Now Reading: Understanding Aerodynamics: A Beginner’s Guide for Grades K-4
-
01
Understanding Aerodynamics: A Beginner’s Guide for Grades K-4
Understanding Aerodynamics: A Beginner’s Guide for Grades K-4
Rapid Summary
- Definition of Aerodynamics: Aerodynamics is the study of how air moves around objects like airplanes,rockets,kites,cars,etc., helping explain flight mechanics.
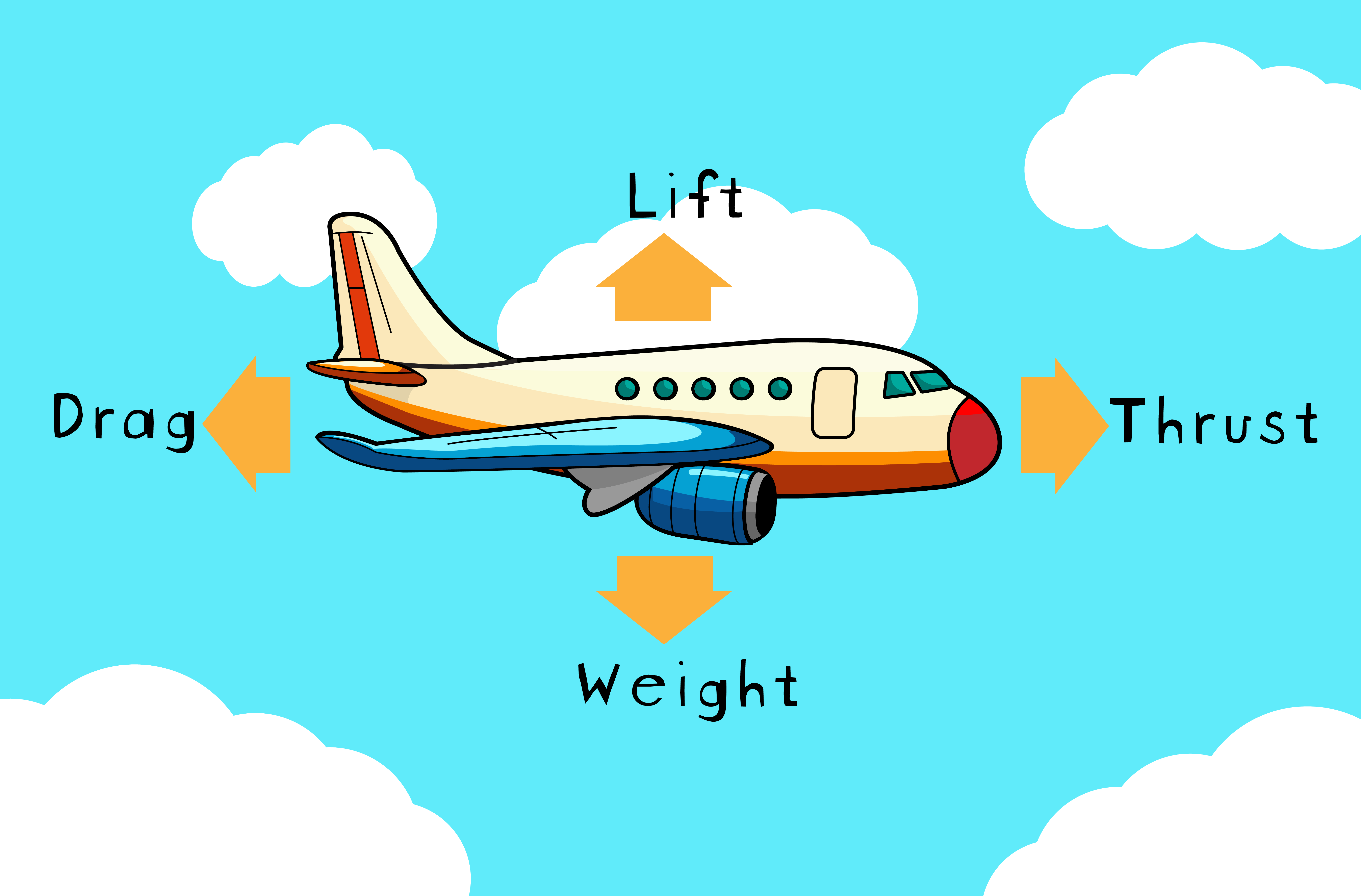
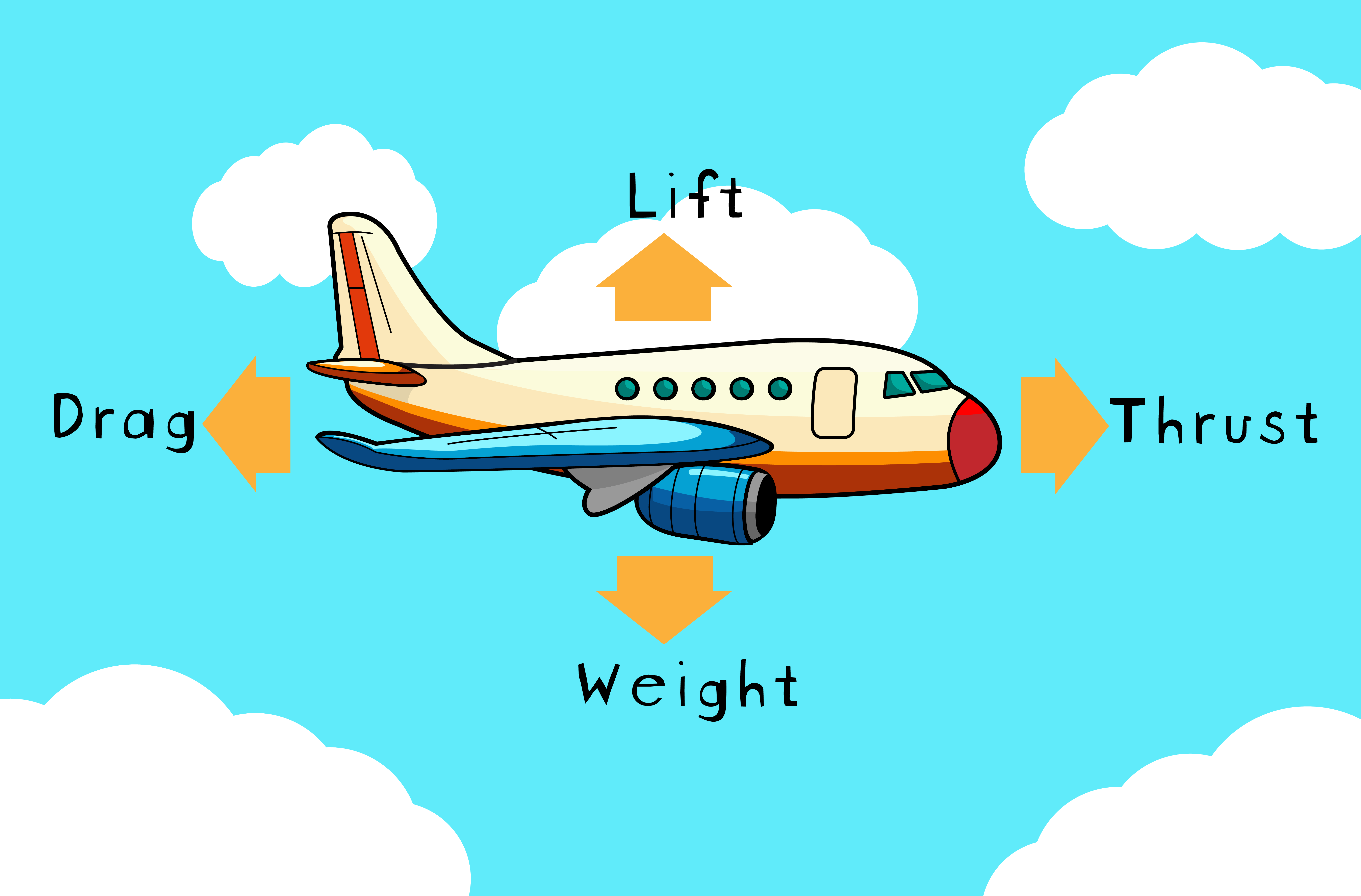
- Four Forces of Flight:
– Lift: The upward force that opposes weight. Aircraft wings and hot air balloons create lift using techniques based on shape and pressure differences.
– Weight: The downward pull from gravity; objects need upward push to counter it for flying.
– Drag: A force slowing down motion; influenced by object shape (round/narrow surfaces create less drag).
– Thrust: The forward-moving force opposing drag; produced by engines or propellers in planes to maintain motion.
- An airplane’s wing shape (curved top and flatter bottom) creates pressure differences allowing lift. Similar principles apply to helicopters, kites, sailboats.
Indian Opinion Analysis
aerodynamics plays a pivotal role in modern engineering applications essential for both civilian and defense industries. India’s active investment in aerospace technology aligns well with these principles-whether through ISRO’s space exploration programs or advancements in aircraft manufacturing. By understanding forces like thrust and drag more deeply, efforts can be directed toward energy-efficient designs for aviation or innovative technologies in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which hold importance for India’s logistics and national security interests.Additionally, India’s rapidly urbanizing transportation networks stand to benefit from aerodynamic optimizations across automotive design-reducing fuel consumption while promoting sustainability goals amid climate commitments. Thus, fostering foundational knowledge on subjects like aerodynamics could play a key role not only within academia but also shaping future indigenous technological breakthroughs.