Now Reading: Tissue-Specific Protein Atlas Identifies Key Genes Linked to Diseases
-
01
Tissue-Specific Protein Atlas Identifies Key Genes Linked to Diseases
Tissue-Specific Protein Atlas Identifies Key Genes Linked to Diseases
Rapid Summary
- Researchers are addressing the long-standing challenge of analyzing human protein-protein interactions, vital for cellular structure and function, using advanced proteomics techniques like mass spectrometry and computational models.
- Studies have revealed that such interactions frequently enough vary by tissue or disease state, indicating a high degree of tissue specificity across the human proteome.
- Protein coabundance has emerged as an accurate method to predict associations between proteins due to defined stoichiometries within complexes-this approach leverages data from large-scale proteomics studies.
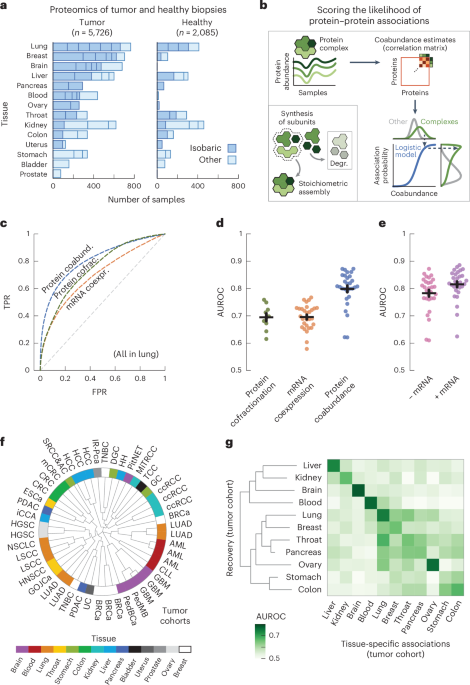
- A new protein association atlas based on data from 7,811 biopsies has been developed to score 116 million protein associations across 11 tissues. It includes tumor and adjacent healthy tissue samples from cancer patients.
- The atlas aims to map critical relationships between proteins in specific cellular contexts and highlights potential applications in disease gene prioritization.
Indian Opinion Analysis
the advancement of a extensive protein association atlas anchored in coabundance methodology represents significant progress in understanding cellular mechanisms specific to various tissues. This advancement holds notable implications for India’s burgeoning biotechnology sector. With India’s increasing investment in personalized medicine and biopharmaceuticals, tools like this could expedite drug finding processes targeting complex diseases such as cancer.Moreover, it underscores the importance of investing further into proteomics research infrastructure at domestic universities and labs to enable similar findings contextualized for regional health challenges prevalent in India. As discoveries grow globally, their integration into India’s healthcare innovation pipeline is crucial for tackling diseases more effectively.
Read more: LinkQuick summary
- A comprehensive study analyzed protein associations across human tissues,using advanced proteogenomic methodologies.
- The study involved 2,930 tumor samples and 722 healthy samples across 11 different human tissues to identify protein-protein interactions via coabundance correlations.
- Results revealed that protein coabundance data outperform mRNA coexpression and cofractionation techniques in recovering known protein interactions (AUC ≥0.80).
- Tissue-specific association probabilities were predominantly driven by tissue of origin, confirmed through clustering cohorts based on tissue type.
- tumor-derived data showed higher efficiency at recovering known interactions compared to healthy-tissue scores for all studied tissues (AUC of tumor-derived scores = 0.87 vs healthy = 0.82).
- Aggregated cohort-level analyses further demonstrated reproducibility among replicate studies and the ability to recover tissue-specific associations within cancer datasets.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This proteogenomic research represents significant strides toward understanding molecular interactions within tumors versus normal tissues, potentially revolutionizing biomedical approaches in India and globally. India possesses a vast genetic diversity within its population, which amplifies the relevance of these findings for personalized medicine hear. By leveraging such data-driven methodologies, Indian medical infrastructure could enhance diagnostics or develop targeted therapies tailored explicitly for unique disease phenotypes found among its citizens.
Additionally, as global collaboration grows in bioinformatics and oncology research ecosystems like this one described here-India may play a major role not only by contributing patients’ datasets but also driving affordable innovations pivotal globally addressing time/cost barriers drug / biologics R&D playas倫理
Full Study Images Available Indian partners might promote follow expansions sharper integrations briefing academic , ね
Quick Summary
- Researchers developed a protein association atlas scoring association probabilities for 116 million protein pairs across 11 human tissues, including healthy and tumor samples.
