Now Reading: Tick-Borne Malaria-Like Disease Spreads to Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia
-
01
Tick-Borne Malaria-Like Disease Spreads to Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia
Tick-Borne Malaria-Like Disease Spreads to Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia

Quick Summary:
- In June 2023, an elderly man in Virginia developed babesiosis, a rare tick-borne disease alongside lyme disease, detected late after important symptoms like jaundice and anemia.
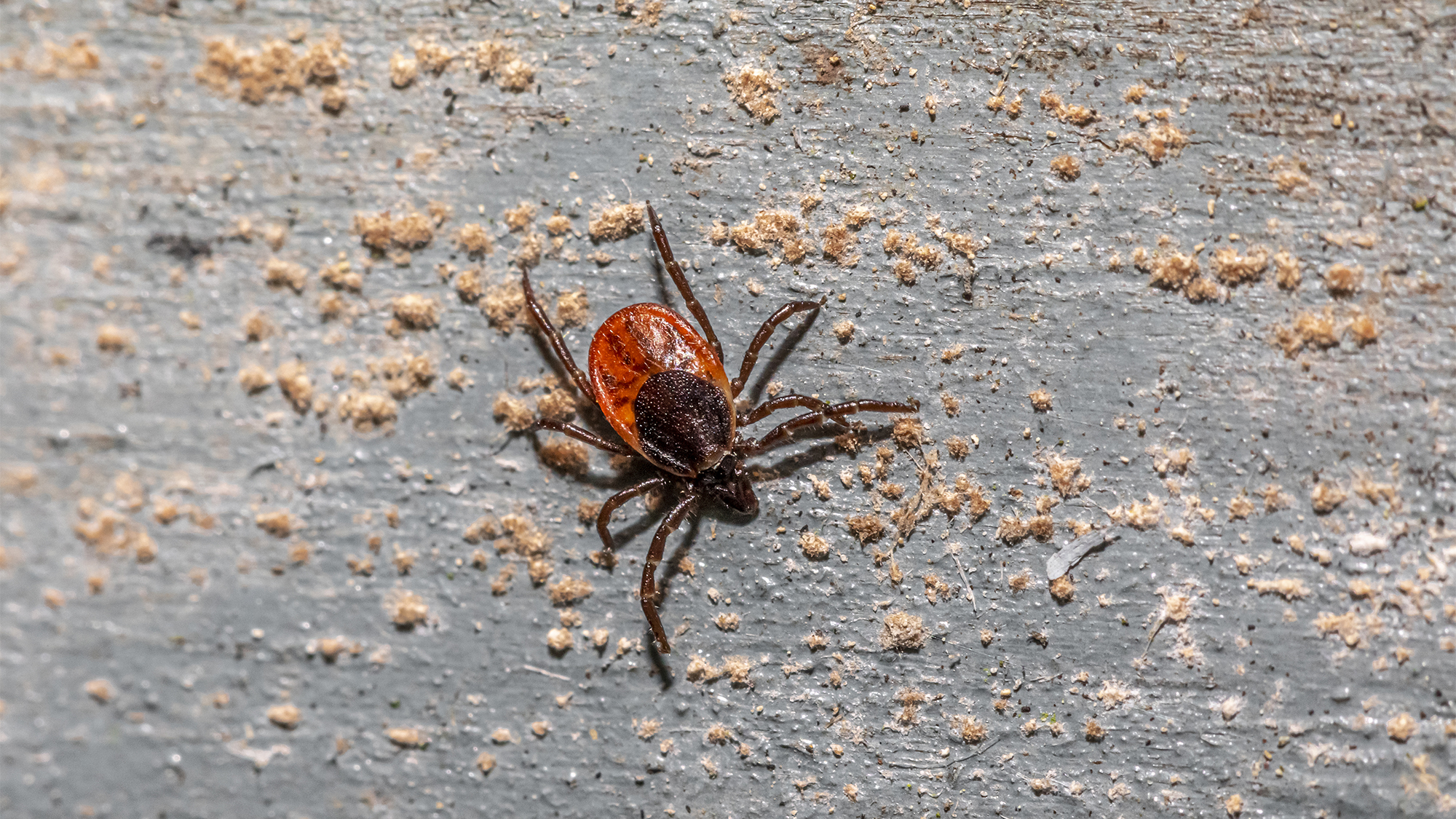
- Babesiosis is caused by the Babesia parasite and transmitted by black-legged ticks.Untreated cases can lead to severe consequences such as organ failure and death.
- A study published in April 2024 revealed that the Babesia parasite is expanding rapidly through the mid-Atlantic region (Virginia, Maryland, Delaware), previously uncommon for babesiosis.
- Factors driving this expansion include warmer winters and excessive rainfall linked to climate change, which create ideal conditions for ticks’ proliferation year-round.
- Findings showed that regions with rising Lyme disease cases are seeing a subsequent increase in babesiosis cases due to shared vectors (ticks).
- Notable hotspots include Baltimore and the Delmarva peninsula; however, underreporting due to low physician awareness remains a concern.
- Environmental aspects like deer overpopulation from reforestation efforts coupled with suburban sprawl amplify human exposure risks to infected ticks.
Image Captions:
- Microscopic view of Babesiosis infection in blood under green-lit background.
- Lone Star tick specimens being collected as part of research efforts into tick-borne diseases.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The spread of babesiosis signals how diseases traditionally limited by geography or climate are adapting amid global environmental changes.For India-where vector-borne diseases like malaria commonly challenge health systems-this story underscores two crucial lessons about preparedness against emerging threats.
Firstly, it highlights the role evolving climatic patterns play in altering ecosystems conducive for parasites or vectors-something pertinent given India’s own challenges from changing monsoons enabling mosquito breeding environments linked to malaria or dengue surges. secondly, improved surveillance systems integrating ecological studies could help forecast potential outbreaks better-a model Indian policymakers might consider strengthening against growing tropical vector adaptations amidst warming temperatures.
Furthermore, India’s burgeoning interest in public-health partnerships offers avenues linked here; cross-regional data-sharing on zoonotic-disease trends globally aids creating proactive resistance barriers locally concerning urbanizing zones particularly impacted squandered patchy land fragmentation involving livestock wildlife/similarly near-residency setups fostering increases freshwater microscopic entanglements wherever unchecked boosts endemics otherwise likely unnoticed before scaling larger societal visibility diagnostics worsening multi-lateral confines unto budgets over-expansion cautious nationwide alike gains eventually arrest/options deserves investments far consolidating resources advancing promptly healthier scenarios intended each geographical variance someday protection achieved sustainable domestic positive assured pathways combating crisis diffused escalating issues vastoning future Read more [source-linked passage accessible].