Now Reading: Understanding Aerodynamics: A Guide for Students (Grades 5-8)
-
01
Understanding Aerodynamics: A Guide for Students (Grades 5-8)
Understanding Aerodynamics: A Guide for Students (Grades 5-8)
Swift Summary
- Aerodynamics: The science of how objects move through air, influencing the movement of rockets, kites, airplanes, and cars.
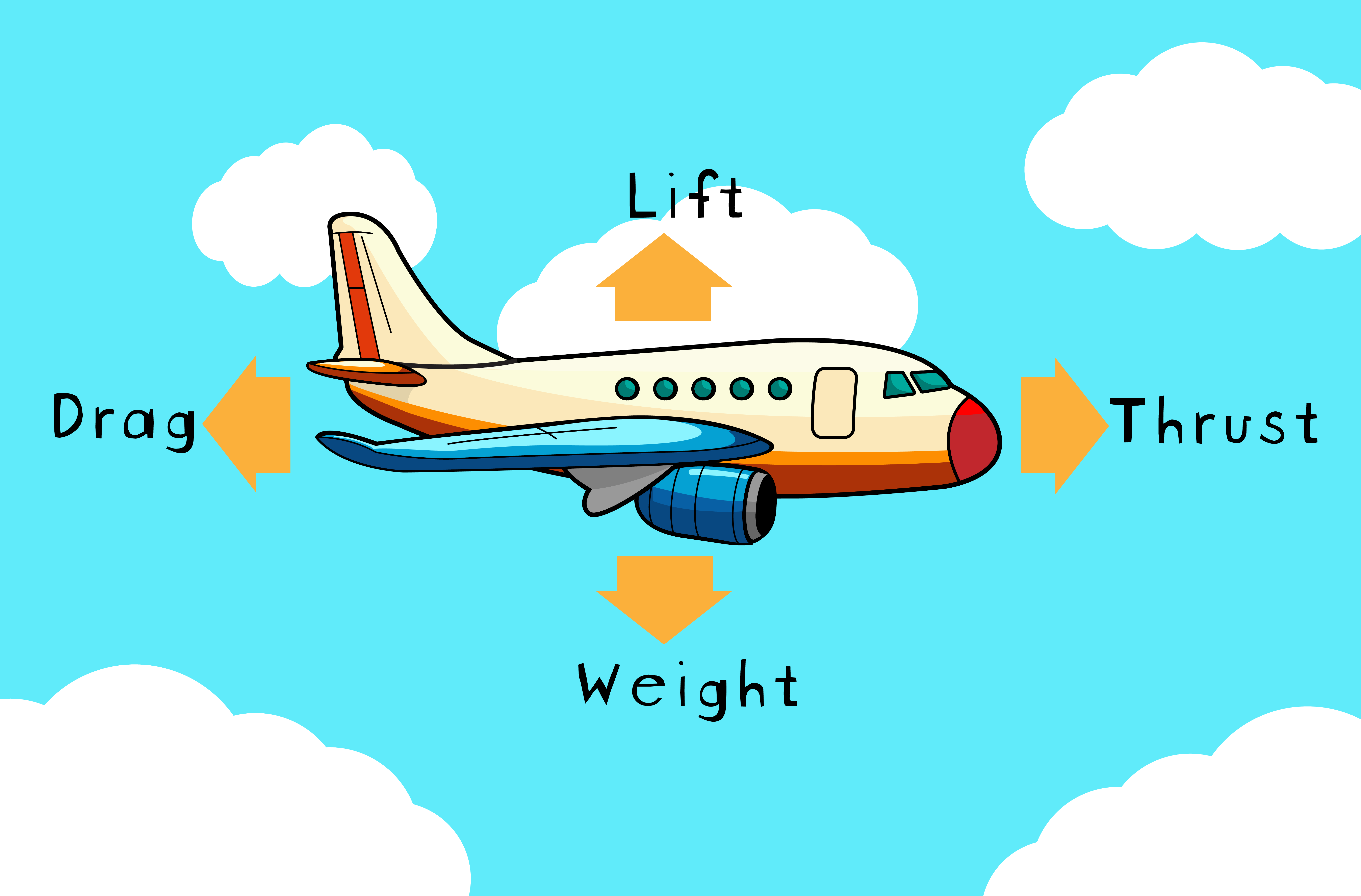
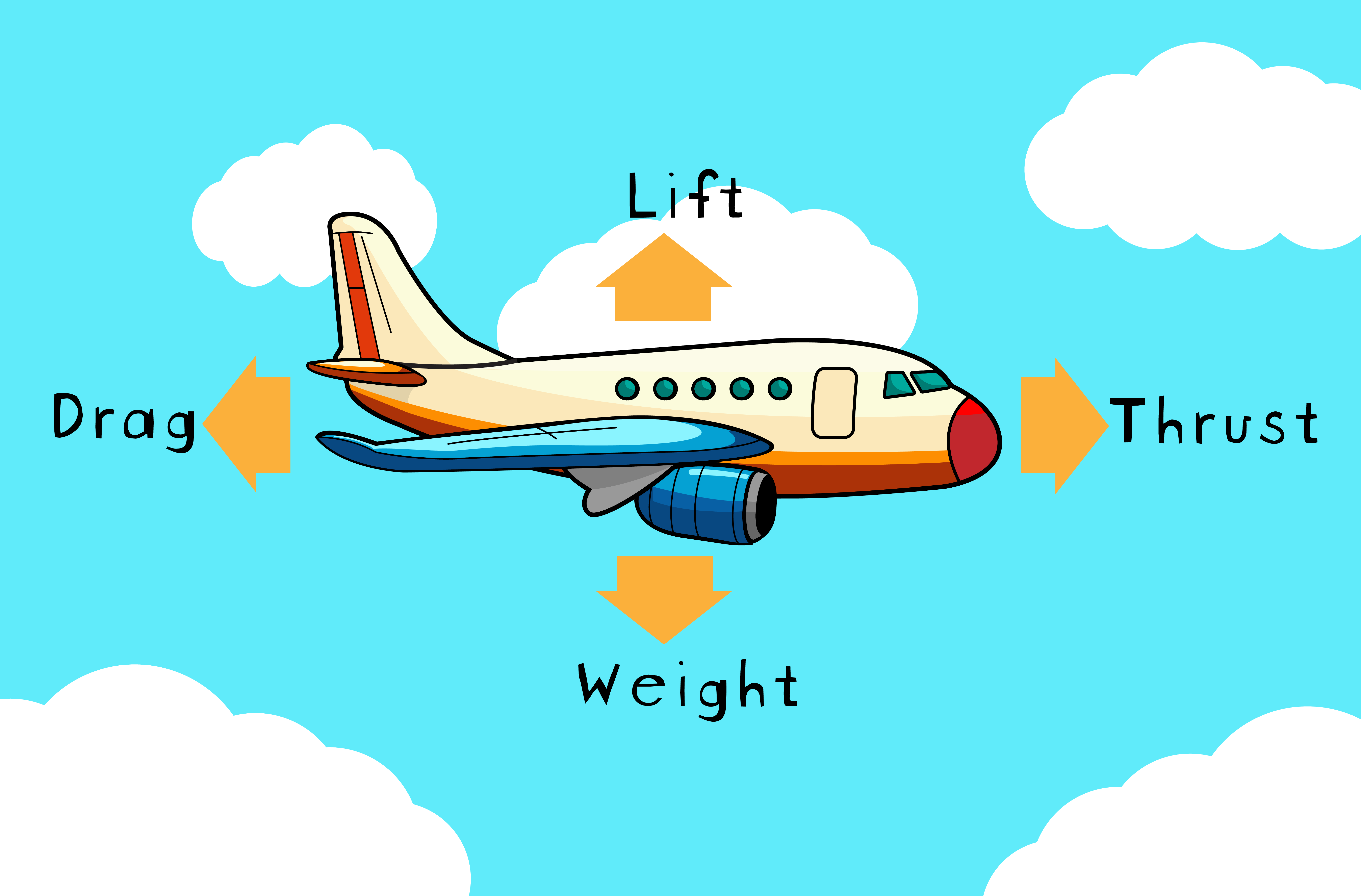
- Four Forces of Flight:
– Lift: Opposes weight; enables upward movement. Wing shape creates lift through air pressure differences.
– Weight: Downward force derived from gravity and mass; must be overcome by lift for flight.- Thrust: Opposes drag; propels forward motion in aircraft via propellers or jet engines.
– Drag: Creates resistance against movement; depends on object shape and surface area exposed to air.
- Various applications include hot-air balloons (lift from lighter hot air), helicopters (rotor blades creating lift), sailboats (curved sails mimicking wing shapes), and gliders relying on momentum to counter drag temporarily.
- NASA emphasizes aerodynamics in its aeronautics research. It facilitates improved aircraft designs and assists planetary missions by adapting aerodynamic principles in diverse atmospheres like Mars.
Indian Opinion Analysis
Aerodynamics plays a meaningful role not only in aviation but also across industries such as automotive design, space exploration, and renewable energy. For India-a nation advancing rapidly in aerospace technology-understanding aerodynamic principles can greatly influence innovation. As efforts like ISRO’s Mars orbiter Mission highlight India’s expertise with cross-atmospheric engineering challenges, continued research on aerodynamics offers benefits such as efficient aircraft designs and space probe performance improvements.
Moreover, this foundational knowledge promotes STEM education among younger generations. encouraging students to engage with thes concepts may inspire future careers critical to leading global advancements while addressing regional development goals like improved transportation systems or sustainable energy solutions through wind turbines.
India stands poised to leverage aeronautical insights both domestically-through sectors such as defense-and globally via partnerships exploring next-generation applications for planetary exploration.