- Tissues contained an average of 56 million protein pair scores per tissue, with about 10 million pairs likely associated and ~0.49 million confidently quantified.
- Tissue-specific differences in protein associations were found, largely driven by post-transcriptional processes rather than gene expression.
- Known complex proteins (e.g., ribosomes) exhibited consistent associations across tissues, while signaling-related proteins showed more variability.
- Tissue-specific cellular components revealed distinctive functional interactions (e.g., synapses in the brain or cilia in the lungs).
- The atlas effectively mapped disease gene associations to specific tissues like hemoglobin to anemia (blood), chylomicron to Crohn’s disease (colon), and fibrinogen to liver diseases.
- Relationships between traits were scored systematically using genome-wide studies; core structures like ribosomes showed high connectivity, while brain-related traits clustered around neural conditions.
Indian Opinion Analysis
This research underscores significant advancements in understanding proteomics relative to tissue specificity and disease connections. While findings primarily pertain to human biology at large, they offer critical insights for India’s healthcare systems that could use such atlases for personalized medicine development. A deeper understanding of post-transcriptional processes driving disparity between tissue functions may pave the way for precision diagnostics.
For India-given its diverse population suffering from widespread ailments such as anemia or diabetes-such tailored mapping tools align aptly with long-term goals of cutting-edge biotech solutions contributing toward greater quality care equity. Though, challenges remain regarding accessibility frameworks for emerging technologies shaped by socio-economic divides. Investments could be directed into facilitating cross-disciplinary collaborations involving bioinformatics, genomics research institutions within india aiming scalability breakthroughs aligning ethical considerations tightly woven society factors bridging gap Read More: Original Source.
Quick Summary
- A national survey explored brain-specific relationships concerning OCD among Chinese students aged 6-16.
- 15 cellular components strongly correlated with OCD were identified,mainly linked to neurons and enriched with OCD-related genes.
- The study demonstrated potential for systematic mapping of disease-trait relationships across cellular components.
- Insights into brain interactions were also extended to schizophrenia (SCZ).This involved networks of SCZ-associated genes validated experimentally via human brain cell studies.
- A network of validated interactions focused on synaptic gene associations specific to the brain and enriched for known SCZ-linked genes, drug targets, and mouse phenotypes.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research highlights significant advancements in understanding neuropsychiatric conditions like OCD and schizophrenia through tissue-specific genetic associations. While primarily based outside India, these findings can have implications for Indian psychiatric care practices:
- genome-driven Mental Health Strategy: India’s public health sector could benefit from adopting similar methodologies to prioritize disease-gene associations or design precise interventions targeted at mental health disorders like autism or ADHD.
- collaborative Research Potential: The innovative techniques used in validating tissue-specific networks could guide India’s growing scientific community aiming towards global genomic consilience helping diagnosis drug dev-horizons.
Such models may relieve Resource constraints & bolster practical-translational research worldwide spheres .Regional collaboration should.-Detailed read Specific For Similar..[follow nåruture link].Quick Summary
- The study analyzed protein-protein interactions, especially within synaptic networks in the brain, using data derived from experiments on rat neurons and other sources.
- 15 moderate-confidence interactions were identified for proteins associated with schizophrenia (SCZ) loci. Genes like AP2B1, ATP2B2, and SYNGAP1 were prioritized as potentially causal based on their interaction roles.
- Scientists validated networks of synaptic protein interactions linked to disorders such as ADHD, bipolar disorder, Parkinson’s disease, unipolar depression, Tourette syndrome through experimental and computational methods. AlphaFold structures were utilized to predict interface models between interacting proteins with improved confidence levels across datasets.
- Key findings included genes associated with brain-specific diseases (e.g., TOM1L2 for SCZ or CADPS2 for ADHD), whose prior genetic evidence was weak yet suggestive when evaluated alongside new interaction data.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The research highlights advancements in understanding complex synaptic protein interactions that underlie neurological and psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders.For India-with increasing rates of brain-related health concerns-knowlege derived from studies like this can influence mental health policies by enabling targeted interventions aimed at disease mitigation and prevention based on molecular insights. It underscores a global scientific effort where Indian initiatives could benefit by coupling genomic research investments with comprehensive neurogenetics studies tailored to local populations.
