanoscale materials for cancer diagnostics.
- Notable developments highlighted include studies on novel ADCs such as Trastuzumab Deruxtecan and Sacituzumab Govitecan addressing HER2-positive breast cancer and their growing impact on oncology treatment landscapes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Antibody-drug conjugates represent an important innovation in precision medicine globally. For India, where the burden of cancer remains significant, these therapies could offer improved outcomes alongside customary treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. challenges persist regarding cost-effectiveness and accessibility-key concerns given India’s resource constraints within public healthcare systems. Continued investment into research partnerships fostering local production or adapting global breakthroughs could reduce costs while perhaps expanding options available to Indian patients. This approach aligns with India’s broader goal to advance biotechnology domestically without compromising affordability or equity in healthcare access.
For detailed reading: Source Link.It seems the raw text provided does not pertain to any specific news or current events in India.Instead, it primarily contains references and citations related to scientific research and publications focused on chemistry and biomedical engineering.
If you have an article specifically about India or a topic relevant to Indian audiences, please provide the text so I can craft an accurate write-up with “Quick summary” and “Indian Opinion Analysis” sections. Thank you!Quick Summary:
- Raw input contains references to academic articles related to chemical biology,cancer therapies,immunomodulatory strategies,and biotherapeutic drug design.
- Publications span journals such as Nature,Science,J. Am. Chem. Soc., and others.
- Key topics include HER2-targeted therapies beyond breast cancer, antibody-drug conjugates for cancer treatment, protein-polymer conjugation advancements in therapeutics.
- Articles also discuss safer oligonucleotide therapeutics and immune cell microenvironment mapping.
- No direct relevance or specific information about India is apparent from the provided raw text material.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The referenced content highlights global advancements in medical science and biotherapeutics that could have indirect implications for India. As a country with a burgeoning biotechnology sector and significant healthcare challenges,the knowledge shared here might serve as valuable input for Indian researchers targeting localized innovations in oncology or precision medicine.Collaboration with institutions focusing on HER2-targeted treatments or developing safer drug delivery systems might propel India’s capabilities forward while addressing pressing health concerns domestically.
Despite its lack of explicit ties to current Indian developments from the provided information, keeping pace with these scientific trends will likely benefit long-term national interests in healthcare innovation.
Link source for read more inaccessible due to raw format limitations present aboveQuick Summary:
- The news article does not directly focus on India, and instead contains references to multiple scientific studies, mostly related to oncology advancements such as monoclonal antibodies, targeted therapy for cancers like HER2-low breast cancer, and protein degradation techniques.
- These studies span global research efforts across different years (1999-2025) and institutions involved in advancing cancer treatment methodologies through innovative drug conjugates or therapeutic technologies.
- No specific mention of India’s role or implications appears in the input text provided.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India has been steadily rising as a contributor to global medical advancements, particularly in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology.Though, while the input text focuses solely on international research findings without reference to India-specific efforts, these developments carry potential for adoption within India’s healthcare sector. Innovations like targeted therapies have vast applicability given india’s high disease burden from various forms of cancer. Bridging access gaps might be critical; increasing collaboration with global researchers could expedite affordable solutions domestically.
For an economy that holds promise as both a market and a hub for medical innovation outsourcing, leveraging such advanced tools could further strengthen the country’s health systems while creating opportunities for local researchers to gain prominence globally.
Read more: [Link not available based on provided input]Quick Summary:
- Focus on targeted protein degradation (TPD), including research tools and therapies for cancer treatment.
- Highlights advancements in PROTAC (Proteolysis-Targeting Chimera) technology supporting research areas like castration-resistant prostate cancer and HER2-positive breast cancers.
- Studies, such as those on BET-proteolysis targeting compounds, underline effective therapy implications for diseases like triple-negative breast cancer.
- MUC1 structure insights detail its potential in epithelial cancers, emphasizing translational applications globally across research catalysts.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
india remains a significant contributor to global pharmaceutical research but often struggles with accessibility to niche breakthrough strategies like PROTACs targeting advanced-stage conditions or intricate case-specific tumor profiles highlighted/documented studies touche-grass set
Quick Summary
- The news article highlights advancements in various scientific studies and technologies, as referenced through academic citations from journals like Nat. Chem., PubMed, and Clin. Cancer Res.
- Key topics include drug delivery systems using polymer brushes, proximity labeling techniques for cellular analysis, proteomics enabled by neural networks (DIA-NN), and innovative mechanisms in biomedical engineering.
- These studies represent global efforts toward improving therapeutic applications, deep tissue penetration methods, reduction of blood glucose levels via novel biomaterials, and exploring stress granule disassembly mechanisms.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The diverse breakthroughs presented in the article underscore the evolving landscape of biochemical research with significant potential for therapeutic innovation globally.For India-where healthcare challenges like diabetes management or cancer treatment remain critical-the adoption or adaptation of such advanced methodologies could transform patient care outcomes. Moreover, integrating AI-driven tools such as DIA-NN within India’s growing genomics and bioinformatics space aligns with its digital transformation agenda.
India must focus on fostering collaborations between academia, government bodies, and private players to align itself with these cutting-edge developments worldwide. Strengthening ties with global research institutions not only accelerates access but also ensures that innovations serve localized health needs effectively.Read more hereQuick Summary
- The article references advancements in proteomics, specifically dia-PASEF data analysis for deep proteomics with minimal sample amounts.
- Tools like FragPipe and DIA-NN are suggested for handling complex low-sample analyses.
- It highlights computational platforms like Perseus for extensive omics data analysis.
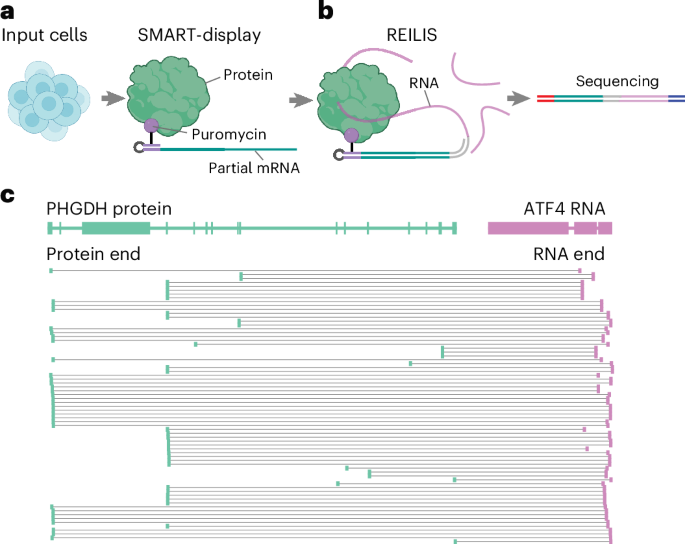
- Use cases include targeted cancer therapy developments using antibody-bottlebrush prodrug conjugates, as outlined in the linked research datasets shared via platforms such as figshare.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Proteomics and computational innovations have significant potential to advance medical research worldwide, including India. These tools can bolster India’s burgeoning biotechnology sector by enabling cutting-edge analysis even with limited biological samples-a critical advantage given constraints observed in specialized labs across the nation. additionally, breakthroughs such as targeted cancer therapies hold promise for improving healthcare outcomes, particularly amid rising incidences of noncommunicable diseases domestically. Investments in computational and research infrastructure aligned with these technological revelations could position India strategically within global medical innovation ecosystems.