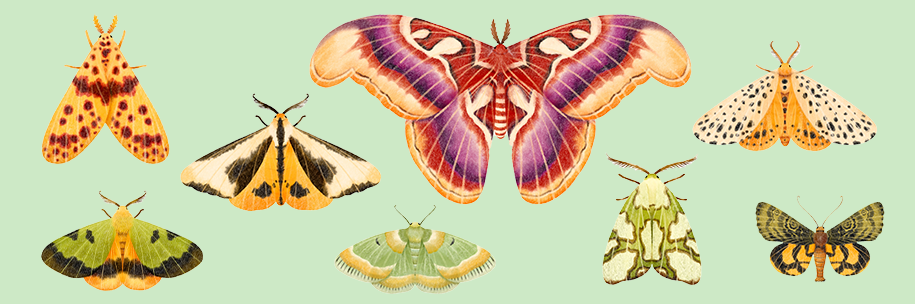
Now Reading: Unveiling the Hidden World of Moths
-
01
Unveiling the Hidden World of Moths
Unveiling the Hidden World of Moths
Swift Summary:
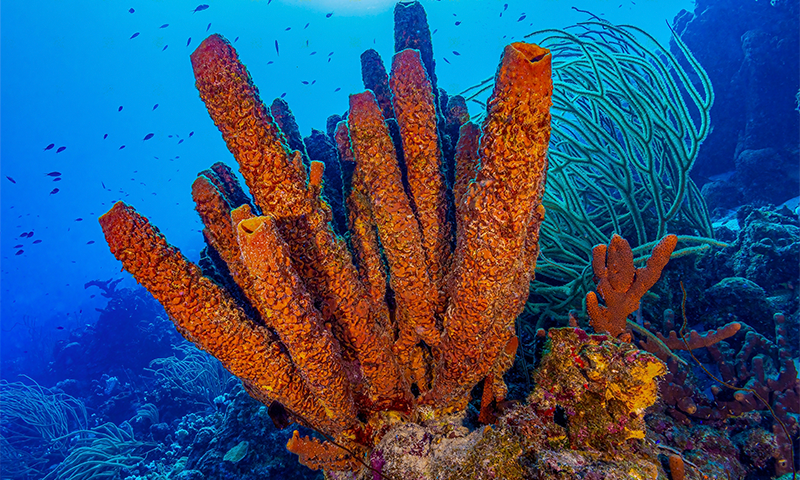
- Moths, often overlooked as pollinators compared to bees adn butterflies, play a pivotal role in supporting ecosystems and crop production.
- A recent global meta-analysis indicates moths contribute significantly to the reproduction of many plant species, equaling or surpassing daytime pollinators in some cases.
- Moth diversity far exceeds that of bees or butterflies, with over 123,000 species documented globally. They aid in pollinating crucial food crops such as apples and avocados.
- However, moths face threats due to habitat loss, pesticides (including nighttime spraying which impacts nocturnal insects), climate change, invasive species depletion, and light pollution. Human activities drive a global annual decline of insect populations by 1-2%.
- Genetic sequencing tools now help researchers identify plants visited by moths via analyzing pollen on their proboscis without extensive captures-offering data for conservation strategies focused on nocturnal species preservation.
- Conservation efforts recommended include planting native flora for nectar resources and minimizing light pollution through timers or motion sensors.
Indian Opinion Analysis:
This research underscores the need for scientific discourse in India’s sustainability agenda to expand beyond familiar pollinators like bees toward lesser-recognized ones like moths-a crucial step given the nation’s agricultural reliance on biodiversity-driven systems. Moths’ vital roles in crops such as soybeans underscore India-specific implications across rural economies dependent heavily upon natural resilience ensuring food security yet widespread monoculture farming-afeerction . Protecting invisible biological is broader.. Ideas.repeat tech innovations-value emerging genetic analysis ensurenatural The challenged_depth proactive stages amidst fragile consistency insects nested resilent growultural adaptive practical esencia public ongoing learn-usefulness holisticكة!