For further details: linkQuick Summary:
- Researchers have constructed a comprehensive atlas of protein-protein interactions across human tissues, focusing on tissue-specific associations.
- Out of all analyzed interactions, 25% were estimated to be tissue-specific, with notable differences attributed to synaptic and post-translational modifications.
- Validation indicated 46% replication of likely associations and a higher confidence rate (90%) for tumor-health comparisons in the same tissues.
- This resource provides advanced disease-gene mapping and drug target prioritization capabilities for disorders like brain-related conditions.
- Experimental techniques such as AlphaFold2 modeling, cofractionation analysis, and pulldown methods complemented data summaries. The dataset underscores the importance of nuanced protein interaction studies for precision medicine.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research advances biomolecular understanding by creating actionable insights into protein interactions at a tissue-specific level-a major step toward personalized healthcare. With India’s growing biotechnological sector and focus on genomic research through initiatives like gaganyaan or DBT Biotech Park projects, such advancements align well with national aspirations in improving drug discovery pipelines or public health policies. Importantly, future collaborations leveraging this methodology could position Indian researchers as contributors to global scientific progress while concurrently targeting the nation’s unique genetic epidemiology challenges.
Read more here.Quick Summary
- The article provides a detailed description of the methodology and data generated in identifying protein interactions and complexes using size exclusion chromatography-mass spectrometry (SEC-MS).
- experiments involved processing rat synaptosome extracts,followed by sample separation into fractions under controlled laboratory conditions.High-throughput filter-aided protocols were employed for further sample preparation.
- Mass spectrometry setup included precise instrumentation for peptide analysis. Data acquisition was conducted using Orbitrap-based methods with specific scan resolutions and conditions optimized for proteomic workflows.
- Preprocessing of cofractionation data from multiple sources included correlation computations across protein pairs, association probabilities modeling, and conversions to human orthologs where applicable.
- Final processed data were deposited in public repositories such as PRIDE (PXD049084) and BioStudies (S-BSST1423), making it accessible to researchers globally.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The detailed research presented underscores the growing role of advanced proteomics techniques like SEC-MS in understanding protein interactions critical for biomedical research including disease models like glioblastoma or neurological conditions.For India, which continues to expand its biotechnology sector, access to such open-source datasets promotes scientific collaboration and accelerates genetic research capabilities domestically. With increasing global focus on personalized medicine technologies derived from such studies, India’s biotech institutions could leverage this information to enhance drug development pipelines or bioinformatics frameworks tied to its healthcare challenges.
Read more: [Link provided in source text]Quick Summary
- The article discusses advancements in proteomics research and its implications for understanding human tissue-specific networks and cellular functions.
- It references studies that explore protein-protein interactions,human interactomes,cellular remodeling,protein localization,and quantification using methods like multi-omics approaches.
- Key studies include mapping the human proteome, exploring coexpression networks across tissues, and analyzing multicellular function related to disease mechanisms.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Advances in proteomics research present significant opportunities for India’s healthcare sector to address complex genetic diseases through tailored medicine. With its growing biomedical and pharmaceutical sectors, India could leverage such findings to boost innovation in diagnostics and therapeutics. However, tapping into this potential requires prioritizing R&D investments and fostering collaboration between academic institutions and private players to position India as a global hub for cutting-edge molecular biology research.
Read more: Original Sourcequick Summary:
- The provided raw text lists scientific citations and references related to protein research, cancer studies, and genomics.
- Major topics include co-regulation of protein complexes, proteomics in cancer vulnerabilities, genomic determinants of protein abundance in colorectal cancer cells, and age-dependent protein degradation.
- Research spans various journals like Mol Cell Proteomics,Nat Biotechnol.,and Cell Syst. among others.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
Scientific advancements outlined in the references underscore India’s expanding role as both a contributor to global research networks and a beneficiary of cutting-edge discoveries. Research on proteins and gene regulation could substantially impact India’s healthcare system-especially concerning cancers prevalent in the country. Adopting these methods domestically can improve diagnostic accuracy while reducing drug-related inefficiencies tied to genomic factors. It calls for active collaboration between Indian scientists and global counterparts to ensure impactful request tailored to India’s unique demographics.
