Now Reading: Unraveling the Mystery of the Curious Butterfly
-
01
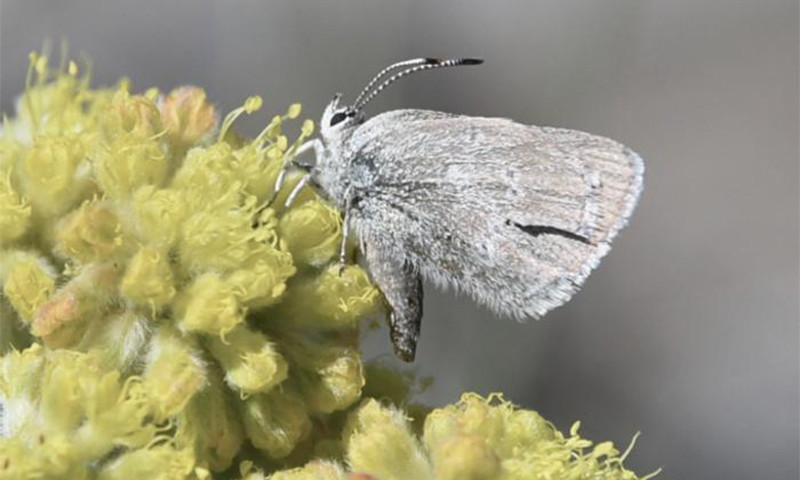
Unraveling the Mystery of the Curious Butterfly
Unraveling the Mystery of the Curious Butterfly

Speedy Summary:
- Revelation of New Butterfly Species: A newly designated butterfly species, Satyrium curiosolus (Curiously Isolated Hairstreak), was discovered in Waterton Lakes National Park, Canada.
- Ecological History: The species has been genetically isolated for approximately 40,000 years with no crossbreeding and has sustained a small population of around 1,000-2,000 individuals through inbreeding and resilience to climate variations.
- Wildfire Impact: A major wildfire in 2017 destroyed over half of its habitat but the population rebounded naturally without human intervention.
- Scientific Efforts: Genome sequencing established the butterfly’s unique evolutionary trajectory and its hermetic history within Blakiston Fan-a geographically confined alluvial region with mild microclimates acting as a refuge during ancient climate shifts like ice ages.
- Comparison to Other Species: Similar genetic adaptations were noted in cheetahs that endured population bottlenecks.Surviving offspring from such communities tend to be highly niche-adapted.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
The discovery highlights broader ecological insights relevant even beyond Canadian borders-such as how isolated populations can endure environmental disruptions and genetic challenges over millennia through adaptation mechanisms like genetic purging. For India, known for its rich biodiversity and clustered endemic species (e.g., Western Ghats or Himalayan ecosystems), this research underscores the importance of protecting localized habitats amidst climate change threats and anthropogenic pressures like deforestation. Lessons from Satyrium curiosolus could inform future conservation strategies vital to safeguarding India’s unique flora and fauna while balancing development goals sustainably.