Now Reading: The 1787 Great Compromise: The Deal That Shaped the U.S
-
01
The 1787 Great Compromise: The Deal That Shaped the U.S
The 1787 Great Compromise: The Deal That Shaped the U.S

Rapid Summary
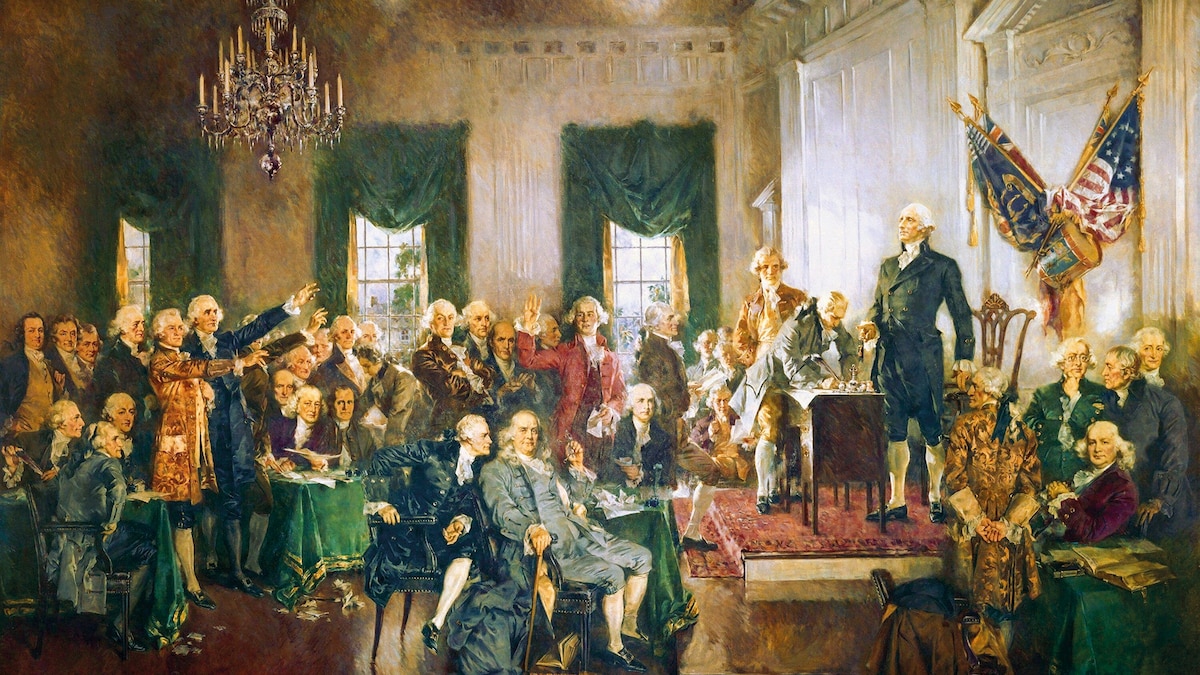
- In 1787, delegates from 12 U.S. states (excluding Rhode Island) met in philadelphia for seven weeks to reshape the articles of Confederation into a more functional national constitution.
- Key leaders included George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton. All delegates were white, male landowners.
- The debate centered on depiction: large states supported the Virginia Plan with proportional representation in Congress based on state population; small states favored the New Jersey Plan proposing equal representation for all states.
- A key breakthrough came with the Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise), led by Roger Sherman:
– Two legislative houses were created:
– Senate – Equal representation for all states.
– House of Representatives – Representation proportional to population.
- Delegates agreed on the controversial Three-Fifths Compromise: enslaved Black individuals counted as three-fifths of a person for taxation and state representation purposes.
- The final compromise narrowly passed on July 16; George Washington described it as imperfect but necessary.
Images from Source:
!Independence Hall Independence Hall in Philadelphia
!articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation at National Archives
Indian Opinion Analysis
While this past event primarily pertains to U.S. constitutional development, it offers relevant insights into governance systems globally-including India’s own democratic structure. The Connecticut Compromise highlights how diverse interests can coexist through negotiation and structural balance-principles that resonate deeply with India’s federal parliamentary constitution balancing state and central powers.
One striking parallel is how debates over proportional versus equal representation echo India’s challenges managing varied populations across regions and linguistic-cultural groups. Such as, India’s Rajya Sabha provides equal state-based membership alongside Lok Sabha’s population-based system-a concept somewhat similar to this historic compromise.
The inclusion of morally contentious policies like the Three-fifths Compromise shows inherent flaws even in critical foundational moments-a reminder that systemic justice evolves over time rather than being instantly achievable. In India’s journey addressing inequities across caste lines or marginalized communities under its Constitution framework also reflects such ongoing progression toward equity.
read More: National Geographic History Article