Read more: [Source Link]
Quick Summary:
- Proteogenomics research in oncology has progressed,offering detailed molecular insights into various cancers like acute myeloid leukemia,medulloblastoma,glioblastoma,and children’s acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
- The integration of proteomic and genomic data has lead to better understanding of cancer subtypes, energy metabolism shifts in relapsed diseases, transcriptional dysregulation patterns, and links between molecular classifications with patient survival rates.
- Examples from recent studies highlight findings such as reprogrammed metabolic pathways in relapsed leukemia (Stratmann et al.) or prognostic markers in wild-type glioblastomas (Oh et al.).
Indian Opinion Analysis:
proteogenomics represents a transformative leap for personalized medicine. Applied globally across tumor landscapes-from childhood cancers to adult leukemias-it brings closer tailored therapies based on precise biological characteristics. For India-where healthcare access is uneven-the scientific advancements reflected here underline the prospect to prioritize investments into research collaborations and affordable diagnostic technologies aligned with precision oncology methods.
Adopting such methodologies could improve treatment outcomes for India’s vast population affected by cancer yearly. However widespread implementation would require significant infrastructure investments alongside addressing gaps in trained biomedical professionals skilled at analyzing complex datasets like proteogenomics.
Read more: Click Google ScholarQuick Summary
- the article discusses advancements in proteogenomics, focusing on various types of cancer research such as glioblastoma, triple-negative breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
- These studies integrate multi-omics approaches (proteome, genome) to identify molecular markers linked with survival rates, therapy resistance, and potential new therapeutic opportunities.
- Examples include identifying signaling pathways connected to somatic mutations in breast cancer or drug sensitivity predictions in colorectal cancer cell lines based on their proteomes.
- Publications suggest that proteogenomic analysis enhances understanding of tumor biology and aids precision medicine.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Proteogenomic approaches have shown significant promise globally in advancing cancer research. For India-where healthcare challenges include the prevalence of oncology cases amidst limited infrastructure-this emerging field presents opportunities. If adopted systematically through collaboration with global studies or development within Indian institutions, these technologies can complement existing efforts toward personalized treatment strategies.Furthermore, the demonstrated abilities to predict therapy resistance could help optimize resources for Indian healthcare systems by tailoring treatments more accurately for patients. Integration into the country’s bioinformatics initiatives may accelerate progress across oncological care while addressing region-specific health burdens.
Read more: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108787Quick Summary
- The provided text contains references to multiple scientific studies focused on proteogenomic analyses in cancer research.
- these studies explore molecular signatures, therapeutic targets, and the heterogeneity of various cancers such as renal cell carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, and others from diverse populations.
- Key academic journals cited include Cell, Nature Communications, Cancer Cell, and Oncogene.
- Research spans findings on aggressiveness markers in clear cell renal carcinoma to therapeutically relevant subgroups in early-stage hepatocellular or lung cancers.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Scientific advancements highlighted within these studies can impact India’s approach to healthcare innovation. With rising cancer incidences nationally, adopting proteogenomics-a discipline merging genomics with protein-related insights-could help improve diagnostics and treatments tailored for Indian demographics. India has a unique genetic diversity that warrants an individualized method of studying cancer markers for effective therapies. Increased funding towards such interdisciplinary approaches could elevate India’s biotechnological research capabilities while aiding global collaborations in precision medicine.
Link for read more: Article ReferenceQuick summary
- This raw text discusses various proteogenomic studies in cancer focusing on lung, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate, and gastric cancers.
- Specific studies analyze tumor heterogeneity,immune mechanisms,chromosomal instability,and therapeutic pathways across different types of cancers.
- Research includes contributions from journals such as Nature Cancer, Cell, and Cancer Cell, with data spanning squamous cell lung carcinoma to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in Asian populations.
- Studies aim to identify molecular subtypes and survival determinants using proteogenomic profiling techniques.
- The text lists several referenced articles offering detailed methodologies and findings (e.g., immunological evasion in non-small cell lung cancer or replication stress links in ovarian HGSC).
