Now Reading: Unveiling the Hidden Struggles Behind Rose Cultivation
-
01
Unveiling the Hidden Struggles Behind Rose Cultivation
Unveiling the Hidden Struggles Behind Rose Cultivation

Swift Summary
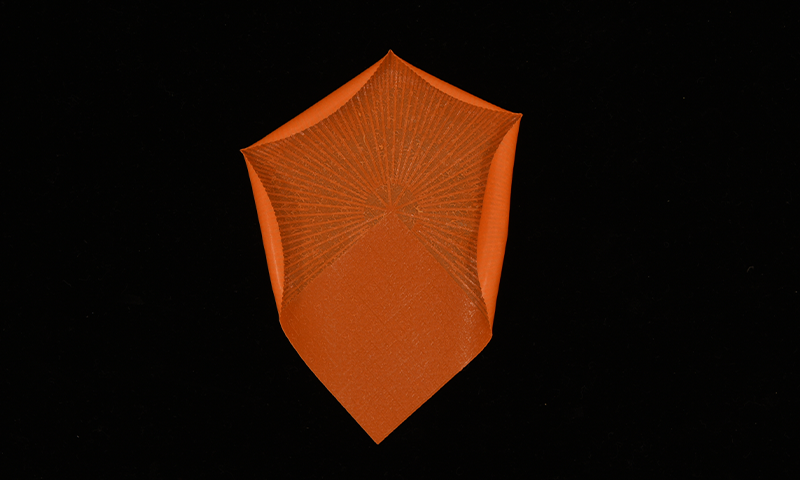
- Scientists have discovered the unique geometric mechanism behind rose petals’ iconic shape.
- Typical plant forms arise due to uneven tissue growth driven by Gauss incompatibility, causing ruffled shapes.
- Rose petals break the Mainardi-Codazzi-Peterson condition, which leads to concentrated stress at petal cusps during growth.
- these stresses result in smooth curves evolving into sharp polygonal edges on rose petals.
- Research methods included cutting actual rose petals, creating faux plastic models, and running computer simulations to test these findings.
- The study suggests that insights into these forces could be applied to developing self-morphing materials for robotics and spaceships.
Indian Opinion analysis
This research deepens our understanding of natural design principles and their underlying physics. For India, a country rich in biodiversity and botanical studies-especially with roses being culturally meaningful-this study opens avenues for progressive scientific exploration. It aligns well with India’s emphasis on leveraging natural phenomena for advancements in technology via programs like ISRO’s space missions or indigenous robotics initiatives. moreover,exploring applications of geometric frustration seen hear could enhance technological innovations tied to environment-amiable designs or adaptive engineering solutions suited for future challenges.