Now Reading: Transformer Coils Stolen Near Jolarpet, Disrupting Power Supply
-
01
Transformer Coils Stolen Near Jolarpet, Disrupting Power Supply
Transformer Coils Stolen Near Jolarpet, Disrupting Power Supply

Quick Summary
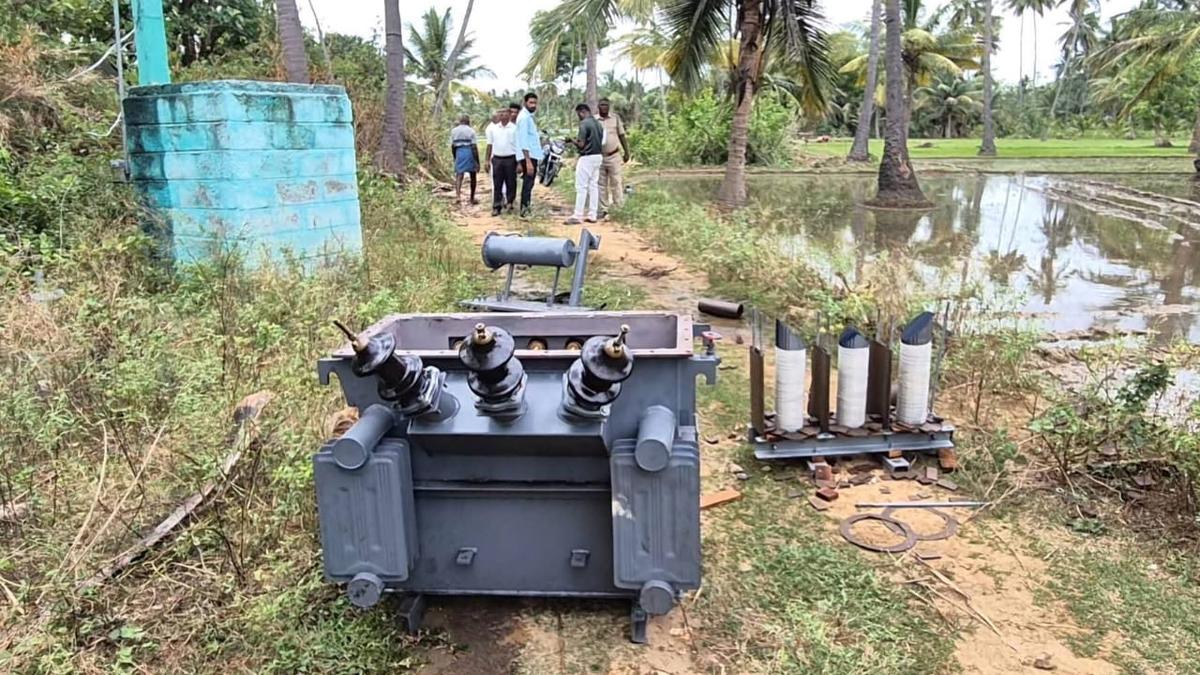
- Copper coils were stolen from a 250 KV electricity transformer at Alasandapuram village near Jolarpet town, Tirupattur, on Friday.
- farmers discovered teh dismantled transformer early in the morning,with copper coils and wires missing.
- Thimmampet police and Tangedco officials inspected the site; surveillance has as been increased in Ambur area with 175 domestic-use transformers.
- Approximately 10-15 kg of copper coils were stolen, valued at ₹50-60 per kilogram in the open market.
- the transformer supplied water pumped via Tamil Nadu Water Supply and Drainage (TWAD) to villages in Jolarpet panchayat union. This theft disrupted daily water supply of 3-4 MLD amid reliance on TWAD due to a dry Palar river.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The theft of essential infrastructure components like copper from transformers highlights vulnerabilities within India’s rural infrastructure network. Such incidents not only affect power supply but also disrupt vital services such as water distribution-a lifeline for communities relying on external supply systems like TWAD amid broader environmental challenges such as resource scarcity (e.g., dry rivers). Increasing surveillance near critical assets is an immediate mitigation measure, but systemic efforts are required to deter such acts through improved security protocols and stricter legislation governing scrap sales markets that facilitate illicit transactions.
It underscores larger concerns about protecting India’s essential service delivery mechanisms for underserved regions while balancing economic incentives for crime prevention efforts.
For detailed reading on this issue: Click Here