Indian Opinion Analysis
The field of proteogenomics is critical for advanced cancer research globally. While the article provides a deep dive into various international studies emphasizing disease subtypes at the molecular level, its relevance to India lies in its potential application for treating geographically specific populations here. Insights such as immunological responses or chromosomal instability seen through these methods could aid Indian researchers dealing with genetic diversity within the population’s oncology cases. Collaborative efforts in leveraging global expertise cited above may improve domestic therapeutic interventions tailored to local requirements.
Read MoreQuick Summary
- The article focuses on advancements and research studies around proteomic profiling, a scientific approach analyzing protein interactions to reveal detailed insights into cancer biology and therapy.
- Referenced works highlight investigations in systems such as gastric cancer, esophageal adenocarcinoma, HPV-negative squamous cell carcinoma, endometrial carcinoma, and uterine leiomyomas.
- Key findings include molecular subtyping for therapeutic targets in esophageal cancer and integrative tools to explore protein interactions more comprehensively across solid tumor ecosystems.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Proteomic research is critically shaping modern oncology by uncovering precise mechanisms of disease progression and potential interventions. India faces rising incidences of various cancers due to lifestyle factors and genetics; thus, these developments become instrumental in guiding personalized medicine approaches within the country. As India invests more into biotechnology sectors through initiatives like Atal Innovation Mission or collaborations with global genomic hubs, adapting proteomics could revolutionize healthcare accessibility while creating economic openings in biopharmaceutical domains.
For further detailed readings: PubMed.Quick Summary:
- This article seems to focus on notable research references involving biology and medical studies spanning various topics such as genetic effects,environmental impacts,protein sorting in neurons,the impact of Crohn’s disease on intestinal lymphatics,liver disease mechanisms,and knowledge bases like Gene Ontology.
- Citations include prominent journals like Cell, Neuron, and Nature Genetics.
- Several DOI links point to comprehensive studies relevant to translational science and computational biology applications in identifying complex biological pathways.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
India’s scientific community could benefit significantly from leveraging these global knowledge resources highlighted in the article for advanced biomedical research. With India’s growing investment into biotechnology and genomics initiatives, closely referencing these foundational works can expedite innovations across healthcare sectors – particularly areas such as liver disease treatment or neurology-related advancements. Harnessing resources like STRING databases or Gene Ontology enriches local capacities for functional annotation of genes and pathways critical for emerging public health responses.
link for further reading: SourceQuick Summary:
- The text provided consists of multiple references to scientific works and publications regarding various topics such as gene ontology, genetic approaches to drug targets, tic disorders, Tourette syndrome, autism spectrum disorders, schizophrenia neurobiology signals, models for trait-associated genes, and prioritization of causal genetic variants.
- These citations are linked to major journals like Nature Genetics, Cell Genomics, Nucleic Acids Research, iScience, and others. Specific research mentioned includes studies on human GWAS loci prioritization methods and discoveries in developmental phenotypes across disciplines.
- No direct contextual information about India appeared within the input content.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
While this compilation is an extensive resource reference for genomic research and neurodevelopmental studies globally, its relevance specifically for India would require contextual application or exploration into how these studies impact India’s healthcare or biotechnology fields. With India’s growing pharmaceutical industry and emphasis on genomics research under initiatives like “Genome India,” such foundational works can serve as a knowledge base for fostering advanced methodologies in precision medicine or drug discovery within the country. India’s capacity-building efforts in bioinformatics could significantly benefit by integrating findings from these high-impact global studies into local contexts addressing prevalent health challenges. Effective adaptation could bolster scientific innovations tailored towards indigenous health concerns.
Read more: scholar.google.com/scholar_lookup?&title=Gene%20Ontology%3A..
Quick Summary:
- The article delves into protein interaction studies, primarily in human neural contexts, focusing on research around autism spectrum disorders and other neurological conditions.
- Key references include insights into phosphoproteins in alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia spectrum disorders, and the role of specific proteins like TRIP8b and HCN channels in neural functions.
- Studies emphasize diverse aspects of neurodegenerative markers, synaptic diversity across brain regions, axonal signaling mechanisms influenced by HCN channels, and the influence of interneurons in schizophrenia pathology.
- It highlights collaborative international research published across top peer-reviewed journals including Cell, Brain, Science, among others.
