Now Reading: World’s Rarest Penguins Thrive in Unexpected Heat
-
01
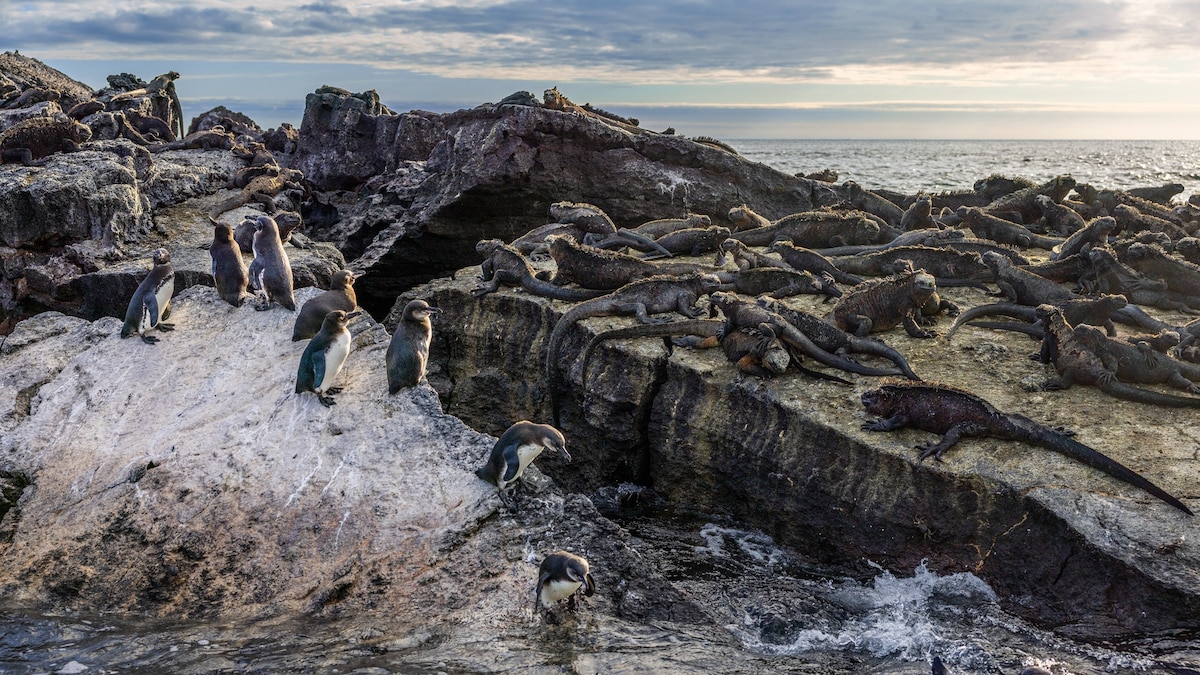
World’s Rarest Penguins Thrive in Unexpected Heat
World’s Rarest Penguins Thrive in Unexpected Heat

Speedy Summary
- Species: The Galápagos penguins are among the smallest and rarest penguins in the world, being the only ones living at the Equator.
- Conservation Efforts: Led by Dee Boersma, researchers monitor colonies to assess health and population trends.Challenges include warming temperatures, introduced predators (rats/cats), habitat destruction, pollution, and fluctuating food supply due to El Niño/La Niña cycles.
- Current Population: approximately 2,000 individuals remain-less than half of what existed 50 years ago.
- threats Addressed:
– Rodenticide programs are underway to eradicate invasive species on floreana Island for safer nesting sites.
– Artificial nests have been designed to supplement natural shaded breeding spaces previously lost due to erosion or environmental pressures.
- Key Adaptations:
– Unique ability to molt and breed based on nutrient availability rather than fixed seasonal cycles.
– Body temperature regulation methods such as panting and standing with flippers outspread help them survive in warmer climates.Read more here.
Indian Opinion Analysis
The conservation efforts for Galápagos penguins hold meaningful lessons for India’s environmental strategies. Similar challenges-climate change effects such as erratic weather patterns disrupting ecosystems, invasive species threatening native biodiversity-are faced by many endangered species within India.The meticulous monitoring methods employed by Dee Boersma’s team demonstrate proactive intervention through scientific research combined with tangible action plans like artificial habitats or eradication of ecological threats.
India’s varied biodiversity hotspots should systematically replicate sustainable approaches that blend human intervention (like building artificial nests) while preserving ecological integrity.Additionally, recognizing specific adaptations of Indian wildlife species will facilitate targeted conservation during climate-induced crises.
This story offers an optimistic perspective that resilient ecosystems can recover when supported by consistent global conservation initiatives-a principle relevant not just globally but also locally within india’s own wildlife sanctuaries like Sundarbans or Western Ghats.