Now Reading: Water Crisis Threatens Lives Across India, Pakistan, Nepal Amid Sharp Decline
-
01
Water Crisis Threatens Lives Across India, Pakistan, Nepal Amid Sharp Decline
Water Crisis Threatens Lives Across India, Pakistan, Nepal Amid Sharp Decline

Speedy Summary
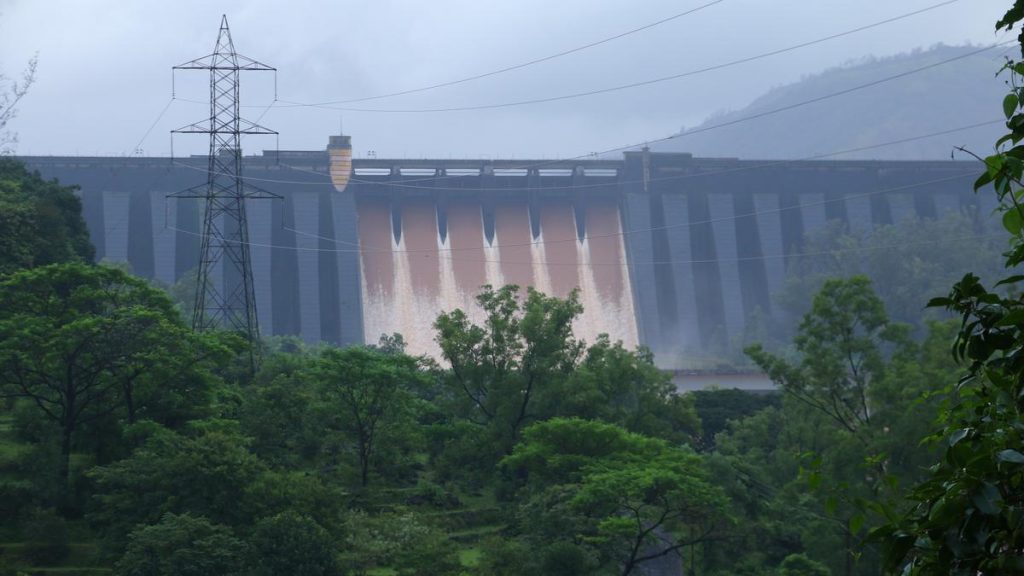
- A report by ICIMOD highlights record-low snow levels in the Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region, with snow persistence 23.6% below normal in 2025-the lowest in 23 years.
- This is the third consecutive year of below-normal snow levels, threatening water availability for nearly two billion people in india and neighboring countries.
- melting snow plays a crucial role as a water source for rivers during dry months, supporting farming, drinking needs, and hydropower.
- Snow reduction was reported across all 12 major river basins of the HKH region:
– Ganges basin: Lowest level in over 20 years; snow persisted at 24.1% below normal.
– Brahmaputra basin: Snow persistence down by 27.9%.
– Indus basin: Experienced a decline of 16%.
– Mekong and Salween basins where hardest hit, with drops exceeding 48%.
- Rising carbon emissions are identified as a contributing factor. Experts urge regional cooperation and science-based policies to address challenges.
- Potential risks include heightened water shortages, increased reliance on groundwater sources, and greater vulnerability to drought.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The findings from ICIMOD underline an urgent environmental concern for India’s water security scenario. The meaningful drop in snow persistence directly impacts critical river systems such as the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus-key lifelines that sustain agriculture-based livelihoods for millions across northern India. Reduced snowfall not only threatens summer irrigation but also pressurizes limited groundwater reserves already under strain.
the attribution to rising carbon emissions advocates an accelerated need for climate-resilient policies both domestically and jointly within the HKH region nations like Nepal or Pakistan that share these interconnected watersheds. Scientific insights into regional hydrology underscore solutions like improved drought response frameworks or more efficient agricultural practices-but implementation requires coordination amidst data gaps and fragmented governance structures.
While individual river basins will demand tailored strategies based on local challenges (e.g.,hydropower versus drinking supply),broader systemic alignment underpinned by actionable targets can mitigate cascading risks like food insecurity or energy shortfalls if future trends persist similarly grim trajectories.
India has much at stake given its demographic dependence conflicting pressures make overdue reforms imperative ensure long-term outcomes sustainable actionable particularly rural agrarian areas mitigating recurring externalities-driven shocks .