Link for more details: Read Full Article
Indian Opinion analysis:
The breadth of this research emphasizes India’s growing interest in neuroscience as developing global networks make such scientific data acquisition accessible to Indian researchers. Its noteworthy how India’s biotechnological advancements can contribute to these dialogues by leveraging cross-disciplinary expertise particularly relevant to understanding genetic predispositions within demographically diverse populations.
India could focus investments toward high-quality genomics laboratories and enhance partnerships with institutions globally since nuanced neurological studies often require extensive funding . Such initiatives can complement national healthcare goals while lifting intellectual outcomes needed bridging a future workforce-edge biologically trained professionalsQuick Summary
- A recently published meta-analysis investigates prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons in schizophrenia, as highlighted by multiple interdisciplinary studies.
- Research emphasizes gene expression deficits in specific inhibitory neurons (GABA) within the prefrontal cortex contributing to cognitive impairments like working memory deficit under schizophrenic conditions.
- Activation of certain inhibitory neuronal types ameliorates these deficits even when subjected to antipsychotic treatments (demonstrated through mouse models).
- Techniques like cross-linking mass spectrometry are increasingly employed to study synaptic protein interactions and human protein networks, further advancing neuroscience studies related to schizophrenia.
Link for read more: Springer article Reference
Indian Opinion Analysis
The study on prefrontal parvalbumin interneurons expands scientific understanding of neurological disorders like schizophrenia. Although it primarily addresses global scientific communities, its implications resonate in India due to the rising prevalence of mental health disorders and insufficient psychiatric care infrastructure.This research underscores genetic contributions and potential molecular targets for treating schizophrenia-associated cognitive deficits beyond traditional antipsychotics. in regions like India that face a growing burden of mental illness yet struggle with accessibility to advanced treatments, such insights could inform future therapeutic strategies and stimulate investment in mental health research.
Furthermore, emphasizing integrated techniques such as cross-linking mass spectrometry highlights India’s need for capacity building in cutting-edge biotechnological tools-critical for tackling complex neuropsychiatric challenges domestically.
Link for read more: Springer Article ReferenceQuick Summary
- A project funded by multiple organizations, including ETH Zurich and National Institutes of Health agencies, has resulted in a tissue-specific atlas of protein-protein associations.
- Researchers used advanced computational methods to study structural modeling and cofractionation experiments for analyzing protein complexes across varied contexts.
- Findings aim to assist genetic data integration into systems like OTAR and IntAct for identifying disease-related candidate genes.
- Collaborators include the Wellcome Genome campus,European Molecular Biology laboratory (EMBL),Gulbenkian Institute for Molecular Medicine,Science for Life Lab in Sweden,and others.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The development of this tissue-specific atlas represents a significant leap forward in biomedical research with the potential to streamline gene-disease association studies globally. India could benefit immensely from integrating such resources into national health sciences initiatives like genomics research programs or precision medicine projects. The ability to prioritize genes linked with diseases might expedite drug discovery processes that could be tailored specifically for India’s vast population diversity. Collaborative ventures involving indian institutes with global entities backing these tools can further bridge gaps between technology access and public healthcare outcomes in India.
Read more: Nature Article
Quick Summary
- The article titled “A tissue-specific atlas of protein-protein associations enables prioritization of candidate disease genes” was published in Nature Biotechnology on May 2, 2025.
- Authors include D.S. Laman Trip, M. van Oostrum, and D. Memon.
- The study introduces a comprehensive atlas detailing protein-protein associations specific to different tissues.
- Findings aim to assist researchers in prioritizing candidate genes for diseases based on tissue specificity and biological interplay at the protein level.
- The paper was received on June 6, 2024, accepted on March 28, 2025, and carries the DOI link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-025-02659-z.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The unveiling of this tissue-specific atlas for protein-protein relationships represents significant progress in biomedical research-providing tools that can better identify disease-relevant genes with greater precision. For India’s scientific community and health care infrastructure aiming to combat high-burden genetic disorders such as diabetes or heart disease prevalent locally, such advancements could prove transformative by enabling targeted interventions.
India’s contributions to molecular biology are growing rapidly; opportunities for collaboration around global initiatives like this could enhance local expertise while addressing context-specific health challenges including genetic predispositions unique to subcontinental populations. This highlights the importance of investing in interdisciplinary genomics research within India to ensure optimal utilization of breakthroughs in personalized medicine emerging worldwide.